9.8 comment function realization and sorting
Here, take the implementation of the comment list of the article page as an example
1, Business analysis
Simulated station B comment service
1.1 business logic
- When accessing an article, try to get the comment list of the article.
- According to the article comment configuration (these configurations are a separate table and have a one-to-one relationship with the article), the corresponding first-level comments and second-level comments are displayed in pages.
- For the first level comments, click show more comments to display all the second level comments under the comments and display them in pages.
- First level comments and second level comments can be sorted by popularity or creation time according to article configuration
1.2 implementation ideas
- Add a parent id for the comment to point to the parent comment, and add a reply id to point to the reply comment.
- Comments are divided into two levels: first level comments and second level comments.
- The parent id of the first level comment is 0, and the parent comment of the second level comment points to the first level comment.
- Reply id refers to the information reply between a comment and the secondary comments under the comment.
1.3 rule analysis
- The parent id of the first level comment is 0L
- Level 2 comments must have a parent id and cannot be 0L
- Secondary comments cannot reply to secondary comments under other parent IDs
- Level 1 comments cannot reply to other comments, and other comments cannot reply to level 1 comments
2, Table structure
2.1 comment
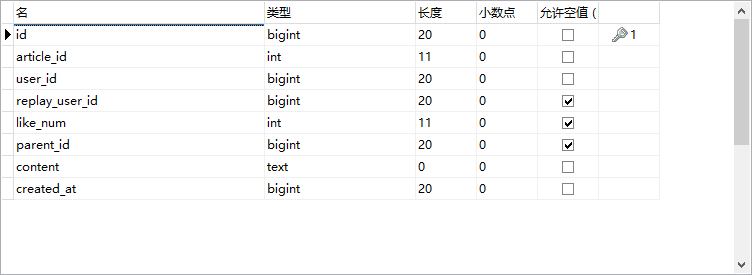
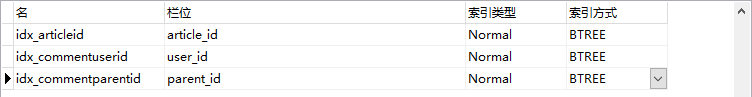
2.2 comment_settings


Three. Model building
Interact with the database using Spring Data Jpa
3.1 Comment
The Comment model internally maintains the User, reply User and sub Comment list
@Entity
@Table(name = "comment")
public class Comment
{
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long id;
private Long articleId;
private Long userId;
private Long replayUserId;
private Long parentId;
private Integer likeNum = 0;
private String content;
@Column(updatable = false)
private Long createdAt;
@Transient
private User user;
@Transient
private User replayUser;
@Transient
private List<Comment> childrenComment;
3.2 CommentSettings
CommentSettings internally maintains the article configuration information
@Entity
@Table(name = "comment_settings")
public class CommentSettings
{
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long id;
private Long articleId;
@Convert(converter = SettingsInfoConverter.class)
private SettingsInfo settings;
}
3.3 SettingsInfo
public class SettingsInfo
{
private Byte sort = CommentSort.CREATEDAT.val();
private Integer pageMax = 10;
}
4, Function realization
Comment functions mainly include saving and list display
4.1 save comments
@Transactional
@Override
public void saveComment(Comment comment)
{
if (comment.getArticleId() == null)
{
throw new ArgumentServiceException("articleId");
}
if (comment.getContent().length() < 6 || StringUtils.isEmpty(comment.getContent()))
{
throw new ArgumentServiceException("content");
}
Long curUserId = UserContexts.getUserId();
if (curUserId == null)
{
throw new SessionServiceException();
}
// If the comment is a secondary comment, check whether its parent comment exists
Long parentId = comment.getParentId();
if (parentId != 0L)
{
getById(parentId);
}
Long replyId = comment.getReplayUserId();
if (replyId != null)
{
// If the reply comment id is not empty, it is not allowed to be a level 1 comment (if you pass this step, it means that the comment is a level 2 comment)
if (parentId == 0L)
{
throw new ArgumentServiceException("replayId");
}
// If the reply comment exists and the comment is not under the same level of comment as it, it does not comply with the provisions.
// If the reply comment exists and it is a first-class comment, it does not comply with the regulations.
Comment replayComment = commentRepository.findByReplayUserId(replyId);
if (replayComment != null && (replayComment.getParentId() != parentId || replayComment.getParentId() == 0L))
{
throw new ArgumentServiceException("replayId");
}
}
comment.setUserId(curUserId);
comment.setCreatedAt(System.currentTimeMillis());
commentRepository.save(comment);
commentCache.remove(comment.getId());
articleService.updateCommentNum(comment.getArticleId(), true);
}
4.2 comment list display function
Here, I divide the implementation of the comment list into three steps
- According to the configuration, judge whether you need to log in or reply to view the comment list at the back of the first page
- Get the comment data according to the parent id in qo
- Get all comment data (including the second level comments under the first level comments), and store the hot second level comments in the cache
- Render user information
@Override
public Page<Comment> commentList(CommentQo qo)
{
// Get configuration
CommentSettings settings = settingsRepository.findByArticleId(qo.getArticleId());
if (settings.getSettings() != null)
{ // If login is required and the current page number is greater than the first page, authentication is required
if (settings.getSettings().getRequiredSignin() == ByteUtils.BYTE_1 && qo.getPageNumber() > 1)
{
Long userId = UserContexts.userId();
if (userId == null)
{
throw new DataNotFoundServiceException("Comments are not visible until you log in");
}
if (settings.getSettings().getRequiredReply() == ByteUtils.BYTE_1)
{
List<Comment> profileComments = commentRepository.findAllByUserId(userId);
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(profileComments))
{
throw new DataNotFoundServiceException("Only visible after replying to the article");
}
}
}
}
// Get source data after paging
Page<Comment> page = commentRepository.findAll(qo);
List<Comment> commentList = page.getContent();
// Get the first three hot comments
getOriginComments(qo, commentList);
// Render User for all comments
wrapperCommentUser(commentList);
return page;
}
getOriginComments
If the parent id passed by the interface is 0L, it means that all contents in the comment list are obtained. (when the parent id of qo is a level-1 comment id, all the obtained comments are level-2 comments, and the commentList is all data at this time)
private void getOriginComments(CommentQo qo, List<Comment> commentList)
{
if (qo.getParentId() == 0L)
{
for (int i = 0; i < commentList.size(); i++)
{
qo.setParentId(commentList.get(i).getId());
// Put it in the cache, because the first three hot data of these first-level comments will be displayed whenever users access the article
List<Comment> childrenCommentList = commentCache.findByKey(qo.getParentId());
if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(childrenCommentList))
{
commentList.get(i).setChildrenComment(childrenCommentList);
}
}
}
}
wrapperCommentUser
- Render User for all comments
- Render replayUser for all comments whose replayid is not null
private void wrapperCommentUser(List<Comment> commentList)
{
// Sort out all user IDs (including the user id of sending comments and the id of replying users)
Set<Long> userIds = new HashSet<>();
for (Comment comment : commentList)
{
userIds.add(comment.getUserId());
for (Comment childrenComment : comment.getChildrenComment())
{
userIds.add(childrenComment.getUserId());
if (childrenComment.getReplayUserId() != null)
{
userIds.add(childrenComment.getReplayUserId());
}
}
}
// Same query
Map<Long, User> users = userService.findByIds(userIds);
// First assemble the comment itself
for (Comment comment : commentList)
{
comment.setUser(users.get(comment.getUserId()));
for (Comment childrenComment : comment.getChildrenComment())
{
childrenComment.setUser(users.get(childrenComment.getUserId()));
}
}
// Then the assembly User replies to the User
for (Comment comment : commentList)
{
for (Comment childrenComment : comment.getChildrenComment())
{
if (childrenComment.getReplayUserId() != null)
{
childrenComment.setReplayUser(users.get(childrenComment.getReplayUserId()));
}
}
}
}