1.Nagios Profile Introduction
Let's start with "private" and "public" services, applications and protocols, where "private" refers to the CPU of the host. load,Memory usage,Disk usage,Logged in users, Running processes and other services, "public" services refer to services that can be obtained through local networks or Internet connections, such as HTTP,POP3,IMAP,FTP and SSH. In fact, there are more basic services in daily use. These services and applications, including the protocols they rely on, can be directly monitored by Nagios without additional plug-ins to support them. On the contrary, "private" services cannot be monitored without some middleware proxy Nagios. For "private" service monitoring on remote Linux/UNIX hosts, you can refer to Section 8.5 NRPE.
This section gives a brief description of some common monitoring configurations for services.
1. Nagios directory structure
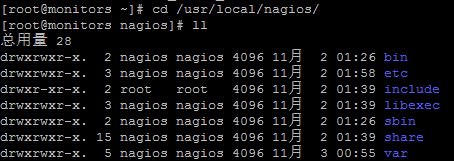
The contents of the corresponding catalogues are as follows:
|
Directory name |
directory content |
|
bin |
Nagios executable directory |
|
etc |
Nagios configuration file directory |
|
sbin |
The directory where the Nagios cgi file is located, that is, the directory where the file needed to execute an external command is located |
|
share |
Nagios Web Page Storage Path |
|
libexec |
Nagios External Plug-in Storage Directory |
|
var |
Nagios log files, Lock and other files in the directory |
|
var/archives |
Nagios log automatic archiving directory |
|
var/rw |
A directory for storing external command files |
2. Nagios configuration file relationships
Nagios configuration files include: main configuration file, resource file, object definition file and CGI configuration file. The main configuration file contains many instructions that affect the way the Nagios Core daemon operates. This configuration file is made by Nagios Core daemons and CGI reads; resource files are used to store user-defined macros, mainly for sensitive configuration information (such as passwords) rather than CGI; object definition files are used to define hosts, services, host groups, contacts, contact groups, commands, and so on; CGI configuration files contain CGIs that affect operation instructions, and it also contains a reference. The main configuration file, which knows the configuration content of Nagios and the location of object definition storage, has the following relationship:
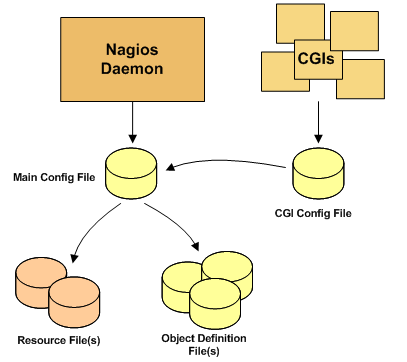
3. Nagios Profile Introduction
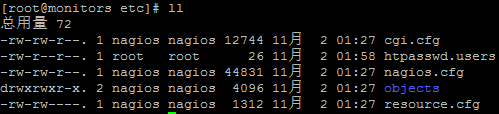
After the successful installation of Nagios, the configuration files of host, service, command, template, etc. will be generated in the / usr/local/nagios/et directory. At the same time, the authentication file htpasswed.users of Nagios authorization directory can be seen, while the Object directory is used to store some configuration file templates, mainly for defining Nagios objects.
Nagios configuration directories and files:
The Nagios object template file is as follows:
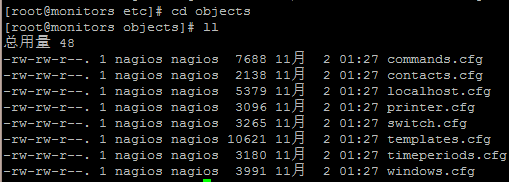
The corresponding profiles are summarized as follows:
|
configuration file |
Explain |
|
cgi.cfg |
Configuration files that control CGI access |
|
nagios.cfg |
Nagios master configuration file |
|
resource.cfg |
A variable definition file, also known as a resource file, defines variables in this file for reference by other configuration files, such as $USER1$ |
|
objects |
Objects is a directory in which there are many configuration file templates for defining Nagios objects |
|
objects/commands.cfg |
A command defines a configuration file in which the defined commands can be referenced by other configuration files |
|
objects/contacts.cfg |
Configuration files defining contacts and groups of contacts |
|
objects/localhost.cfg |
Define configuration files for monitoring local hosts |
|
objects/printer.cfg |
Define a configuration file template for monitoring printers, which is not enabled by default |
|
objects/switch.cfg |
A configuration file template for monitoring routers, which is not enabled by default |
|
objects/templates.cfg |
A template configuration file defining hosts and services that can be referenced in other configuration files |
|
objects/timeperiods.cfg |
Configuration file defining Nagios monitoring period |
|
objects/windows.cfg |
Monitor a configuration file template for Windows hosts, which is not enabled by default |
|
Remarks: |
Nagios is very flexible in configuration, and default configuration files are not required. You can use these default configuration files. You can also create your own configuration file and refer to it in the main configuration file nagios.cfg. |
2.Nagios configuration template
Nagios configuration process can start with five steps, see the next five sections:
2.1. Define contacts and groups of contacts to notify when a host or service is in trouble
1.contact is used to identify people to contact when problems arise in the network.
Definition format:
define contact{
contact_name contact_name(*)
alias alias(*)
contactgroups contactgroup_names
host_notifications_enabled [0/1](*)
service_notifications_enabled [0/1](*)
host_notification_period timeperiod_name(*)
service_notification_period timeperiod_name(*)
host_notification_options [d,u,r,f,s,n](*)
service_notification_options [w,u,c,r,f,s,n](*)
host_notification_commands command_name(*)
service_notification_commands command_name(*)
email email_address
pager pager_number or pager_email_gateway
addressx additional_contact_address
can_submit_commands [0/1]
retain_status_information [0/1]
retain_nonstatus_information [0/1]
...
}Definition sample:
define contact{
contact_name jdoe
alias John Doe
host_notifications_enabled 1
service_notifications_enabled 1
service_notification_period 24x7
host_notification_period 24x7
service_notification_options w,u,c,r
host_notification_options d,u,r
service_notification_commands notify-by-email
host_notification_commands host-notify-by-email
email jdoe@localhost.localdomain
pager 555-5555@pagergateway.localhost.localdomain
address1 xxxxx.xyyy@icq.com
address2 555-555-5555
can_submit_commands 1
}Host_notification_options, service_notification_options:
1)Host_notification_options:
- d = notify on DOWN host states,
- u = notify on UNREACHABLE host states
- r = notify on host recoveries (UP states)
- f = notify when the host starts and stops flapping
- s = send notifications when host or service scheduled downtime starts and ends
- (none) as an option, the contact will not receive any type of host notifications.
2)service_notification_options:
- w = notify on WARNING service states
- u = notify on UNKNOWN service states
- c = notify on CRITICAL service states
- r = notify on service recoveries (OK states)
- f = notify when the service starts and stops flapping
- n (none) as an option, the contact will not receive any type of service notifications.
Common settings
- host_notification_options: d,u,r
- service_notification_options:w,u,c,r
2. Contact group is used to group one or more contacts together to send alerts/recovery notifications, defining formats:
define contactgroup{
contactgroup_name contactgroup_name(*)
alias alias(*)
members contacts(*)
contactgroup_members contactgroups
...
}Definition sample:
define contactgroup{
contactgroup_name novell-admins
alias Novell Administrators
members jdoe,rtobert,tzach
}2.2. Define host, host group, service and service group
The configuration files involved in this step are: / usr/local/nagios/etc/objects/hosts.cfg, / usr/local/nagios/etc/objects/services.cfg. For the basic configuration of host, hostgroup, service and service group, see the definition in / usr/local/nagios/etc/objects/timeperiods.cfg.
1.hosts.cfg configuration
1) hosts.cfg is used to configure hosts and hostgroups. The format can refer to the definition of hosts and hostgroups in localhost.cfg.
host is defined as a physical server, workstation or device that exists in the network. Detailed formats (marked (*) are necessary and others are optional):
define host{
host_name host_name(*)
alias alias(*)
display_name display_name
address address(*)
parents host_names
hostgroups hostgroup_names
check_command command_name
initial_state [o,d,u]
max_check_attempts #(*)
check_interval #
retry_interval #
active_checks_enabled [0/1]
passive_checks_enabled [0/1]
check_period timeperiod_name(*)
obsess_over_host [0/1]
check_freshness [0/1]
freshness_threshold #
event_handler command_name
event_handler_enabled [0/1]
low_flap_threshold #
high_flap_threshold #
flap_detection_enabled [0/1]
flap_detection_options [o,d,u]
process_perf_data [0/1]
retain_status_information [0/1]
retain_nonstatus_information [0/1]
contacts contacts(*)
contact_groups contact_groups(*)
notification_interval #(*)
first_notification_delay #
notification_period timeperiod_name(*)
notification_options [d,u,r,f,s]
notifications_enabled [0/1]
stalking_options [o,d,u]
notes note_string
notes_url url
action_url url
icon_image image_file
icon_image_alt alt_string
vrml_image image_file
statusmap_image image_file
2d_coords x_coord,y_coord
3d_coords x_coord,y_coord,z_coord
...
}Definition sample:
define host{
host_name bogus-router
alias Bogus Router #1
address 192.168.1.254
parents server-backbone
check_command check-host-alive
check_interval 5
retry_interval 1
max_check_attempts 5
check_period 24x7
process_perf_data 0
retain_nonstatus_information 0
contact_groups router-admins
notification_interval 30
notification_period 24x7
notification_options d,u,r
}define hostgroup{
hostgroup_name hostgroup_name(*)
alias alias(*)
members hosts
hostgroup_members hostgroups
notes note_string
notes_url url
action_url url
...
}Definition sample:
define hostgroup{
hostgroup_name novell-servers
alias Novell Servers
members netware1,netware2,netware3,netware4
}1) Service service is defined as some kind of "application service" running on the host, which defines the format:
define service{
host_name host_name(*)
hostgroup_name hostgroup_name
service_description service_description(*)
display_name display_name
servicegroups servicegroup_names
is_volatile [0/1]
check_command command_name(*)
initial_state [o,w,u,c]
max_check_attempts #(*)
check_interval #(*)
retry_interval #(*)
active_checks_enabled [0/1]
passive_checks_enabled [0/1]
check_period timeperiod_name(*)
obsess_over_service [0/1]
check_freshness [0/1]
freshness_threshold #
event_handler command_name
event_handler_enabled [0/1]
low_flap_threshold #
high_flap_threshold #
flap_detection_enabled [0/1]
flap_detection_options [o,w,c,u]
process_perf_data [0/1]
retain_status_information [0/1]
retain_nonstatus_information [0/1]
notification_interval #(*)
first_notification_delay #
notification_period timeperiod_name(*)
notification_options [w,u,c,r,f,s]
notifications_enabled [0/1]
contacts contacts(*)
contact_groups contact_groups(*)
stalking_options [o,w,u,c]
notes note_string
notes_url url
action_url url
icon_image image_file
icon_image_alt alt_string
...
}
define service{
host_name linux-server
service_description check-disk-sda1
check_command check-disk!/dev/sda1
max_check_attempts 5
check_interval 5
retry_interval 3
check_period 24x7
notification_interval 30
notification_period 24x7
notification_options w,c,r
contact_groups linux-admins
}define servicegroup{
servicegroup_name servicegroup_name(*)
alias alias(*)
members services
servicegroup_members servicegroups
notes note_string
notes_url url
action_url url
...
}Definition examples:
define servicegroup{
servicegroup_name dbservices
alias Database Services
members ms1,SQL Server,ms1,SQL Server Agent,ms1,SQL DTC
}2.3 Define monitoring commands
The definition of command includes commands such as service checking, service notification, service event handler, host checking, host notification and host event handler. The configuration file is / usr/local/nagios/etc/objects/commands.cfg.
Definition format:
define command{
command_name command_name(*)
command_line command_line(*)
...
}Definition examples:
define command{
command_name check_pop
command_line /usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_pop -H $HOSTADDRESS$
}2.4 Define monitoring time cycle
Time period defines the "valid" time list for notification and service checks, with the cycle time range and the configuration file as / usr / local / Nagios / etc / objects / timeperiod s. cfg.
Definition format:
define timeperiod{
timeperiod_name timeperiod_name(*)
alias alias(*)
[weekday] timeranges
[exception] timeranges
exclude [timeperiod1,timeperiod2,...,timeperiodn]
...
}Definition examples:
define timeperiod{
timeperiod_name nonworkhours
alias Non-Work Hours
sunday 00:00-24:00 ; Every Sunday of every week
monday 00:00-09:00,17:00-24:00 ; Every Monday of every week
tuesday 00:00-09:00,17:00-24:00 ; Every Tuesday of every week
wednesday 00:00-09:00,17:00-24:00 ; Every Wednesday of every week
thursday 00:00-09:00,17:00-24:00 ; Every Thursday of every week
friday 00:00-09:00,17:00-24:00 ; Every Friday of every week
saturday 00:00-24:00 ; Every Saturday of every week
}
define timeperiod{
timeperiod_name misc-single-days
alias Misc Single Days
1999-01-28 00:00-24:00 ; January 28th, 1999
monday 3 00:00-24:00 ; 3rd Monday of every month
day 2 00:00-24:00 ; 2nd day of every month
february 10 00:00-24:00 ; February 10th of every year
february -1 00:00-24:00 ; Last day in February of every year
friday -2 00:00-24:00 ; 2nd to last Friday of every month
thursday -1 november 00:00-24:00 ; Last Thursday in November of every year
}
define timeperiod{
timeperiod_name misc-date-ranges
alias Misc Date Ranges
2007-01-01 - 2008-02-01 00:00-24:00 ; January 1st, 2007 to February 1st, 2008
monday 3 - thursday 4 00:00-24:00 ; 3rd Monday to 4th Thursday of every month
day 1 - 15 00:00-24:00 ; 1st to 15th day of every month
day 20 - -1 00:00-24:00 ; 20th to the last day of every month
july 10 - 15 00:00-24:00 ; July 10th to July 15th of every year
april 10 - may 15 00:00-24:00 ; April 10th to May 15th of every year
tuesday 1 april - friday 2 may 00:00-24:00 ; 1st Tuesday in April to 2nd Friday in May of every year
}
define timeperiod{
timeperiod_name misc-skip-ranges
alias Misc Skip Ranges
2007-01-01 - 2008-02-01 / 3 00:00-24:00 ; Every 3 days from January 1st, 2007 to February 1st, 2008
2008-04-01 / 7 00:00-24:00 ; Every 7 days from April 1st, 2008 (continuing forever)
monday 3 - thursday 4 / 2 00:00-24:00 ; Every other day from 3rd Monday to 4th Thursday of every month
day 1 - 15 / 5 00:00-24:00 ; Every 5 days from the 1st to the 15th day of every month
july 10 - 15 / 2 00:00-24:00 ; Every other day from July 10th to July 15th of every year
tuesday 1 april - friday 2 may / 6 00:00-24:00 ; Every 6 days from the 1st Tuesday in April to the 2nd Friday in May of every year2.5 Configuration of the main configuration file nagios.cfg
Add the files configurated in the above four steps to the / usr/local/nagios/etc/nagios.cfg file through cfg_file and cfg_dir, and refer to the existing configurations in the file, which will not be discussed here. Complete all the above configurations, and restart the corresponding Nagios and plug-in services, you can see the results of the configuration on the web side of nagios.
For other content about Nagios, please pay attention to the author's updates.
Attachment: This article refers to Nagios official documents, and will continue to improve, shortcomings welcome criticism and correction!