First, we need to create an empty examstudent table in the database:
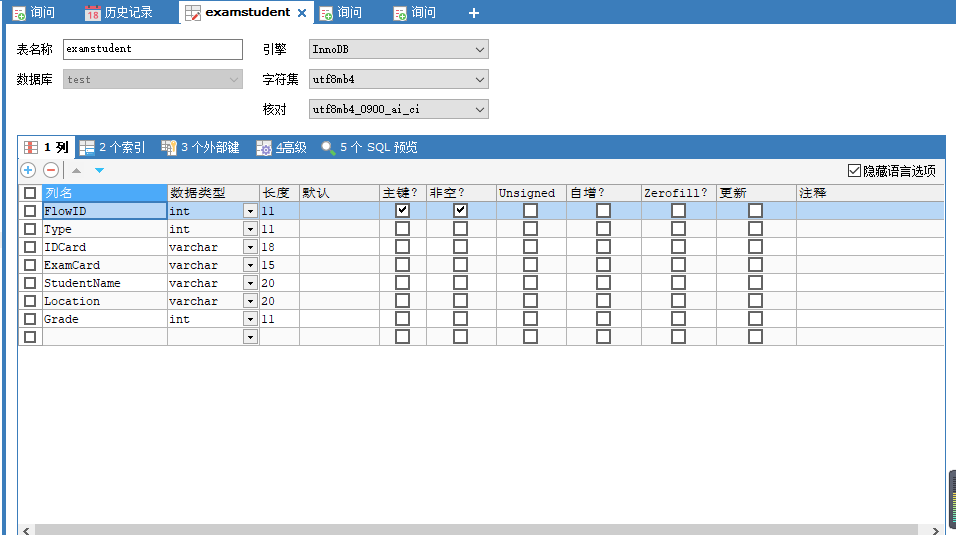
Second, create a student class corresponding to the contents in the table:
package com.atguigu.jdbc;
public class Student {
// Serial number
private int flowId;
// Examination type
private int type;
// ID number
private String idCard;
// Ticket number
private String examCard;
// Student name
private String studentName;
// Student address
private String location;
// Examination score
private int grade;
public int getFlowId() {
return flowId;
}
public void setFlowId(int flowId) {
this.flowId = flowId;
}
public int getType() {
return type;
}
public void setType(int type) {
this.type = type;
}
public String getIdCard() {
return idCard;
}
public void setIdCard(String idCard) {
this.idCard = idCard;
}
public String getExamCard() {
return examCard;
}
public void setExamCard(String examCard) {
this.examCard = examCard;
}
public String getStudentName() {
return studentName;
}
public void setStudentName(String studentName) {
this.studentName = studentName;
}
public String getLocation() {
return location;
}
public void setLocation(String location) {
this.location = location;
}
public int getGrade() {
return grade;
}
public void setGrade(int grade) {
this.grade = grade;
}
public Student(int flowId, int type, String idCard, String examCard, String studentName, String location,
int grade) {
super();
this.flowId = flowId;
this.type = type;
this.idCard = idCard;
this.examCard = examCard;
this.studentName = studentName;
this.location = location;
this.grade = grade;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student [flowId=" + flowId + ", type=" + type + ", idCard=" + idCard + ", examCard=" + examCard
+ ", studentName=" + studentName + ", location=" + location + ", grade=" + grade + "]";
}
}
Thirdly, write a JDBC tools tool class for database addition, deletion and modification:
package com.atguigu.jdbc;
import java.beans.Statement;
import java.io.Closeable;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.Properties;
import com.mysql.jdbc.Connection;
/**
* The tool class for handwritten JDBC operations encapsulates some tool methods Version 1
*/
public class JDBCTools {
/**
* 1. Get a connection from the database server by reading the configuration file
*
* @return
* @throws Exception
*/
public static Connection getConnection() throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException, SQLException {
// 1. Prepare 4 strings to connect to the database
// 1). Create Properties object
Properties properties = new Properties();
// 2). Get the input stream corresponding to jdbc.properties
InputStream in = JDBCTools.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("jdbc.properties");
// 3). Load 2) corresponding input stream
properties.load(in);
// 4) determine the four strings of user and password
String user = properties.getProperty("user");
String password = properties.getProperty("password");
String jdbcUrl = properties.getProperty("jdbcUrl");
String driver = properties.getProperty("driver");
// 2. Load the database Driver (corresponding to the static code block of registered Driver in the Driver implementation class)
Class.forName(driver);
// 3. Get database connection through getConnection() method of DriverManager
return (Connection) DriverManager.getConnection(jdbcUrl, user, password);
}
/**
* Close ResultSet, Statement, and Connectionh: similar to the stack, open first and then close, then open first and then close
*
* @param statement
* @param conn
*/
public static void release(ResultSet rs, java.sql.Statement statement, Connection conn) {
// Close ResultSet object
if (rs != null) {
try {
rs.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
// Close Statement object
if (statement != null) {
try {
statement.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
// Close conn object
if (conn != null) {
try {
conn.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
/**
* How to execute SQL
*
* @param sql:insert
* update Or delete without select
*/
public static void update(String sql) {
// 1. Get database connection
Connection conn = null;
java.sql.Statement statement = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try {
conn = JDBCTools.getConnection();
// 2. Prepare the SQL statement to be inserted
// a. insertion
// sql = "INSERT INTO customers(ID, NAME, EMAIL, BIRTH) "
// +"VALUES ('2018 ',' Wang Xiaoer ',' 163 @ erpang. Com ',' 1999-04-24 ')";
// b. delete
// sql = "DELETE FROM customers WhERE ID = '2018'";
// c. update
// sql = "UPDATE customers SET EMAIL = '163 @ Er Pang. com' WHERE ID = '2017'";
System.out.println(sql);
// 3. Insert
// 1) get Statement object of SQL Statement: call createStatement() method of Connection to get
statement = conn.createStatement();
// 2) call executeUpdate(sql) of Statement object to execute SQL Statement for insertion
statement.executeUpdate(sql);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// Close connection
JDBCTools.release(rs, statement, conn);
}
}
}
Finally, the operation of entering student information into the database:
package com.atguigu.jdbc;
import java.util.Scanner;
import org.junit.Test;
public class JDBCStudent {
/**
* Test of entering student information into database
*/
@Test
public void testAddNewStudent() {
Student student = getStudentFromConsole();
addNewStudent(student);
}
/**
* Enter student information from the console
* @return
*/
private Student getStudentFromConsole() {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
Student student = new Student(0, 0, null, null, null, null, 0);
System.out.print("FlowId: ");
student.setFlowId(scanner.nextInt());
System.out.print("Type: ");
student.setType(scanner.nextInt());
System.out.print("IdCard: ");
student.setIdCard(scanner.next());
System.err.print("ExamCard: ");
student.setExamCard(scanner.next());
System.out.print("StudentName: ");
student.setStudentName(scanner.next());
System.out.print("Location: ");
student.setLocation(scanner.next());
System.out.print("Grade: ");
student.setGrade(scanner.nextInt());
return student;
}
public void addNewStudent(Student student) {
//1. Prepare an sql statement:
String sql = "INSERT INTO examstudent "
+ "VALUES(" + student.getFlowId()
+ "," + student.getType()
+ ",'" + student.getIdCard()
+ "','" + student.getExamCard()
+ "','" + student.getStudentName()
+ "','" + student.getLocation()
+ "'," + student.getGrade() + ")";
}
}
5. Enable sql update:
//2. Call the update(sql) method of the JDBC tools class to perform the insert operation JDBCTools.update(sql);
6. After inputting information from the console, let's see whether the information is successfully input into the database:
It's very good. Our door is successful!
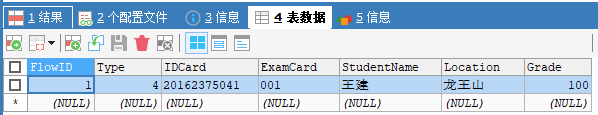
But is this really a good way? No, I will optimize this method later. Let's pay attention to this method first.