1. Introduction to MVC
MVC is an architectural mode. It does not introduce new functions. It is only used to guide us to improve the architecture of the application and separate the application Model and View, so as to obtain better development and maintenance efficiency. In MVC mode, the application is divided into three parts: Model, View and Controller.
- Model: the functions that programmers should have when writing programs (realizing algorithms, etc.), database experts for data management and database design (realizing specific functions);
- Controller: responsible for forwarding requests and processing requests;
- View: interface designers design graphical interfaces.
2. Working principle of MVC
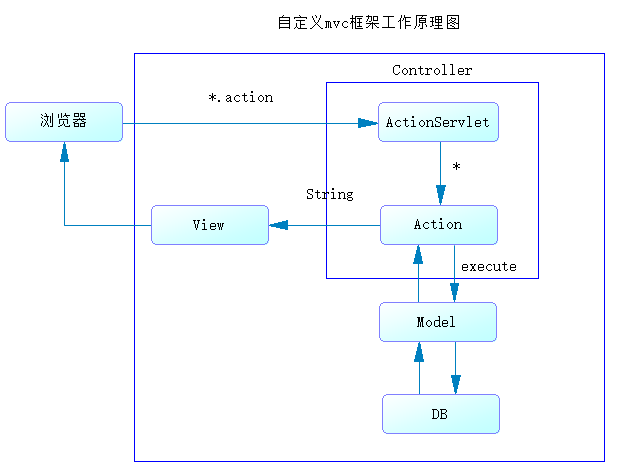
give an example:
< a href = "Ser. Do? Name = add" > Add</a>
< a href = "Ser. Do? Name = delete" > delete</a>
< a href = "Ser. Do? Name = UPD" > Modify</a>
< a href = "Ser. Do? Name = sele" > query</a>
In the previous development process, each interface needs a servlet to operate data, and finally achieve the goal, but the development efficiency is not high
High; It can be seen that the method call depends on name, so we put all the required methods in a servlet through name
The call of value control method is indeed a lot easier, but each time a new method is added, the original logic must be changed
In other words, it is always necessary to judge and add. We can use radiation to read the methods that can realize the requirements through name
package com.wyy.web;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
@WebServlet("/ser.do")
public class setvlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
doPost(req, resp);
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
String name = req.getParameter("name");
// if("add".equals(name)) {
// add();
// }else if("delete".equals(name)) {
// del();
// }else if("upd".equals(name)) {
// upd();
// }else if("sele".equals(name)) {
// find();
//
// }
try {
//Reflection acquisition method
Method m = this.getClass().getDeclaredMethod(name, HttpServletRequest.class,HttpServletResponse.class);
//Open permissions
m.setAccessible(true);
m.invoke(this, req,resp);
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private void sele(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("Query.........");
}
private void upd(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("Modify.........");
}
private void delete(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("Delete.........");
}
private void add(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) {
System.out.println("Increase.........");
}
}
Background output:
Increase.........
You can see that the problem of changing code is solved through reflection, which makes the code more flexible. We just need to add methods
This code is equivalent to the central controller and does not directly process the browser request. It is the method (sub controller) that processes the browser request
So let's think about a problem: for example, book s need to be added, deleted and checked, and goods also need to be added, deleted and checked
Both bookServlet and goodsServlet need to write reflection. Once there are more requirements, the reflection code will become repetitive, but it
It is also necessary. We can adjust the position of this code, that is, it needs to be further optimized
Action Extract all the methods that handle the request as the parent class (child controller)
package com.wyy.framework;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
/**
* Sub controller
* Processing requests
* @author T440s
*
*/
public interface Action {
//Abstract method of all request processing methods
//Process all requests
public void execte(HttpServletRequest req,HttpServletResponse resp);
}
ActionSupport
Implement the Action to override the execte method and obtain the corresponding method through reflection (process all requests)
Function: when there are more requirements, you only need to inherit ActionSupport class
package com.wyy.framework;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
public class ActionSupport implements Action {
/**
* Process all requests
*/
@Override
public void execte(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) {
String parameter = req.getParameter("mathname");
try {
Method Method = this.getClass().getDeclaredMethod(parameter,HttpServletRequest.class,HttpServletResponse.class);
Method.setAccessible(true);
Method.invoke(this, req,resp);
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
return invoke;
}
}
DispatchServlet (central controller)
Functions of the central controller: 1. Obtain the browser request URL 2. Find the sub controller that can process the request
- There must be a set of all sub controllers stored in the central controller
- Initialize all sub controllers into the central controller
We found that the set of sub controllers is placed in the central controller. When there are new requirements, we need to add the sub controllers to the set
It means the code that needs to be changed. Then, we put the sub controller into the configuration file. During initialization, we use xml modeling to put the sub controller into the configuration file
Read out the sub controller, so that no matter how many requirements there are, we only need to configure it in the configuration file.
package com.wyy.framework;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Map.Entry;
import java.util.Set;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import org.apache.commons.beanutils.BeanUtils;
import org.dom4j.DocumentException;
import com.wyy.web.BookAction;
/**
* The central controller
* @author T440s
*
*/
@WebServlet("*.action")
public class DispatchServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
doPost(req, resp);
}
//private Map<String , ActionSupport> map=new HashMap<String, ActionSupport>();
private ConfigModel config=null;
/**
* There must be a set of all sub controllers in the current central controller
* Defect: if there is an addition, deletion, modification and query of goods -- > it means to change the code -- > the design of the code is not flexible enough
* The advantage of putting it in the configuration file is that the code is more flexible,
*/
/**
* Initialize all sub controllers to the central controller
*/
@Override
public void init() throws ServletException {
//map.put("book", new BookAction());
try {
//xml modeling reads the information in the configuration file through modeling
config= new ConfigModelFactory().buibl();
} catch (DocumentException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
//Find a sub controller that can handle the request
//Get the URL of the browser
String url = req.getRequestURI();
url=url.substring(url.indexOf("b"), url.lastIndexOf("."));
//ActionSupport action = map.get(url);
//action.execte(req, resp);
/**
* Find the corresponding object through the url
* Get full pathname from object
* Reflect instanced objects
*/
ActionModel popcon = config.popcon(url);
//Full pathname
String type = popcon.getType();
try {
// Reflect instantiated object bookAction
ActionSupport action = (ActionSupport) Class.forName(type).newInstance();
action.execte(req, resp);
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
xml configuration file
<action path="book" type="com.wyy.web.BookAction">
<forward name="list" path="booklist.jsp" redirect="false" />
<forward name="toEdit" path="toEdit.jsp" redirect="true" />
</action>
Get request parameters (req.getparameter(""))
Usually, we will obtain various parameters on the page through request, and the code is redundant
ModelDriver Help the central controller to complete the parameter packaging project
package com.wyy.framework;
/**
* Model driven interface
* @author T440s
*
* @param <T>
*/
public interface ModelDriver<T> {
/**
* Method of obtaining model object
* @return
*/
T getModel();
}
Page Jump mode, code redundancy
xml file
<forward name="list" path="booklist.jsp" redirect="false" />
<forward name="toEdit" path="toEdit.jsp" redirect="true" />
name is Call the method, path is the jump path, and redirect is to determine the jump method
Modify the return method of the abstract method exece, and control the page Jump through the return value of exece
Central controller optimization
package com.wyy.framework;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Map.Entry;
import java.util.Set;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import org.apache.commons.beanutils.BeanUtils;
import org.dom4j.DocumentException;
import com.wyy.web.BookAction;
/**
* The central controller
*
* @author T440s
*
*/
@WebServlet("*.action")
public class DispatchServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
doPost(req, resp);
}
// private Map<String , ActionSupport> map=new HashMap<String, ActionSupport>();
private ConfigModel config = null;
/**
* In the current central controller, there is bound to be a set defect of all sub controllers: if there are additions, deletions, modifications and queries of commodities -- > it means that the code needs to be changed -- > the design of the code is not flexible enough
* The advantage of putting it in the configuration file is that the code is more flexible,
*/
/**
* Initialize all sub controllers to the central controller
*/
@Override
public void init() throws ServletException {
// map.put("book", new BookAction());
try {
// xml modeling reads the information in the configuration file through modeling
config = new ConfigModelFactory().buibl();
} catch (DocumentException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
// Find a sub controller that can handle the request
// Get the URL of the browser
String url = req.getRequestURI();
url = url.substring(url.indexOf("b"), url.lastIndexOf("."));
// System.out.println(url);
// ActionSupport action = map.get(url);
// action.execte(req, resp);
/**
* Find the corresponding object through the url, obtain the full pathname through the object, and reflect the instantiated object
*/
ActionModel popcon = config.popcon(url);
// Full pathname
String type = popcon.getType();
try {
// Reflect instantiated object bookAction
ActionSupport action = (ActionSupport) Class.forName(type).newInstance();
// Complete the encapsulation of entity class parameters
if (action instanceof ModelDriver) {
// The current sub controller implements the model driven interface
ModelDriver m = (ModelDriver) action;
// Get object
Object model = m.getModel();
// Current request parameter set
Map<String, String[]> map = req.getParameterMap();
// BeanUtils.populate(model, map);
Set<Entry<String, String[]>> entrySet = map.entrySet();
// Get object properties by reflection
Field[] fie = model.getClass().getDeclaredFields();
for (Field field : fie) {
field.setAccessible(true);
// Get property name
String name = field.getName();
for (Entry<String, String[]> entry : entrySet) {
// When the object property name obtained by reflection is the same as the parameter name
if (entry.getKey().equals(name)) {
// Get parameter value
String val = entry.getValue()[0];
// Get parameter data type
String type3 = field.getType().toString();
Object o = val;
if (val != null) {
if (type3.equals("int")) {
o = Integer.parseInt(val);
}
if (type3.equals("float")) {
o = (float) Integer.parseInt(val);
}
}
field.set(model, o);
}
}
}
}
// Execute business
// Control redirection or forwarding by return value
String execte = action.execte(req, resp);
// Get model object
ForwardModel pop = popcon.pop(execte);
// Get jump path
String path = pop.getPath();
// Get jump method
boolean isRedirect = pop.isRedirect();
if (isRedirect) {
resp.sendRedirect(path);
} else {
req.getRequestDispatcher(path).forward(req, resp);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
Obtain the full path name of the object through the browser request modeling, obtain the object through reflection, and judge whether the object inherits the model driven interface, because only by inheriting the model driven interface can we obtain the class object (book), obtain the parameter set, and assign the parameters to the corresponding object properties through reflection.
package com.wyy.web;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import com.wyy.framework.ActionSupport;
import com.wyy.framework.ModelDriver;
/**
* Inheriting the exece method of the parent class, that is, inheriting reflection calls dynamic methods
* @author T440s
*
*/
public class BookAction extends ActionSupport implements ModelDriver<Book>{
private Book b=new Book();
public String add(HttpServletRequest req,HttpServletResponse resp) {
System.out.println("----------------"+b);
return "list";
}
@Override
public Book getModel() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return b;
}
}
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
</head>
<body>
<a href="book.action?mathname=add" >increase</a>
<form action="book.action">
<input name="mathname" value="add" hidden=""/>
id<input name="bid"/>
title<input name="bname"/>
Price<input name="price"/>
<button>Submit</button>
</form>
</body>
</html>Spooling
----------------Book [bid=1, bname=23, price=4.0]
