Topology required for the experiment:
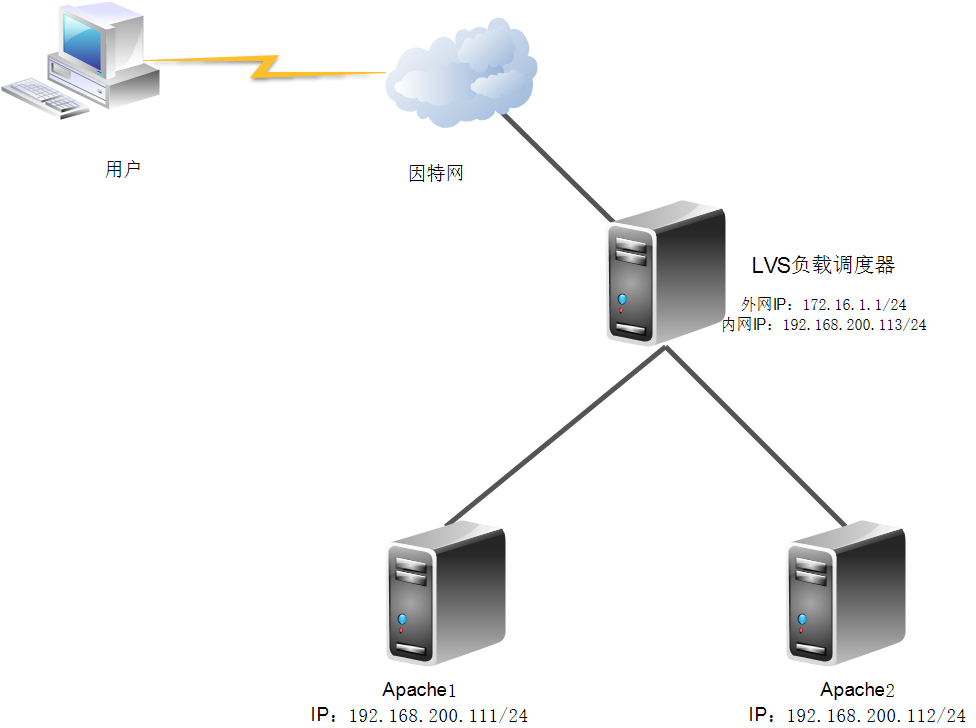
First, three machines shut down selinux and firewall.
[root@hostlocal ~]# systemctl stop firewalld [root@hostlocal ~]# iptables -F [root@hostlocal ~]# setenforce 0 // temporary, if permanently closed, modify / etc/sysconfig/selinux and change enforcing to disabled
Configure Apache
yum installation is used here.
[root@hostlocal ~]# yum -y install httpd
Write a test page to observe the experiment.
Apache1:
[root@hostlocal ~]# echo "111111" > /var/www/html/index.html
Apache2:
[root@hostlocal ~]# echo "22222222" > /var/www/html/index.html
Open the httpd service
[root@hostlocal ~]# systemctl start httpd
At the same time, the gateway of the two machines specifies the intranet IP of the scheduler.
[root@hostlocal ~]# vim /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eno16777728 ###### ** GATEWAY=192.168.200.113 ** ######
Configuration scheduler
First turn on its routing forwarding
[root@hostlocal ~]# vim /etc/sysctl.conf ###### net.ipv4.ip_forward=1 //Manual addition [root@hostlocal ~]# Sysctl-p // Effective
Install ipvsadm
[root@hostlocal ~]# yum -y install ipvsadm
Configuring load balancing allocation strategy
[root@hostlocal ~]# ipvsadm -A -t 172.16.1.1:80 -s rr [root@hostlocal ~]# ipvsadm -a -t 172.16.1.1:80 -r 192.168.200.111:80 -m -w 1 [root@hostlocal ~]# ipvsadm -a -t 172.16.1.1:80 -r 192.168.200.112:80 -m -w 1 [root@hostlocal ~]# ipvsadm -Ln IP Virtual Server version 1.2.1 (size=4096) Prot LocalAddress:Port Scheduler Flags -> RemoteAddress:Port Forward Weight ActiveConn InActConn TCP 172.16.1.1:80 rr -> 192.168.200.111:80 Masq 1 0 0 -> 192.168.200.112:80 Masq 1 0 0
Here we add a point of ipvsadm parameter description: - A means adding virtual server, - t is used to specify VIP address and TCP port, - s is used to specify load scheduling algorithm - polling (rr), weighted polling (wrr), least connection (lc), weighted least connection (wlc), and so on.
test
Here we use elinks to test
[root@hostlocal ~]# elinks --dump http://172.16.1.1 111111 [root@hostlocal ~]# elinks --dump http://172.16.1.1 22222 [root@hostlocal ~]# elinks --dump http://172.16.1.1 111111 [root@hostlocal ~]# elinks --dump http://172.16.1.1 22222 [root@hostlocal ~]# elinks --dump http://172.16.1.1 111111 [root@hostlocal ~]# elinks --dump http://172.16.1.1 22222 [root@hostlocal ~]# elinks --dump http://172.16.1.1 111111 [root@hostlocal ~]# ipvsadm -Lnc IPVS connection entries pro expire state source virtual destination TCP 01:19 TIME_WAIT 172.16.1.1:56271 172.16.1.1:80 192.168.200.112:80 TCP 01:15 TIME_WAIT 172.16.1.1:56262 172.16.1.1:80 192.168.200.111:80 TCP 00:45 TIME_WAIT 172.16.1.1:56259 172.16.1.1:80 192.168.200.112:80 TCP 00:46 TIME_WAIT 172.16.1.1:56260 172.16.1.1:80 192.168.200.111:80 TCP 00:44 TIME_WAIT 172.16.1.1:56257 172.16.1.1:80 192.168.200.112:80
So far, the experiment is over.