Join query: If a query involves two or more tables, it is called join query.
Join queries can be divided into:
- Equivalent connection
- Non-Equijoin
- Natural Connection
- Self-connection
- External connection
- Compound Conditional Connection
The following routines are exemplified by the following three tables:
CREATE TABLE Student (
Sno INT(6) PRIMARY KEY, # Student ID
Sname VARCHAR(20) NOT NULL, # Full name
Ssex CHAR(2) NOT NULL, # Gender
Sage INT NOT NULL, # Age
Sdept VARCHAR(10) NOT NULL # Department
);
CREATE TABLE Course (
Cno INT PRIMARY KEY, # Course Number
Cname VARCHAR(40) NOT NULL, # Course Name
Cpno INT, # Pre-course
Ccredit INT NOT NULL # credit
);
CREATE TABLE SC (
Sno INT(6), # Student ID
Cno INT, # Class Title
Grade INT # Score
);
INSERT INTO Student VALUES (950001, 'Li Dayong', 'male', 20, 'CS');
INSERT INTO Student VALUES (950002, 'Liu Xiaochen', 'female', 19, 'CS');
INSERT INTO Student VALUES (950003, 'Wang min.', 'female', 18, 'MA');
INSERT INTO Student VALUES (950004, 'Were successfully', 'male', 19, 'IS');
INSERT INTO Course VALUES (1, 'data base', 5, 4);
INSERT INTO Course (Cno, Cname, Ccredit) VALUES (2, 'Mathematics', 2);
INSERT INTO Course VALUES (3, 'information system', 1, 4);
INSERT INTO Course VALUES (4, 'operating system', 6, 3);
INSERT INTO Course VALUES (5, 'data structure', 7, 6);
INSERT INTO Course (Cno, Cname, Ccredit) VALUES (6, 'data processing', 4);
INSERT INTO Course VALUES (7, 'C language', 6, 4);
INSERT INTO SC VALUES (950001, 1, 90);
INSERT INTO SC VALUES (950001, 2, 88);
INSERT INTO SC VALUES (950001, 3, 79);
INSERT INTO SC VALUES (950002, 2, 93);
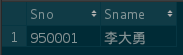
INSERT INTO SC VALUES (950002, 3, 80);Student table
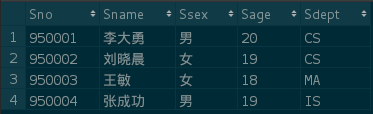
Course table
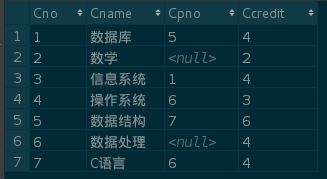
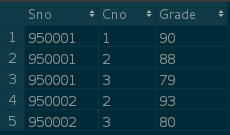
SC table
Equivalent connection and non-equivalent connection
Equivalent join: Equivalent join when the comparison operator of the join is =
Non-Equivalent Connections: Contrary to Equivalent Connections
Question: Find out the names of each student and their elective courses.
SELECT Student.Sname,SC.Cno FROM Student,SC WHERE Student.Sno = SC.Sno;
Self-connection
Self-join: The join operation is performed in the same table, i.e. self-join itself
Question: Inquire about the indirect elective courses of each course, that is, the pre-elective courses of the pre-elective courses:
SELECT A.Cno ,B.Cpno FROM Course AS A,Course AS B WHERE A.Cpno = B.Con;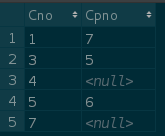
Note: When joining, different aliases must be given to the same table in order to distinguish, otherwise the joining itself can not be completed.
External connection
External connection can be divided into: left external connection, right external connection and total external connection.
CREATE TABLE A(
id int PRIMARY KEY ,
name VARCHAR(20) ,
score INT
);
INSERT INTO A VALUES (1,'zp',80);
INSERT INTO A VALUES (2,'hh',75);
INSERT INTO A VALUES (3,'ee',89);
INSERT INTO A VALUES (4,'rr',86);
CREATE TABLE B(
id INT PRIMARY KEY ,
type VARCHAR(20),
s INT
);
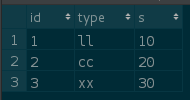
INSERT INTO B VALUES (1,'ll',10);
INSERT INTO B VALUES (2,'cc',20);
INSERT INTO B VALUES (3,'xx',30);A table 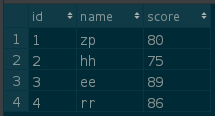
B table
Internal connection:
SELECT * FROM A INNER JOIN B ON A.id = B.id;
CONCLUSION: Internal connections only connect matched rows
Left outer connection:
SELECT * FROM A LEFT JOIN B ON A.id = B.id;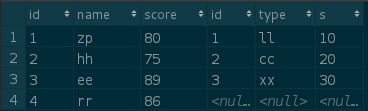
CONCLUSION: Left outer join contains all the contents of left table (A) and right table (B) matching.
Right External Connection
SELECT * FROM A RIGHT JOIN B ON A.id = B.id;
CONCLUSION: The right outer join contains all the contents of the right table (B) and the matching contents of the left table (A).
SELECT * FROM A FULL JOIN B ;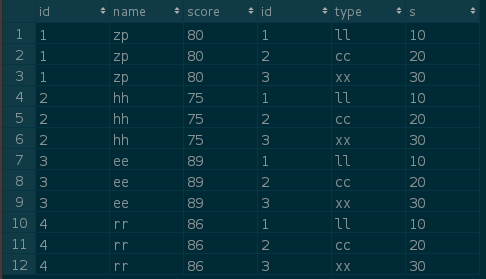
CONCLUSION: Full join refers to the connection of all the contents of the two tables. As to why there are 12 rows, it is related to the connection implementation of DBMS.
We can think of it as a two-tier for loop. The first row of table A is connected with the third row of table B, and then the second row, and so on.
Compound Conditional Connection
WHERE clause has several connection conditions, which are called compound conditional connection.
Example: Query the number and name of students who have taken database courses and have scored 90 or more points.
SELECT SC.Sno,Student.Sname FROM Student,SC,Course WHERE SC.Sno = Student.Sno AND SC.Cno=Course.Cno AND SC.Grade >= 90 AND Course.Cname = "data base";