1, Build three Mongodb instances
See the following for the construction steps: Construction of MongoDB.
The planning is as follows:
| ip | MongoDB port | Replica role | Mongodb version |
|---|---|---|---|
| 172.16.113.137 | 27017 | Primary | 3.2.10 |
| 172.16.113.137 | 27018 | Secondary | 3.2.10 |
| 172.16.113.129 | 27017 | Secondary | 3.2.10 |
Parameter Description:
| parameter | explain | Example |
|---|---|---|
| replSet | Replica set name | rs0 |
| oplogSize | Operation log size | 128 |
What we built above is the single instance method of MongoDB. Many parameters are not added, so we must specify some parameters when starting, as shown in the table above.
mongod --replSet rs0 --port 27017 --bind_ip localhost,<hostname(s)|ip address(es)> --dbpath /data/mongodb/rs0-0 --oplogSize 128
I choose to write the used parameters into the configuration file and start it
vim mongod.conf ... replSet=rs0 oplogSize=128 keyFile=/usr/bin/mongo/mongodb-keyfile ....
keyFile must be configured, or communication cannot be performed. The specific configuration method can be seen Master slave replication of mongodb
Then start it
2, Initialize replica set
Use mongo to enter the first mongod example, and use rs.initiate() to initialize
rsconf = {
_id: "rs0",
members: [
{
_id: 0,
host: "172.16.113.137:27017"
},
{
_id: 1,
host: "172.16.113.137:27018"
},
{
_id: 2,
host: "172.16.113.129:27017"
}
]
}
rs.initiate( rsconf )
see
Execute rs.conf() in the mongo shell to see the host, arbiterOnly, hidden, priority, votes, slaveDelay and other attributes in each node.
rs0:PRIMARY> rs.conf()
{
"_id" : "rs0",
"version" : 3,
"protocolVersion" : NumberLong(1),
"members" : [
{
"_id" : 0,
"host" : "172.16.113.137:27017",
"arbiterOnly" : false,
"buildIndexes" : true,
"hidden" : false,
"priority" : 1,
"tags" : {
},
"slaveDelay" : NumberLong(0),
"votes" : 1
},
{
"_id" : 1,
"host" : "172.16.113.137:27018",
"arbiterOnly" : false,
"buildIndexes" : true,
"hidden" : false,
"priority" : 1,
"tags" : {
},
"slaveDelay" : NumberLong(0),
"votes" : 1
},
{
"_id" : 2,
"host" : "172.16.113.129:27017",
"arbiterOnly" : false,
"buildIndexes" : true,
"hidden" : false,
"priority" : 1,
"tags" : {
},
"slaveDelay" : NumberLong(0),
"votes" : 1
}
],
"settings" : {
"chainingAllowed" : true,
"heartbeatIntervalMillis" : 2000,
"heartbeatTimeoutSecs" : 10,
"electionTimeoutMillis" : 10000,
"getLastErrorModes" : {
},
"getLastErrorDefaults" : {
"w" : 1,
"wtimeout" : 0
},
"replicaSetId" : ObjectId("61502b5d8887b4e8bf7c27b6")
}
}
rs0:PRIMARY>
Check the status and role assignment of the current replica set
rs0:PRIMARY> rs.status();
{
"set" : "rs0",
"date" : ISODate("2021-09-26T08:40:27.280Z"),
"myState" : 1,
"term" : NumberLong(1),
"heartbeatIntervalMillis" : NumberLong(2000),
"members" : [
{
"_id" : 0,
"name" : "172.16.113.137:27017",
"health" : 1,
"state" : 1,
"stateStr" : "PRIMARY",
"uptime" : 1850,
"optime" : {
"ts" : Timestamp(1632645189, 1),
"t" : NumberLong(1)
},
"optimeDate" : ISODate("2021-09-26T08:33:09Z"),
"electionTime" : Timestamp(1632643933, 2),
"electionDate" : ISODate("2021-09-26T08:12:13Z"),
"configVersion" : 7,
"self" : true
},
{
"_id" : 1,
"name" : "172.16.113.137:27018",
"health" : 1,
"state" : 2,
"stateStr" : "SECONDARY",
"uptime" : 509,
"optime" : {
"ts" : Timestamp(1632645189, 1),
"t" : NumberLong(1)
},
"optimeDate" : ISODate("2021-09-26T08:33:09Z"),
"lastHeartbeat" : ISODate("2021-09-26T08:40:26.016Z"),
"lastHeartbeatRecv" : ISODate("2021-09-26T08:40:27Z"),
"pingMs" : NumberLong(0),
"syncingTo" : "172.16.113.137:27017",
"configVersion" : 7
},
{
"_id" : 2,
"name" : "172.16.113.129:27017",
"health" : 1,
"state" : 2,
"stateStr" : "SECONDARY",
"uptime" : 319,
"optime" : {
"ts" : Timestamp(1632645189, 1),
"t" : NumberLong(1)
},
"optimeDate" : ISODate("2021-09-26T08:33:09Z"),
"lastHeartbeat" : ISODate("2021-09-26T08:40:26.253Z"),
"lastHeartbeatRecv" : ISODate("2021-09-26T08:40:24.166Z"),
"pingMs" : NumberLong(0),
"configVersion" : 7
}
],
"ok" : 1
}
rs0:PRIMARY>
Here, the replica set is built successfully
3, Function test
3.1 data synchronization
Let's insert some data in the Primary node
rs0:PRIMARY> show dbs
admin 0.000GB
gengjin 0.000GB
hello 0.001GB
kobe 0.001GB
local 0.000GB
nihao 0.000GB
rs0:PRIMARY> use nihao
switched to db nihao
rs0:PRIMARY> show tables;
nihao
rs0:PRIMARY> db.nihao.insert({"name":"gengjin"})
WriteResult({ "nInserted" : 1 })
rs0:PRIMARY>
Check in two SECONDARY
rs0:SECONDARY> use admin
switched to db admin
rs0:SECONDARY> db.auth("root","root")
1
rs0:SECONDARY> show dbs
admin 0.000GB
gengjin 0.000GB
hello 0.000GB
kobe 0.001GB
local 0.000GB
nihao 0.000GB
rs0:SECONDARY> db.getMongo().setSlaveOk()
rs0:SECONDARY> use nihao
switched to db nihao
rs0:SECONDARY> db.nihao.find()
{ "_id" : ObjectId("614fedaae07683d6c0444a00"), "nihao" : "shazi" }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("615033b83f5bc322a1cf609b"), "name" : "gengjin" }
rs0:SECONDARY>
Data synchronization is normal
3.2 automatic failover
You can directly stop the primary node 172.16.113.137:27017 to test that after the primary node hangs up, the replica node elects a new primary node, that is, Automatic Failover
rs0:PRIMARY> use admin switched to db admin rs0:PRIMARY> db.shutdownServer() server should be down... 2021-09-26T16:54:29.518+0800 I NETWORK [thread1] trying reconnect to 127.0.0.1:27017 (127.0.0.1) failed 2021-09-26T16:54:30.600+0800 I NETWORK [thread1] Socket recv() errno:104 Connection reset by peer 127.0.0.1:27017 2021-09-26T16:54:30.600+0800 I NETWORK [thread1] SocketException: remote: (NONE):0 error: 9001 socket exception [RECV_ERROR] server [127.0.0.1:27017] 2021-09-26T16:54:30.600+0800 I NETWORK [thread1] reconnect 127.0.0.1:27017 (127.0.0.1) failed failed 2021-09-26T16:54:30.602+0800 I NETWORK [thread1] trying reconnect to 127.0.0.1:27017 (127.0.0.1) failed 2021-09-26T16:54:30.603+0800 W NETWORK [thread1] Failed to connect to 127.0.0.1:27017, reason: errno:111 Connection refused 2021-09-26T16:54:30.603+0800 I NETWORK [thread1] reconnect 127.0.0.1:27017 (127.0.0.1) failed failed > >
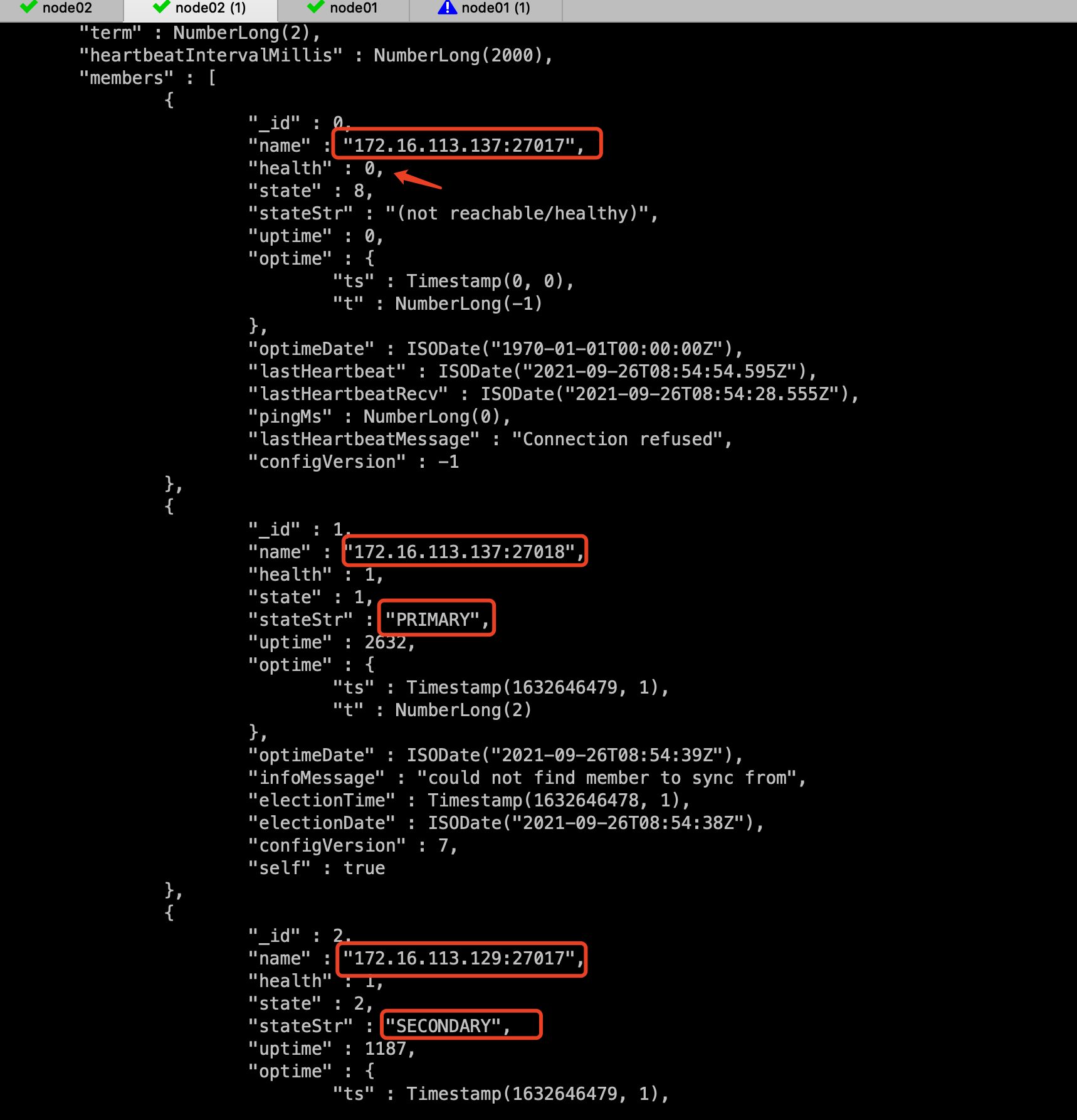
View rs.status(); It can be found that 172.16.113.137:27018 has been promoted to the Primary, and the health of the old Primary is 0
View the promotion log of the new Primary
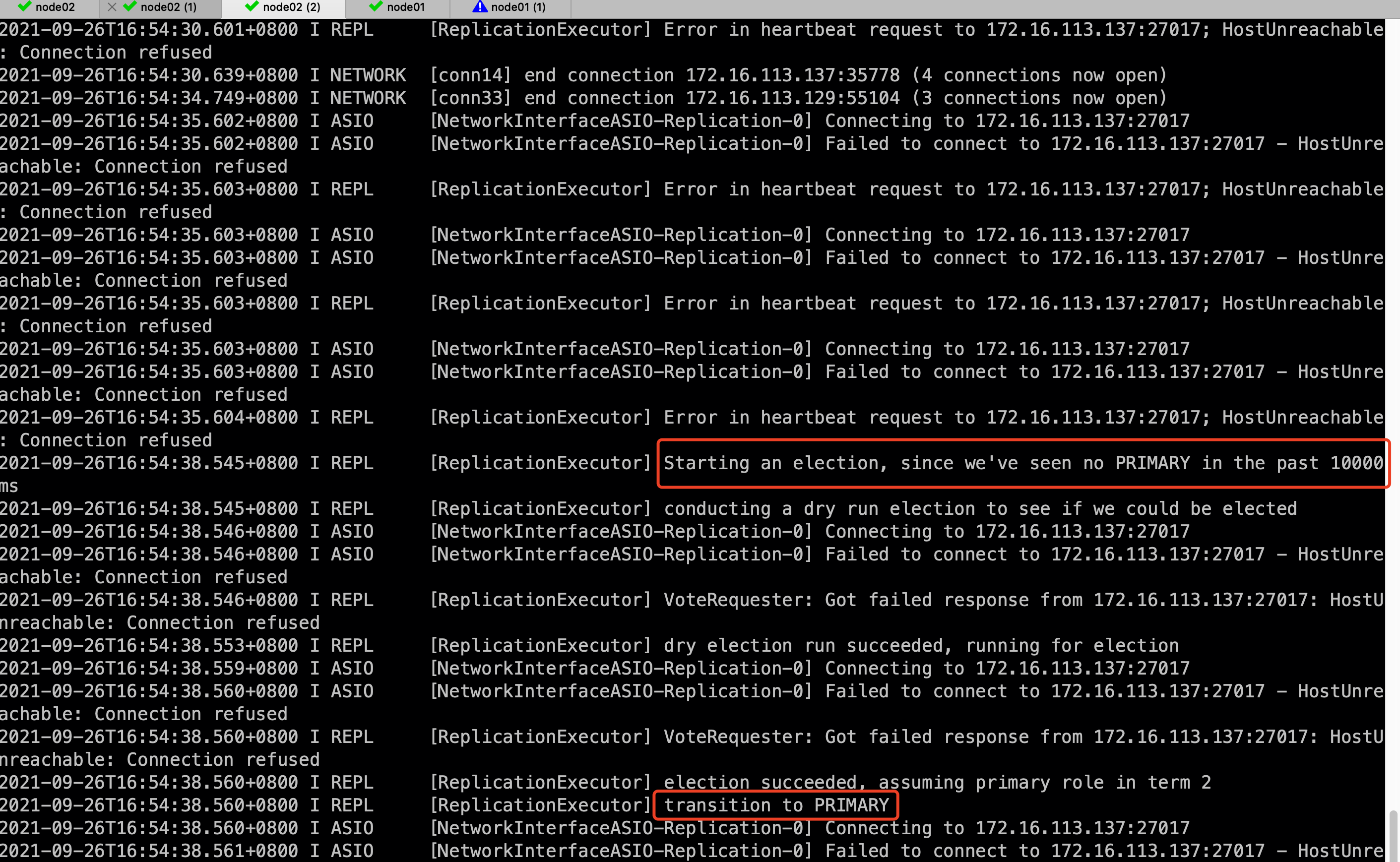
No Primary was found within 1000 milliseconds, so I decided to run for Primary and succeeded. The old master will be restarted later, and it will be pulled into the cluster by the new master again.
3.3 maintaining replica clusters
3.3.1 adding and deleting nodes
#add to
rs.add("192.168.199.164:27020")
#delete
rs.remove("192.168.199.164:27020")
Remember to delete the corresponding data directory after deleting the replica set
3.3.2 replace replica set node
cfg = rs.conf() cfg.members[0].host = "192.168.199.164:27021" rs.reconfig(cfg)
3.3.3 manually switch the Primary node
Add the priority of the specified node to the maximum to become the master node:
From the priority in rs.conf(), we can see that each node can be configured with priority, and the node with the highest priority will become the master node
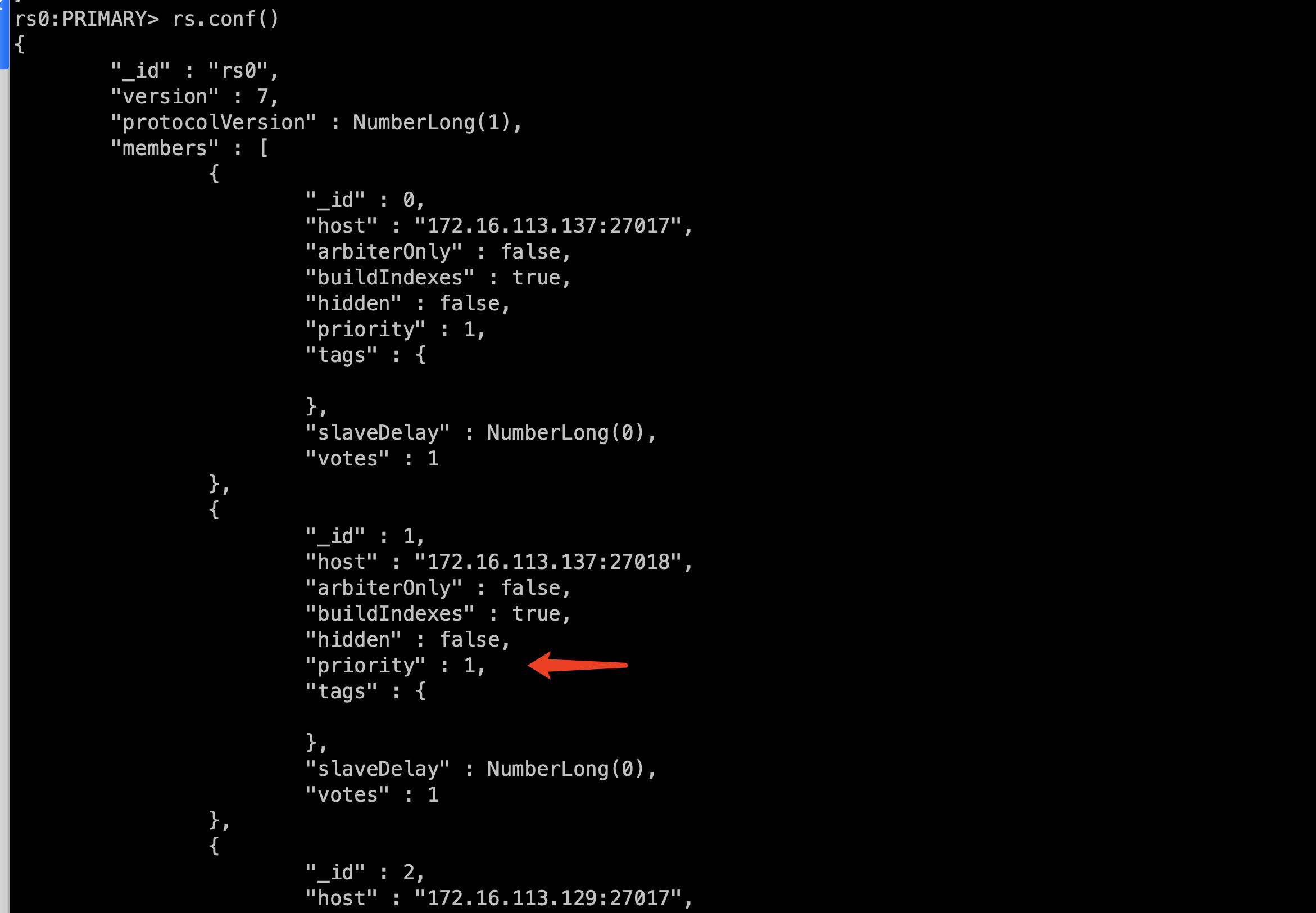
#Modify the priority so that 27017 becomes the master node
#Modify priority
rs0:PRIMARY> conf.members[0].priority = 2 #Adjust [0 / 1 / 2] if you change other ones
2
rs0:PRIMARY>
#Reload the configuration file and force an election. During this period, all nodes are Secondary nodes
rs0:PRIMARY> rs.reconfig(conf)
{ "ok" : 1 }
You can see that the switch has occurred, and the instance whose priority is adjusted to 2 becomes the master
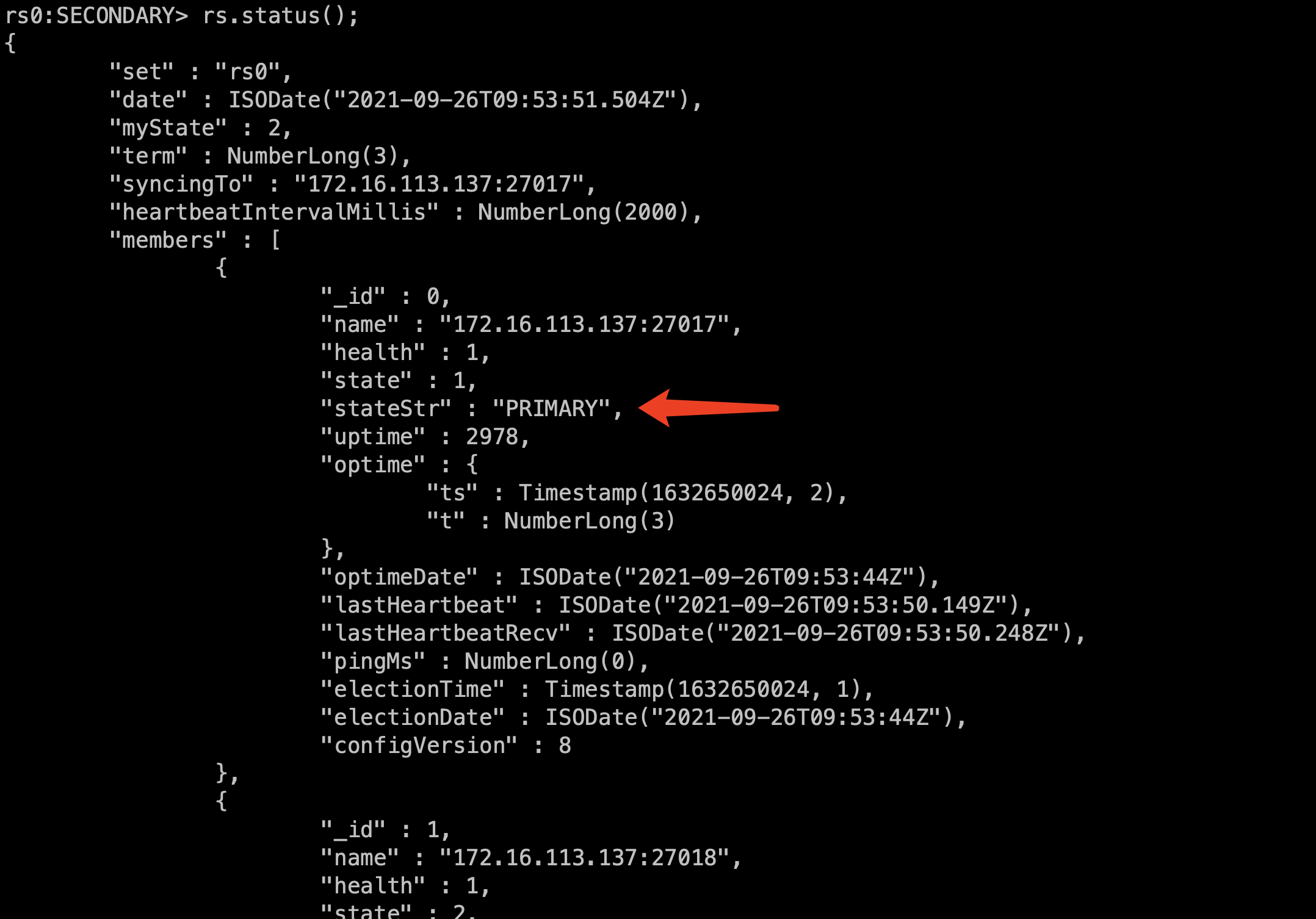
3.3.4 add arbitration node
Adding a quorum node is the same as adding a data node. It only needs to be called when adding. The instance configuration is consistent with that of the SECONDARY node
rs.addArb("172.16.113.129:27018")
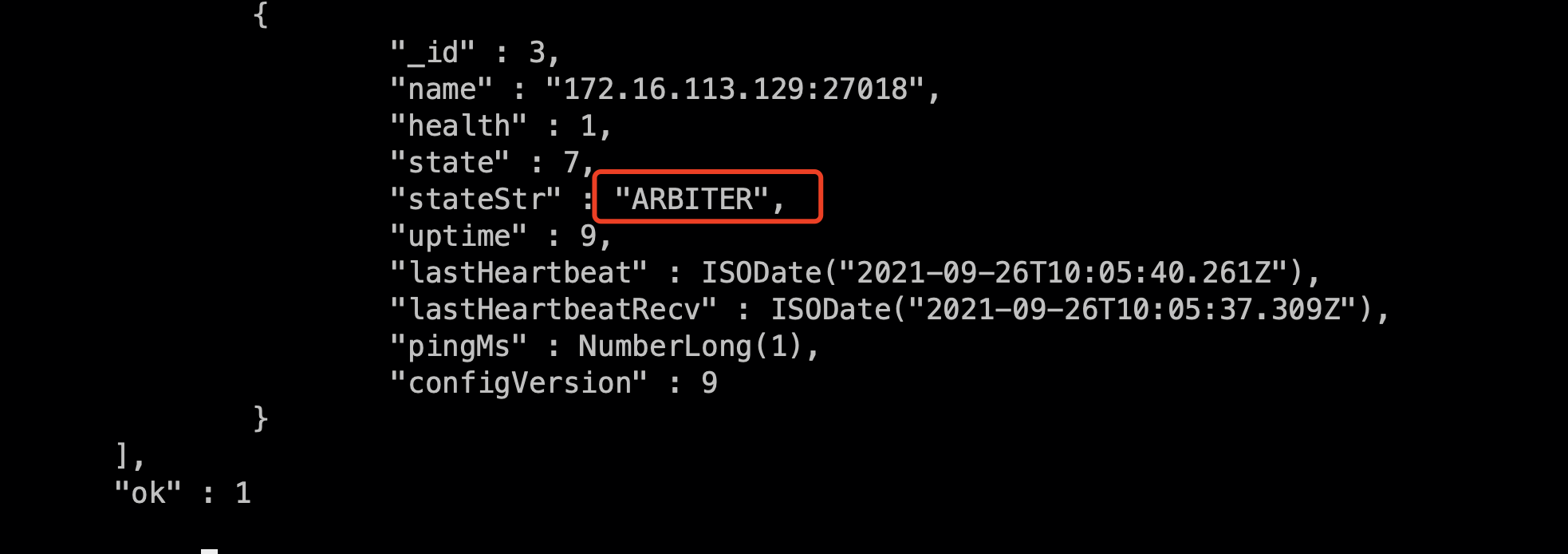
Replica sets require an odd number of nodes to vote. When our data set nodes are even, you can add an arbitration node to form an odd number. The arbitration node only participates in voting and does not own data. It requires little physical resources.
Through the actual test, it is found that when 50% of the nodes (including arbitration nodes) in the whole replica set cluster are unavailable, the remaining nodes can only become secondary nodes, and the whole cluster can only read and write. For example, when there is one primary node, two secondary nodes and one orbit node in the cluster: when the two secondary nodes hang up, the remaining original primary nodes can only be degraded to secondary nodes; When there is a primary node, a secondary node and an orbit node in the cluster, even if the primary node hangs, the remaining secondary nodes will automatically become the primary node. Because the arbitration node does not copy data, the arbitration node can achieve the minimum machine overhead and achieve the effect of hot standby of two nodes.
3.3.5 adding backup nodes
hidden (members are used to support special functions): after this setting, this machine is not visible in reading and writing, and will not be elected as Primary, but can vote. It is generally used to back up data.
Due to limited resources, we delete the arbitration node just added and add the dedicated function node again:
#delete
rs0:PRIMARY> rs.remove("172.16.113.129:27018")
{ "ok" : 1 }
rs0:PRIMARY>
#add to
rs0:PRIMARY> rs.add({"_id":3,"host":"172.16.113.129:27018","priority":0,"hidden":true})
{ "ok" : 1 }
#see
{
"_id" : 3,
"name" : "172.16.113.129:27018",
"health" : 1,
"state" : 9,
"stateStr" : "ROLLBACK",
"uptime" : 16,
"optime" : {
"ts" : Timestamp(1632650626, 1),
"t" : NumberLong(3)
},
"optimeDate" : ISODate("2021-09-26T10:03:46Z"),
"lastHeartbeat" : ISODate("2021-09-26T10:12:58.614Z"),
"lastHeartbeatRecv" : ISODate("2021-09-26T10:12:57.652Z"),
"pingMs" : NumberLong(0),
"syncingTo" : "172.16.113.129:27017",
"configVersion" : 11
}
],
"ok" : 1
3.3.6 add delay node
Delayed: you can specify a time delay to synchronize data from the primary node. It is mainly used to deal with the inconsistency caused by accidentally deleting data and immediately synchronizing it to the slave node.
$ rs.add({"_id":3,"host":"172.16.113.129:27018","priority":0,"hidden":true,"slaveDelay":60}) #Unit s
The details are as follows:
| role | Primary (yes or no) | Client visible | Participate in voting | Delay synchronization | Copy data |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Default | √ | √ | √ | X | √ |
| Secondary-Only | X | √ | √ | X | √ |
| Hidden | X | X | √ | X | √ |
| Delayed | X | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| Arbiters | X | X | √ | X | X |
| Non-Voting | √ | √ | X | X | √ |
4, Read write separation
The MongoDB replica set supports read-write separation through the Read Preferences feature, which is very complex and flexible. To set read-write separation, you need to set setSlaveOk on the SECONDARY node
The application driver sets how to read the replica set through the read reference. By default, all read operations of the client driver directly access the primary node, so as to ensure the strict consistency of data.
There are several modes:
| pattern | describe |
|---|---|
| primary | The primary node is in the default mode. The read operation is only on the primary node. If the primary node is unavailable, an error is reported or an exception is thrown. |
| primaryPreferred | The primary node is preferred. In most cases, the read operation is on the primary node. If the primary node is unavailable, such as failover, the read operation is on the slave node. |
| secondary | From the slave node, the read operation is only at the slave node. If the slave node is unavailable, an error is reported or an exception is thrown. |
| secondaryPreferred | The slave node is preferred. In most cases, the read operation is in the slave node, and in special cases (such as single master node architecture), the read operation is in the master node. |
| nearest | For the nearest node, the read operation is performed on the nearest member, which may be the master node or the slave node. For the nearest member, please refer to the official website nearest |
Attachment: node status
| name | describe |
|---|---|
| STARTUP | Without any active nodes, all nodes are started in this state to resolve the replica set configuration |
| PRIMARY | Master node of replica set |
| SECONDARY | The replica set can read data from the node |
| RECOVERING | Members can vote, perform a startup self-test, or complete rollback or resynchronization. |
| STARTUP2 | The node joins and runs the initial synchronization |
| UNKNOWN | From other nodes, the node is unknown |
| ARBITER | Arbiter, do not copy data for voting |
| DOWN | In the view of other nodes, the node is unreachable |
| ROLLBACK | The node is performing rollback and cannot read data |
| REMOVED | The node is deleted |
Copy related methods in mongo shell
| Method name | describe |
|---|---|
| rs.add() | Add node to replica set |
| rs.addArb() | Add quorum node to replica set |
| rs.conf() | Gets the configuration document for the replica set |
| rs.freeze() | The current node cannot be the Primary node for a specified period of time |
| rs.help() | Basic method of getting replica set |
| rs.initiate() | Initializes a new replica set |
| rs.printReplicationInfo() | Print the status report of the Primary node of the replica set |
| rs.printSlaveReplicationInfo() | Print the status report of the Secondary node of the replica set |
| rs.reconfig() | Reconfigure replica set |
| rs.remove() | Delete a node |
| rs.slaveOk() | Set the readpref of the current connection, and use readPref() and mongosereadpref() to set the read preference |
| rs.status() | Documents that return replica set status information |
| rs.stepDown() | Force the current Primary node to become a Secondary node and trigger voting |
| rs.syncFrom() | Set a new synchronization target and overwrite the default synchronization target |
Commands for copying databases
| name | describe |
|---|---|
| replSetFreeze | Prevent the current node from competing with the Primary node for a period of time |
| replSetGetStatus | Documents that return replica set status information |
| replSetInitiate | Initializes a new replica set |
| replSetMaintenance | Enable or disable the maintenance mode to bring the Secondary node into the recovery state |
| replSetReconfig | Reconfigure replica set |
| replSetStepDown | Force the current Primary node to become a Secondary node and trigger voting |
| replSetSyncFrom | Set a new synchronization target and overwrite the default synchronization target |
| resync | Force resynchronization, valid only in master-slave synchronization |
| applyOps | Internal command to apply oplog to the current dataset |
| isMaster | Displays whether the node is the master node and other related information |
| replSetGetConfig | Returns the configuration object of the replica set |