
Introduction to SCCA
SCCA is called spring-cloud-config-admin, and Spring Boot applications (including Spring Cloud) are unified configuration management platforms under micro services.
- Github address: spring-cloud-config-admin
- Core Contributors: Programmer DD | stone-jin
- Tags: lightweight, easy to use, visually good, interactive
Deploy SCCA
1. Run MySQL, already exists, please ignore this step
docker run --name mariadb -e MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=scca-pwd -d mariadb
2. Create a configuration file, assuming the path is ~/scca/bootstrap.properties
# server spring.application.name=scca-server server.port=8080 # scca-rest-server api url prefix scca.rest.context-path=/xhr # scca-ui-server embed scca-rest-server scca.ui.use-embed-scca-rest-server=true # Datasource spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://mariadb:3306/config-db spring.datasource.username=root spring.datasource.password=scca-pwd spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver # embed config server # warning : create env set contextPath spring.cloud.config.server.prefix=/scca-config-server encrypt.key=anoyi
3. Run SCCA
docker run -d --name scca \ --link mariadb:mariadb \ -p 8080:8080 \ -v ~/scca/bootstrap.properties:/bootstrap.properties \ -e SPRING_PARAMS="spring.config.location=/bootstrap.properties" \ registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/micro-java/micro-core-config
Applying SCCA
Before using SCCA, learn three basic concepts:
- Environment: e.g. development environment, test environment, production environment, etc.
- Project: Each Spring Boot application is a project
- Version: A branch of the Git repository, e.g. master, 1.0.0, etc.
Suppose you have a Spring Boot application [ samples-server The configuration is as follows:
server: port: 8081 spring: grpc: enable: true port: 6565
How can I apply it to SCCA?
1. New Environment
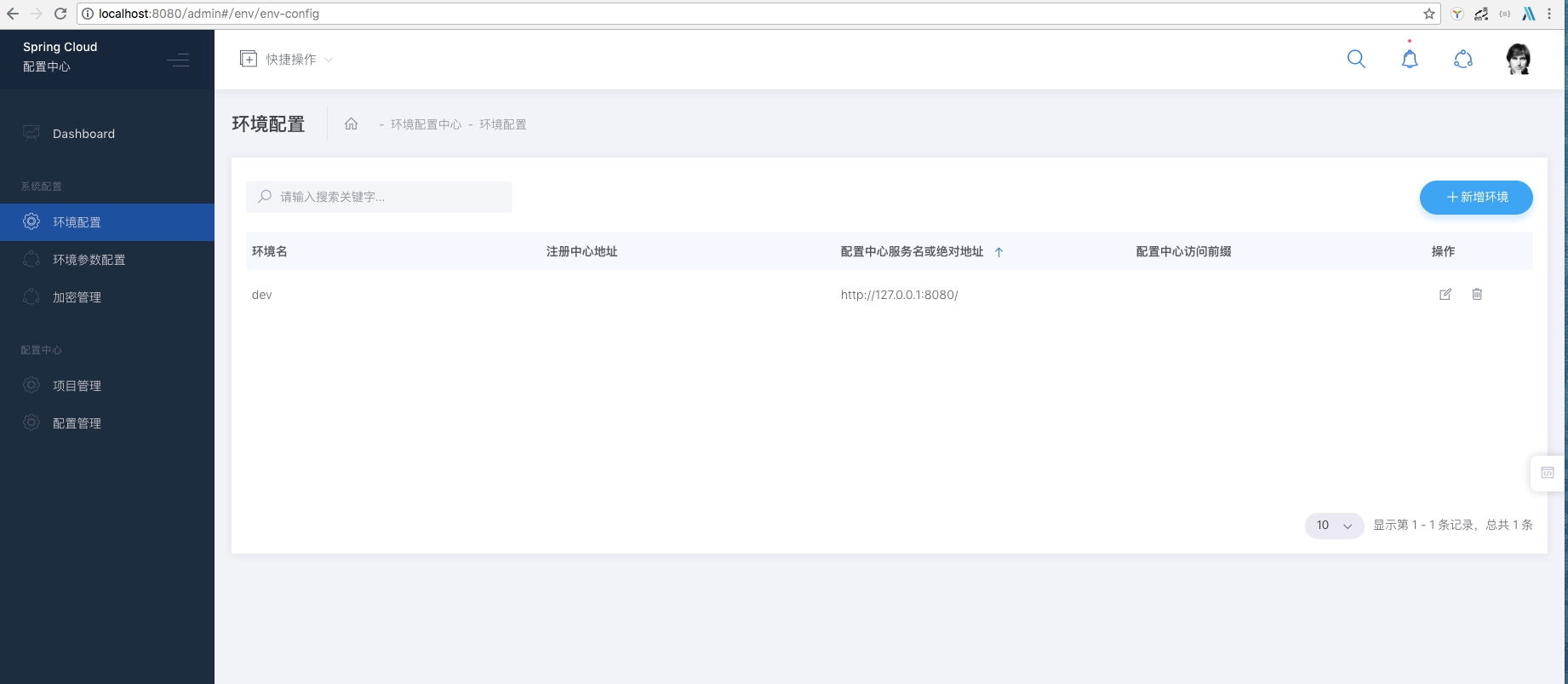
2. Create Project
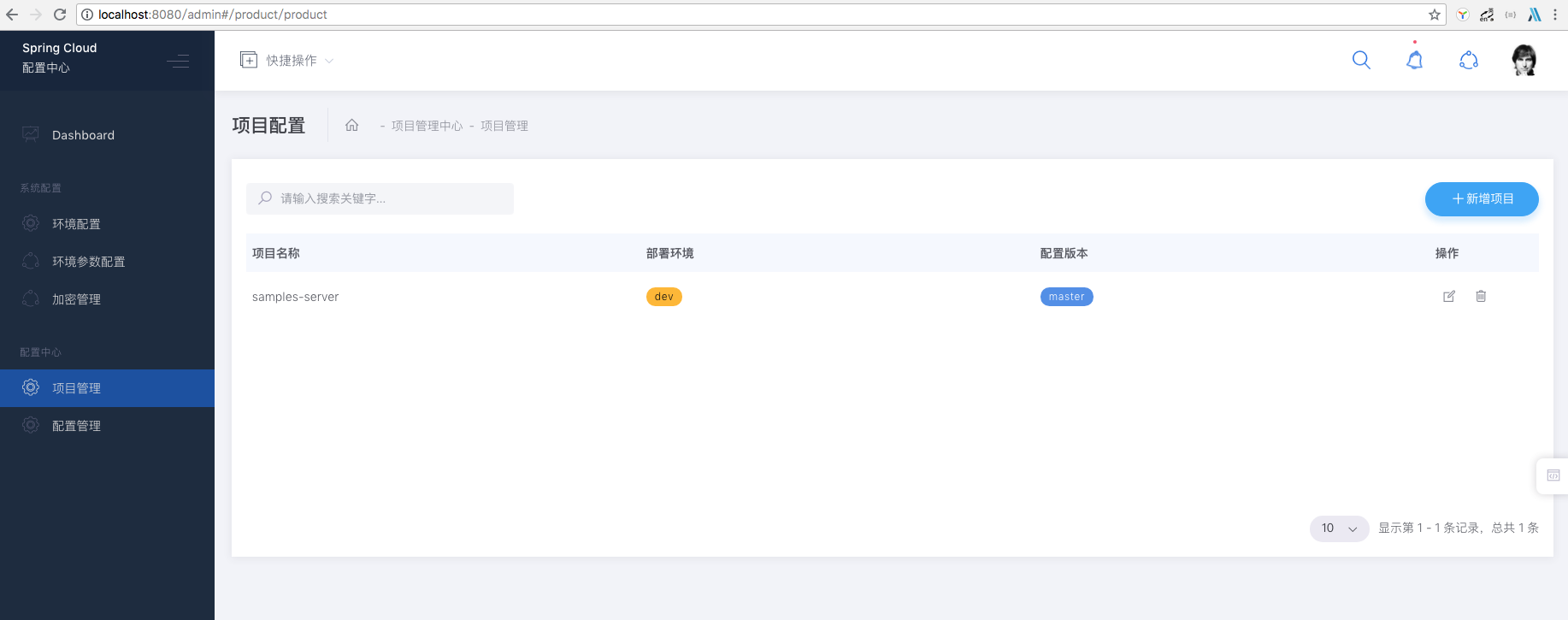
3. Add Configuration
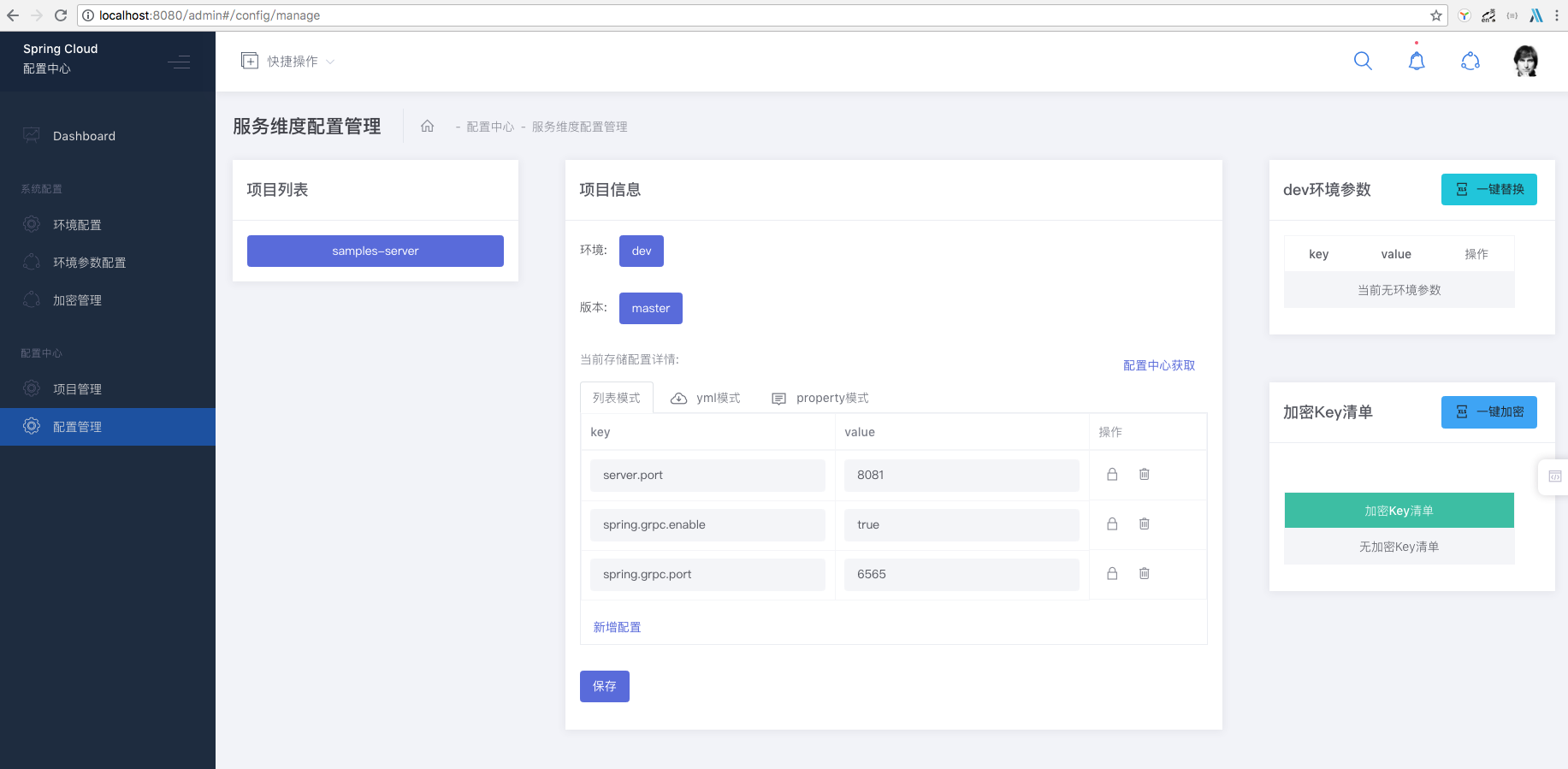
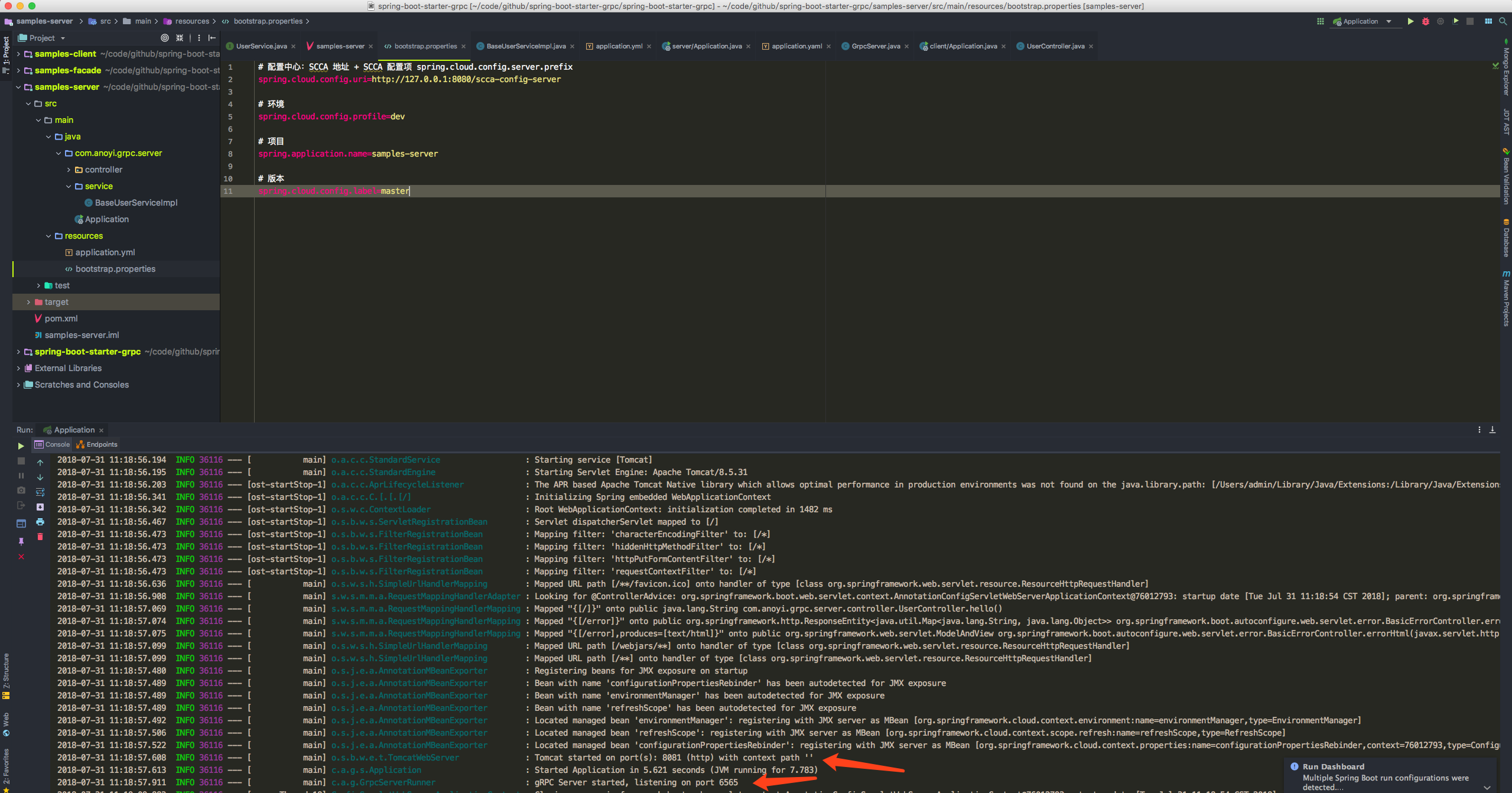
4. SpringBoot Application Started by SCCA
First, add Maven dependencies:
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-config</artifactId> <version>2.0.0.RELEASE</version> </dependency>
Then add the configuration file resources/bootstrap.properties, which can be used as a generic configuration template:
# Configuration Center: SCCA address + SCCA configuration item spring.cloud.config.server.prefix spring.cloud.config.uri=http://127.0.0.1:8080/scca-config-server # Environmental Science spring.cloud.config.profile=dev # project spring.application.name=samples-server # Edition spring.cloud.config.label=master
Finally, start the app!
SCCA Advancement
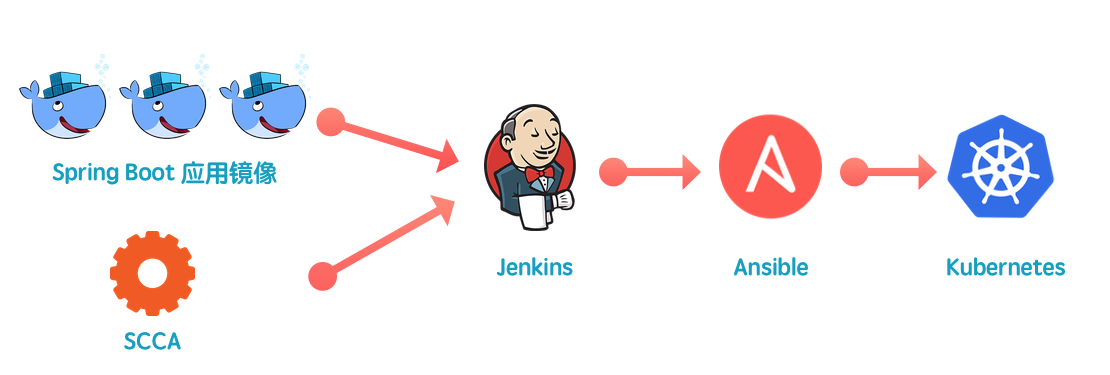
SCCA can unify the configuration of all Spring Boot applications, which brings great convenience to operation and maintenance!
1. First, you can define a universal Dockerfile
FROM openjdk:8-jre-alpine ENV TZ="Asia/Shanghai" JVM_PARAMS="" APP_CONFIG_URL="" APP_ENV="" APP_NAME="" APP_VERSION="" ADD target/*.jar /server.jar CMD java $JVM_PARAMS -Djava.security.egd=file:/dev/./urandom -jar /server.jar --spring.cloud.config.uri=$APP_CONFIG_URL --spring.cloud.config.profile=$APP_ENV --spring.application.name=$APP_NAME --spring.cloud.config.label=$APP_VERSION
| parameter | describe |
|---|---|
| JVM_PARAMS | JVM Related Parameter Configuration |
| APP_CONFIG_URL | Address of the configuration center, corresponding to spring.cloud.config.uri |
| APP_ENV | Apply the published environment for spring.cloud.config.profile |
| APP_NAME | Service name, corresponding to spring.application.name |
| APP_VERSION | Service version, corresponding to spring.cloud.config.label |
2. Then build a generic Jenkins pipeline
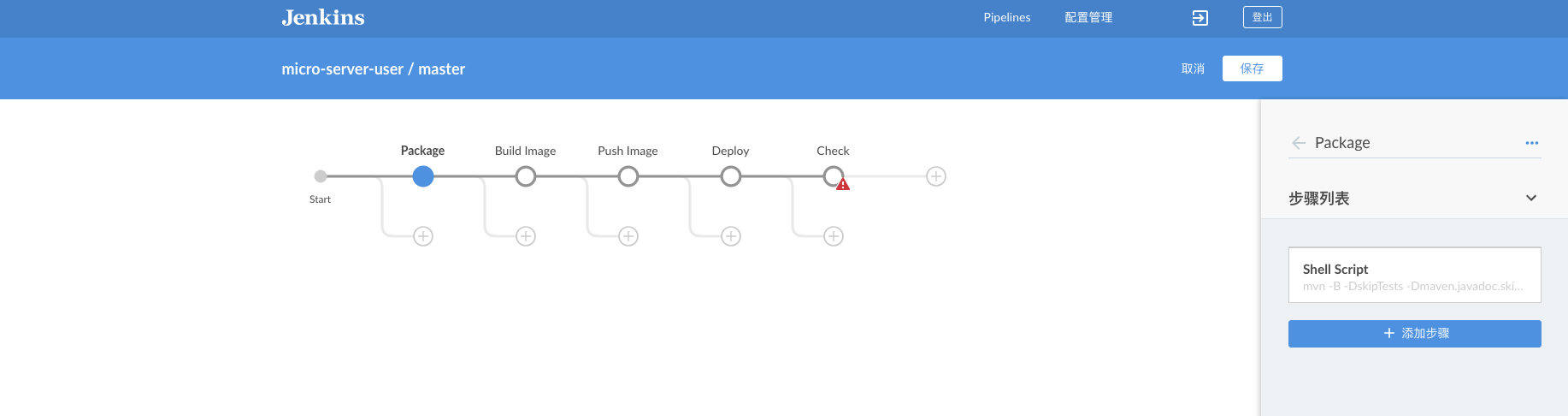
Jenkins uses Maven to package the code, build a Docker image, then push it to the mirror repository, then use Ansible to deploy the service to the Kubernetes cluster through different variable settings, and finally verify the successful deployment of the service through a shell script.
Scavenger watches me:

This article is published by blog OpenWrite Release!