#include<stdio.h> int main() { int i,a[10]; for(i=0;i<=9;i++) a[i]=i; for(i=9;i>=0;i--) printf("%d ",a[i]); printf("\n"); return 0; } #include<stdio.h> int main() { int i,a[10]; for(i=0;i<=9;i++) a[i]=i; for(i=9;i>=0;i--) printf("%d ",a[i]); printf("\n"); return 0; }
The operation results are as follows
Example 6.2 solving Fibonacci sequence with array
#include<stdio.h> int main() { int i; int f[20]={1,1}; for(i=2;i<20;i++) f[i]=f[i-2]+f[i-1]; for(i=0;i<20;i++) { if(i%5==0) printf("\n"); printf("%12d",f[i]); } printf("\n"); return 0; }
The operation results are as follows: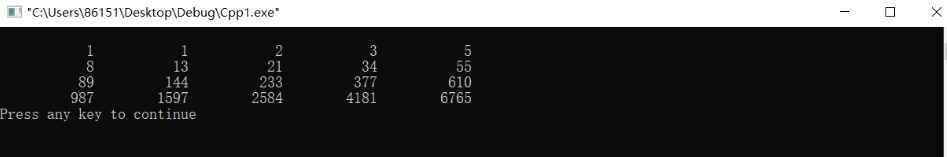
Example 6.3 there are 10 areas, which need to be arranged in order of small to large
#include<stdio.h> int main() { int a[10]; int i,j,t; printf("input 10 numbers:\n"); for(i=0;i<10;i++) scanf("%d",&a[i]); printf("\n"); for(j=0;j<9;j++) for(i=0;i<9-j;i++) if(a[i]>a[i+1]) {t=a[i];a[i]=a[i+1];a[i+1]=t;} printf("the sorted numbers:\n"); for(i=0;i<10;i++) printf("%d ",a[i]); printf("\n"); return 0; }
The operation results are as follows
Example 6.4 interchange the elements of a two-dimensional array row and column and store them in another two-dimensional array
#include<stdio.h> int main() { int a[2][3]={{1,2,3},{4,5,6}}; int b[3][2],i,j; printf("array a:\n"); for(i=0;i<=1;i++) { for(j=0;j<=2;j++) { printf("%5d",a[i][j]); b[j][i]=a[i][j]; } printf("\n"); } printf("array b:\n"); for(i=0;i<=2;i++) { for(j=0;j<=1;j++) printf("%5d",b[i][j]); printf("\n"); } return 0; }
The operation results are as follows:
Example 6.5 has a 3 * 4 matrix, which requires the program to find out the element with the largest value, as well as the row number and column number
#include<stdio.h> int main() { int i,j,row=0,colum=0,max; int a[3][4]={{1,2,3,4},{9,8,7,6},{-10,10,-5,2}}; max=a[0][0]; for(i=0;i<=2;i++) for(j=0;j<=3;j++) if(a[i][j]>max) {max=a[i][j]; row=i; colum=j; } printf("max=%d\nrow=%d\ncolum=%d\n",max,row,colum); return 0; }
The operation results are as follows:
Example 6.6 output a known string
#include<stdio.h> int main() { char c[15]={'I',' ','a','m',' ','a','s','t','d','e','n','t','.'}; int i; for(i=0;i<15;i++) printf("%c",c[i]); printf("\n"); return 0; }
The operation results are as follows:
Example 6.7 output a diamond
#include<stdio.h> int main() {char diamond[ ][5]={{' ',' ','*'},{' ','*',' ','*'},{'*',' ',' ',' ','*'},{' ','*',' ','*'},{' ',' ','*'}}; int i,j; for(i=0;i<5;i++) { for(j=0;j<5;j++) printf("%c",diamond[i][j]); printf("\n"); } return 0; }
The operation results are as follows:
Example 6.9 there are three strings to find the "largest" one
#include<stdio.h> #include<string.h> int main() { char str[3][20]; char string[20]; int i;for(i=0;i<3;i++) gets(str[i]); if(strcmp(str[0],str[1])>0) strcpy(string,str[0]); else strcpy(string,str[1]); if(strcmp(str[2],string)>0) strcpy(string,str[2]); printf("\nthe largest string is:\n%s\n",string); return 0; }
The operation results are as follows: Data)
Data)