The purpose of cloning is to quickly create a copy of an existing object.
Cloning steps:
- Create an object
- Import the data of the original object into the newly created data
1. clone() source code of Object
clone method first decides whether the object implements Cloneable interface, and if not throws CloneNotSupportedException. Finally, internalClone. intervalClone is called as a native method. Generally speaking, the execution efficiency of native method is higher than that of non-native method.
When a class overrides the clone method, it inherits the Cloneable interface. Usually cloned objects are cloned by super.clone() method.
2. Shallow clone
Cloning is copying a copy of an object. If only the field values of the object need to be copied (for basic data types, such as int,long,float, etc.), then the field values are copied; for composite data types, only the field values, such as array variables, copy the address; and for object variables, copy the reference of the object.
Example:
Then test:
The result is:
Precloning c1: a=100 b=1000
Pre-cloning c1: a=100 b=5
Cloned c2: a=50 b[0]=5
Object models for c1 and c2:
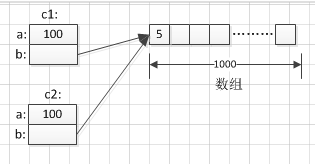
As you can see, shallow cloning can be used for basic types, while for reference types, because the reference content is the same, changing the attributes in the c2 instance object will affect c1. So reference types need to use deep cloning. In addition, when developing an immutable class, if the members of the immutable class have reference types, deep cloning is needed to achieve the immutable purpose.
3. Deep clone
The difference between deep cloning and shallow cloning is the replication of composite data types. If a field in an object is of composite type, an object needs to be recreated for that field when cloning the object.
Example:
The result is:
Precloning c1: a=100 b=1000
Precloning c1: a=100 b=1000Cloned c2: a=50 b[0]=5
Object Model:
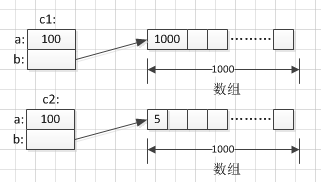
4. Summary:
- Clone method is used to create copies of objects. In order to use clone method, classes must implement java.lang.Cloneable interface to override the protected method clone. If Clonebale interface is not implemented, CloneNotSupportedException will be thrown.
- Constructors are not called when cloning java objects
- java provides a default way to implement clone, called shallow copy, by creating a copy of an object and then copying the content by assigning values, which means that if your class contains reference types, then both the original object and the clone will point to the same reference content, which is dangerous because any change in a variable field will be reflected in the same reference they refer to. Let it be. In order to avoid this situation, it is necessary to clone the referenced content in depth.