We have experienced it for the first time, and the robustness of crawler code has been upgraded to PLUS. It's all analyzed to this point. Is there something missing? Yes, we haven't saved the data yet? Don't save it. Isn't it just a chore?
Items
Item is our container for storing data, which is similar to a dictionary in python. The advantage of using item is: item provides additional protection against undefined field errors caused by misspelling. Look at the chestnuts:
import scrapy class Doubantop250Item(scrapy.Item): title = scrapy.Field() #Film name star = scrapy.Field() #Film rating quote = scrapy.Field() #A popular saying movieInfo = scrapy.Field() #Description information of the film, including director, leading actor and film type
Pipelines
pipelines.py is generally used to save data. Some of its methods are shown in the figure below. Next, I will save our data in many ways to avoid you playing hooligan.

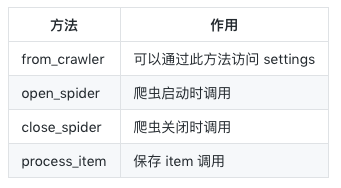
Save to Json
import json
class JsonPipeline(object):
file_name = base_dir + '/doubanTop250/data.json' #json file path
def process_item(self, item, spider):
file = open(self.file_name, 'r', encoding='utf-8')
load_data = json.load(file)
load_data.append({"title": item["title"].strip()}) #Additional data
file = open(self.file_name, 'w', encoding='utf-8')
json.dump(load_data, file, ensure_ascii=False) #Save data
file.close()
return item

Save to CSV
def appendDta2Csv(self, file_name, new_headers, new_data): with open(file_name,'r') as f: f_csv = csv.reader(f) try:#How to transfer the call to the active file without headers headers = next(f_csv) except: headers = new_headers old_data = list(f_csv) old_data.append(new_data) #Add new data with open(file_name, 'w') as f2:#Save data f_csv = csv.writer(f2) f_csv.writerow(headers) f_csv.writerows(old_data) f2.close() f.close() def process_item(self, item, spider): self.appendDta2Csv(self.file_name, ["title"], [item["title"].strip()]) return item
Save to MongoDB
from pymongo import MongoClient
import os
base_dir = os.getcwd()
class MongoPipeline(object):
#Implementation of classes saved to mongo database,
collection = 'douban' #collection name of mongo database
def __init__(self, mongo_uri, db_name, db_user, db_pass):
self.mongo_uri = mongo_uri
self.db_name = db_name
self.db_user = db_user
self.db_pass = db_pass
@classmethod
def from_crawler(cls, crawler):
#A method is provided for us to access settings. Here,
#We need to get the URI and database name of the database from the settings.py file
return cls(
mongo_uri=crawler.settings.get('MONGO_URI'),
db_name=crawler.settings.get('DB_NAME'),
db_user=crawler.settings.get('DB_USER'),
db_pass=crawler.settings.get('DB_PASS'))
def open_spider(self, spider): #Call when the crawler starts, connect to the database
self.client = MongoClient(self.mongo_uri)
self.zfdb = self.client[self.db_name]
self.zfdb.authenticate(self.db_user, self.db_pass)
def close_spider(self, spider): #Call when the crawler is closed to close the database connection
self.client.close()
def process_item(self, item, spider):
self.zfdb[self.collection].insert({"title": item["title"].strip()})
return item
Save to MySQL
from sqlalchemy import create_engine, Column, Integer, String, BIGINT, ForeignKey, UniqueConstraint, Index, and_, \ or_, inspect from sqlalchemy.orm import sessionmaker, relationship, contains_eager class MysqlPipeline(object): MYSQL_URI = 'mysql+pymysql://username:password@localhost:3306/db_name' #True echo will output SQL native statement engine = create_engine(MYSQL_URI, echo=True) from sqlalchemy.ext.declarative import declarative_base Base = declarative_base() #Create a single table class Movie(Base): __tablename__ = 'movies' id = Column(BIGINT, primary_key=True, autoincrement=True) title = Column(String(200)) #Initialize database def init_db(self): self.Base.metadata.create_all(self.engine) #Delete database def drop_db(self): self.Base.metadata.drop_all(self.engine) def open_spider(self, spider): #Call when the crawler starts, connect to the database self.init_db() Session = sessionmaker(bind=self.engine) self.session = Session() def process_item(self, item, spider): new_movie = self.Movie(title=item["title"].strip()) self.session.add(new_movie) self.session.commit() return item
After writing the relevant pipeline, you need to enable the relevant pipeline in settings.py. The following number is the priority of the call. The number is 0-1000. You can customize it. You can save all the formats or comment out the others. Keep one value.
ITEM_PIPELINES = {
'doubanTop250.pipelines.MongoPipeline': 300,
'doubanTop250.pipelines.MysqlPipeline': 301,
'doubanTop250.pipelines.CsvPipeline': 302,
'doubanTop250.pipelines.JsonPipeline': 303,
}
Blind Bibi
That's what data preservation is all about