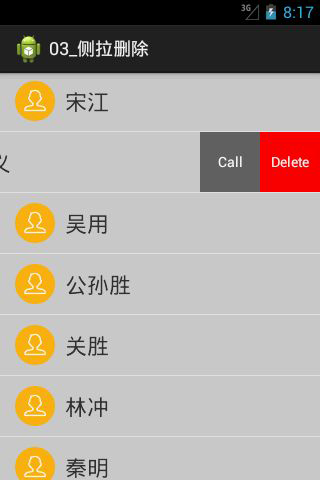
SwipeLayout Side-pull Delete
- Grasp the usage of ViewDragHelper
- Grasp the Principle of Flat Sliding Painting and Callback of State Update Events
Application Scenario: QQ Chat Record, Mail Management, Scenario that need to expand the function of the entry, rendering:
ViewDragHelper initialization
Create custom control SwipeLayout inherits FrameLayout
public class SwipeLayout extends FrameLayout {
private ViewDragHelper mHelper;
public SwipeLayout(Context context) {
this(context,null);
}
public SwipeLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
this(context, attrs,0);
}
public SwipeLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyle) {
super(context, attrs, defStyle);
//1. Create ViewDragHelper
mHelper = ViewDragHelper.create(this, mCallback);
}
//2. Handing over touch events, intercepting judgments, and handling touch events
@Override
public boolean onInterceptTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev) {
return mHelper.shouldInterceptTouchEvent(ev);
};
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
try {
//There are some small bug s in multi-touch. Better catch them.
mHelper.processTouchEvent(event);
} catch (Exception e) {
}
//Consumer events, return true
return true;
};
//3. Handling callback events
ViewDragHelper.Callback mCallback = new ViewDragHelper.Callback() {
@Override
public boolean tryCaptureView(View child, int pointerId) {
return false;
}
};
}Lines 3-8 intermodulate the three constructors by constructing them so that the initialization code only needs to be written in the third constructor.
Lines 11-37 ViewDrag Helper uses a trilogy
Interface Initialization
Layout SwipeLayout into activity_main.xml
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".MainActivity" >
<com.example.swipe.SwipeLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="60dp" >
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="right"
android:layout_height="match_parent" >
<TextView
android:layout_width="60dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="#666666"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="Call"
android:textColor="#FFFFFF" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="60dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="#FF0000"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="Delete"
android:textColor="#FFFFFF" />
</LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="#33000000"
android:gravity="center_vertical" >
<ImageView
android:layout_width="40dp"
android:layout_height="40dp"
android:layout_marginLeft="10dp"
android:src="@drawable/head_1" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginLeft="10dp"
android:text="Song Jiang" />
</LinearLayout>
</com.example.swipe.SwipeLayout>
</RelativeLayout>Rewriting the mCallback method in SwipeLayout to achieve simple drag and drop
//3. Handling callback events
ViewDragHelper.Callback mCallback = new ViewDragHelper.Callback() {
//The return value determines whether the child can be dragged or not.
@Override
public boolean tryCaptureView(View child, int pointerId) {
//Children dragged by users
return true;
}
//The return value determines where to move, and no real movement has taken place yet.
@Override
public int clampViewPositionHorizontal(View child, int left, int dx) {
//left recommends moving to a location
return left;
}
};Delivery of drag events
Limit drag range
The first child view is named after the layout, and the second child view is named before the layout.
private View mBackView;
private View mFrontView;
//Find controls in this method
@Override
protected void onFinishInflate() {
super.onFinishInflate();
mBackView = getChildAt(0);
mFrontView = getChildAt(1);
};Get control width and drag range
private int mRange;
private int mWidth;
private int mHeight;
@Override
protected void onSizeChanged(int w, int h, int oldw, int oldh) {
super.onSizeChanged(w, h, oldw, oldh);
//The width of mBackView is the drag range of mFrontView.
mRange = mBackView.getMeasuredWidth();
//Control width
mWidth = getMeasuredWidth();
//Control height
mHeight = getMeasuredHeight();
}Rewriting mCallback callback method
ViewDragHelper.Callback mCallback = new ViewDragHelper.Callback() {
//The return value determines whether the child can be dragged or not.
@Override
public boolean tryCaptureView(View child, int pointerId) {
return true;
}
//Returns the drag range, returns a value greater than 0, calculates the execution time of the animation, and whether the horizontal direction can be slipped away.
@Override
public int getViewHorizontalDragRange(View child) {
return mRange;
}
//The return value determines where to move, and no real movement has taken place yet.
@Override
public int clampViewPositionHorizontal(View child, int left, int dx) {
// left recommends moving to location
if (child == mFrontView) {
//Limit the drag-and-drop range of the front layout
if (left < -mRange) {
//The left-hand position of the smallest front layout should not be less than-mRange
left = -mRange;
} else if (left > 0) {
//The largest left-hand position of the front layout should not be greater than 0
left = 0;
}
} else if (child == mBackView) {
//Limited drag-and-drop range for post-layout
if (left < mWidth - mRange) {
//The minimum left position of the rear layout should not be less than mWidth - mRange
left = mWidth - mRange;
} else if (left > mWidth) {
//The maximum left-hand position of the rear layout should not be greater than mWidth
left = mWidth;
}
}
return left;
}
};Lines 7-11 need to return a drag range greater than 0
Lines 14-37 calculate drag-and-drop ranges for the front and back layouts by mRange
Delivery of drag events
Override SwipeLayout's onLayout() method by initializing the position of the layout before and after initialization
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int left, int top, int right,
int bottom) {
super.onLayout(changed, left, top, right, bottom);
//The default is closed state
layoutContent(false);
};
private void layoutContent(boolean isOpen) {
//Set up the front layout location
Rect rect = computeFrontRect(isOpen);
mFrontView.layout(rect.left, rect.top, rect.right, rect.bottom);
//Calculate the post-layout position according to the pre-layout position
Rect backRect = computeBackRectViaFront(rect);
mBackView.layout(backRect.left, backRect.top, backRect.right, backRect.bottom);
}
private Rect computeBackRectViaFront(Rect rect) {
int left = rect.right;
return new Rect(left, 0, left + mRange, mHeight);
}
/**
* Calculate the rectangular area where the layout is located
* @param isOpen
* @return
*/
private Rect computeFrontRect(boolean isOpen) {
int left = 0;
if(isOpen){
left = -mRange;
}
return new Rect(left, 0, left + mWidth, mHeight);
}Line 2-7 Place the child view again
Lines 8-15 Because the back layout is connected and slides behind the front layout, the position of the back layout can be calculated by the position of the front layout.
The front and back layouts transfer the variation to each other in the dragging process
ViewDragHelper.Callback mCallback = new ViewDragHelper.Callback() {
// The return value determines whether the child can be dragged or not.
@Override
public boolean tryCaptureView(View child, int pointerId) {
return true;
}
// Returns the drag range, returns a value greater than 0, calculates the execution time of the animation, and whether the horizontal direction can be slipped away.
@Override
public int getViewHorizontalDragRange(View child) {
return mRange;
}
// The return value determines where to move, and no real movement has taken place yet.
@Override
public int clampViewPositionHorizontal(View child, int left, int dx) {
// left recommends moving to location
if (child == mFrontView) {
// Limit the drag-and-drop range of the front layout
if (left < -mRange) {
// The left-hand position of the smallest front layout should not be less than-mRange
left = -mRange;
} else if (left > 0) {
// The largest left-hand position of the front layout should not be greater than 0
left = 0;
}
} else if (child == mBackView) {
// Limited drag-and-drop range for post-layout
if (left < mWidth - mRange) {
// The minimum left position of the rear layout should not be less than mWidth - mRange
left = mWidth - mRange;
} else if (left > mWidth) {
// The maximum left-hand position of the rear layout should not be greater than mWidth
left = mWidth;
}
}
return left;
}
//When the position changes, the changes of the front and back layouts transfer to each other.
@Override
public void onViewPositionChanged(View changedView, int left, int top,
int dx, int dy) {
super.onViewPositionChanged(changedView, left, top, dx, dy);
//The Latest Horizontal Position of left
//Horizontal changes just occurred in dx
//When the position changes, the horizontal variation is transmitted to another layout.
if(changedView == mFrontView){
//Dragging is the front layout, passing the change dx that just happened to the back layout
mBackView.offsetLeftAndRight(dx);
}else if(changedView == mBackView){
//Dragging is the post layout, passing the change dx that just happened to the front layout
mFrontView.offsetLeftAndRight(dx);
}
//Compatible with low version, redraw the interface once
invalidate();
}
};In line 38-54, when dragging the front layout, the change of the front layout is passed to the back layout. When dragging the back layout, the change of the back layout is passed to the front layout, so that the front layout and the back layout can move together.
End animation
Jump animation
// 3. Handling callback events
ViewDragHelper.Callback mCallback = new ViewDragHelper.Callback() {
// The return value determines whether the child can be dragged or not.
@Override
public boolean tryCaptureView(View child, int pointerId) {
return true;
}
// Returns the drag range, returns a value greater than 0, calculates the execution time of the animation, and whether the horizontal direction can be slipped away.
@Override
public int getViewHorizontalDragRange(View child) {
return mRange;
}
// The return value determines where to move, and no real movement has taken place yet.
@Override
public int clampViewPositionHorizontal(View child, int left, int dx) {
// left recommends moving to location
if (child == mFrontView) {
// Limit the drag-and-drop range of the front layout
if (left < -mRange) {
// The left-hand position of the smallest front layout should not be less than-mRange
left = -mRange;
} else if (left > 0) {
// The largest left-hand position of the front layout should not be greater than 0
left = 0;
}
} else if (child == mBackView) {
// Limited drag-and-drop range for post-layout
if (left < mWidth - mRange) {
// The minimum left position of the rear layout should not be less than mWidth - mRange
left = mWidth - mRange;
} else if (left > mWidth) {
// The maximum left-hand position of the rear layout should not be greater than mWidth
left = mWidth;
}
}
return left;
}
@Override
public void onViewPositionChanged(View changedView, int left, int top,
int dx, int dy) {
super.onViewPositionChanged(changedView, left, top, dx, dy);
//The Latest Horizontal Position of left
//Horizontal changes just occurred in dx
//When the position changes, the horizontal variation is transmitted to another layout.
if(changedView == mFrontView){
//Dragging is the front layout, passing the change dx that just happened to the back layout
mBackView.offsetLeftAndRight(dx);
}else if(changedView == mBackView){
//Dragging is the post layout, passing the change dx that just happened to the front layout
mFrontView.offsetLeftAndRight(dx);
}
//Compatible with low version, redraw the interface once
invalidate();
}
//Called when hands are released
@Override
public void onViewReleased(View releasedChild, float xvel, float yvel) {
super.onViewReleased(releasedChild, xvel, yvel);
//The velocity in the horizontal direction of xvel is - to the left and - to the right.+
if(xvel == 0 && mFrontView.getLeft() < -mRange * 0.5f){
//When xvel becomes zero, and the left side of the front layout is less than half of - mRange
open();
}else if (xvel < 0){
//When xvel is - Open
open();
}else{
//Others are closed
close();
}
}
};
public void close() {
//The method of layout sub view before invoking jumps directly to the closed position
layoutContent(false);
}
public void open() {
//The method of layout sub view before calling jumps directly to the open position
layoutContent(true);
}Lines 55-70 override the onViewReleased() method of Callback, which is called after loosening hands, and the end of the animation needs to be done here.
Smooth animation
public void close() {
close(true);
}
public void open() {
open(true);
}
public void close(boolean isSmooth) {
int finalLeft = 0;
if(isSmooth){
if(mHelper.smoothSlideViewTo(mFrontView, finalLeft, 0)){
ViewCompat.postInvalidateOnAnimation(this);
};
}else{
layoutContent(false);
}
}
public void open(boolean isSmooth) {
int finalLeft = -mRange;
if (isSmooth) {
//mHelper.smoothSlideViewTo(child, finalLeft, finalTop) opens a sliding drawing that will child
//Move to final Left, final Top. This method returns true to indicate that the current location is not the final location and needs to be redrawn
if(mHelper.smoothSlideViewTo(mFrontView, finalLeft, 0)){
//Call the redraw method
//invalidate(); frame may be lost. ViewCompat.postInvalidateOnAnimation() is recommended here.
//The parameter must be passed to the container where the child is located, because only the container knows where the child should be placed.
ViewCompat.postInvalidateOnAnimation(this);
};
} else {
layoutContent(true);
}
}
//The computeScroll() method is called when redrawing
@Override
public void computeScroll() {
super.computeScroll();
//mHelper.continueSettling(deferCallbacks) maintains the continuation of the animation and returns true to indicate that it needs to be redrawn
if(mHelper.continueSettling(true)){
ViewCompat.postInvalidateOnAnimation(this);
}
}Lines 1-31 overload the open(), close() methods, retain the jump painting, add the smooth sliding painting
Lines 32-39 rewrite the computeScroll() method to maintain the animation continuation, which must be rewritten here, otherwise there will be no animation effect.
Monitor callback
Define callback interface
Define open interfaces in Swipe Layout
//Control has three states
public enum Status{
Open,Close,Swiping
}
//Initial state is closed
private Status status = Status.Close;
public Status getStatus() {
return status;
}
public void setStatus(Status status) {
this.status = status;
}
public interface OnSwipeListener{
//Notify that the outside world has opened
public void onOpen();
//Notify that the outside world is closed
public void onClose();
//Notify that the outside world is about to open
public void onStartOpen();
//Notify the outside world that it will be closed
public void onStartClose();
}
private OnSwipeListener onSwipeListener;
public OnSwipeListener getOnSwipeListener() {
return onSwipeListener;
}
public void setOnSwipeListener(OnSwipeListener onSwipeListener) {
this.onSwipeListener = onSwipeListener;
}Lines 20-23 SwipeLayout, as an item of ListView, needs to notify other items to do the corresponding processing when it is about to open or close, so add these two methods
Update status and callback monitoring
Modify the onViewPositionChanged() method of Callback
@Override
public void onViewPositionChanged(View changedView, int left, int top,
int dx, int dy) {
super.onViewPositionChanged(changedView, left, top, dx, dy);
//The Latest Horizontal Position of left
//Horizontal changes just occurred in dx
//When the position changes, the horizontal variation is transmitted to another layout.
if(changedView == mFrontView){
//Dragging is the front layout, passing the change dx that just happened to the back layout
mBackView.offsetLeftAndRight(dx);
}else if(changedView == mBackView){
//Dragging is the post layout, passing the change dx that just happened to the front layout
mFrontView.offsetLeftAndRight(dx);
}
//Update status and call monitoring
dispatchDragEvent();
//Compatible with low version, redraw the interface once
invalidate();
}Lines 15-16 call update status and callback monitoring methods
dispatchDragEvent() method
/**
* Update status callback listener
*/
protected void dispatchDragEvent() {
//You need to record the last state, compare the current state with the last state, and call the listener when the state changes.
Status lastStatus = status;
//Get the update status
status = updateStatus();
//Call listeners when state changes
if(lastStatus != status && onSwipeListener != null){
if(status == Status.Open){
onSwipeListener.onOpen();
}else if(status == Status.Close){
onSwipeListener.onClose();
}else if(status == Status.Swiping){
if(lastStatus == Status.Close){
//If the last state is closed, it is now dragged, indicating that it is open
onSwipeListener.onStartOpen();
}else if(lastStatus == Status.Open){
//If the last state is open, it is now dragged, indicating that it is closing
onSwipeListener.onStartClose();
}
}
}
}
private Status updateStatus() {
//Current status can be determined by the position on the left side of the front layout
int left = mFrontView.getLeft();
if(left == 0){
return Status.Close;
}else if(left == -mRange){
return Status.Open;
}
return Status.Swiping;
}Modify activity_main.xml to add id to SwipeLayout
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".MainActivity" >
<com.example.swipe.SwipeLayout
android:id="@+id/sl"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="60dp" >
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="right"
android:layout_height="match_parent" >
<TextView
android:layout_width="60dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="#666666"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="Call"
android:textColor="#FFFFFF" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="60dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="#FF0000"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="Delete"
android:textColor="#FFFFFF" />
</LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="#33000000"
android:gravity="center_vertical" >
<ImageView
android:layout_width="40dp"
android:layout_height="40dp"
android:layout_marginLeft="10dp"
android:src="@drawable/head_1" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginLeft="10dp"
android:text="Song Jiang" />
</LinearLayout>
</com.example.swipe.SwipeLayout>
</RelativeLayout>Setting up listen callbacks in MainActivity
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
SwipeLayout swipeLayout = (SwipeLayout) findViewById(R.id.sl);
swipeLayout.setOnSwipeListener(new OnSwipeListener() {
@Override
public void onStartOpen() {
Utils.showToast(getApplicationContext(), "I'm going to open it.");
}
@Override
public void onStartClose() {
Utils.showToast(getApplicationContext(), "It's going to close down.");
}
@Override
public void onOpen() {
Utils.showToast(getApplicationContext(), "It's open.");
}
@Override
public void onClose() {
Utils.showToast(getApplicationContext(), "It's closed.");
}
});
}
}Utils provides a single Toast method
public class Utils {
private static Toast toast;
public static void showToast(Context context, String msg) {
if (toast == null) {
toast = Toast.makeText(context, "", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT);
}
toast.setText(msg);
toast.show();
}
}Integrate into ListView
Modify activity_main.xml
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".MainActivity" >
<ListView
android:id="@+id/lv"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" >
</ListView>
</RelativeLayout>Data required by ListView
public class Cheeses {
public static final String[] NAMES = new String[]{"Song Jiang", "Lu Jun Yi", "Wu Yong",
"Gong Sun Sheng", "Guan Sheng", "Lin Chong", "Qin Ming", "Hu Yan Zhuo", "Huarong", "Chai Jin", "Li Ying", "Zhu Tong", "Lu Zhishen",
"Wu Song", "Dong Ping", "Zhang Qing", "Yang Zhi", "Xu Ning", "Suo Chao", "Dai Zong", "Liu Tang", "Li Kui", "Shi Jin", " Mu Hong",
"Lei Heng", "Li Jun", "Xiao Er yuan", "Zhang Heng", "Ruan Xiao Wu", " Zhang Shun", "Ruan Xiao Qi", "Yang Xiong", "Shi Xi", " Xie Zhen",
" Xie Bao", "Yanqing", "Zhu Wu", "Huang Xin", "Sun Li", "Xuan Zan", "Hao Si Wen", "Han Tao", "Peng Peng", "Dan Ting ",
"Wei Ding Guo", "Xiao Rong", "Po Chung", "Ou Peng", "Dunfee", " Yan Shun", "Yang Lin", "Ling Zhen", "Jiang Jing", "David Lui ",
"Guo Sheng", "An Dao Quan", "Huang Fu end", "Wang Ying", "Hu San Niang", "Bao Xu", "Fan Rui", "Kong Ming", "Kong Liang", " Item filling",
"Li Gang", "Jin Da Jian", "Ma Lin", "Tong Wei", "Tong Meng", "Meng Kang", "Hou Jian", "Chen Da", "Yang Chun", "Tian Sheng Zheng ",
"Tao Chung Wang", "Song Qing", "Yue He", "Gong Wang", "Ding De sun", "Mu Chun", "Cao Zheng", "Song Wan", "Du Qian", "Xue Yong ", "Mercy",
"Zhou Tong", "Li Zhong", "Duchenne", "Tang Long", "Zou yuan", "Zou run", "Zhu Fu", "Zhu GUI", "Cai Fu", "Cai Qing", " Li Li",
"Li Yun", "Jiao Ting", "Shi Yong", "Sun Xin", "Gu Da sister-in-law", "Zhang Qing", "Sun Er Nan", " Wang Ding Liu", "Yu Bao Si", " Bai Sheng",
"Time move", "Duan Jing Zhu"};
}Modify SwipeLayout's OnSwipeListener interface to pass itself out when calling back the interface method
public interface OnSwipeListener{
//Notify that the outside world has opened
public void onOpen(SwipeLayout swipeLayout);
//Notify that the outside world is closed
public void onClose(SwipeLayout swipeLayout);
//Notify that the outside world is about to open
public void onStartOpen(SwipeLayout swipeLayout);
//Notify the outside world that it will be closed
public void onStartClose(SwipeLayout swipeLayout);
}Adadapter for ListView
public class MyAdapter extends BaseAdapter {
private Context context;
//Record the last open item
private SwipeLayout lastOpenedSwipeLayout;
public MyAdapter(Context context) {
super();
this.context = context;
}
@Override
public int getCount() {
return Cheeses.NAMES.length;
}
@Override
public Object getItem(int position) {
return Cheeses.NAMES[position];
}
@Override
public long getItemId(int position) {
return position;
}
@Override
public View getView(int position, View convertView, ViewGroup parent) {
if(convertView == null){
convertView = View.inflate(context, R.layout.list_item, null);
}
TextView name = (TextView) convertView.findViewById(R.id.name);
name.setText(Cheeses.NAMES[position]);
SwipeLayout swipeLayout = (SwipeLayout) convertView;
swipeLayout.setOnSwipeListener(new OnSwipeListener() {
@Override
public void onOpen(SwipeLayout swipeLayout) {
//When the current item is opened, record the item
lastOpenedSwipeLayout = swipeLayout;
}
@Override
public void onClose(SwipeLayout swipeLayout) {
}
@Override
public void onStartOpen(SwipeLayout swipeLayout) {
//Close the last open item when the current item is about to open
if(lastOpenedSwipeLayout != null){
lastOpenedSwipeLayout.close();
}
}
@Override
public void onStartClose(SwipeLayout swipeLayout) {
}
});
return convertView;
}
}