Reference resources:
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_21573899/article/details/78843075 [refer to this document for most of this article]
https://www.cnblogs.com/Mchn/p/9984186.html
Technological process:
1. Install Mysql normally. The default installation directory is / usr/local/mysql data file directory / usr/local/mysql/data.
2. Modify the data file directory to / home/mysql/data [requirements]
Operation:
Step one:
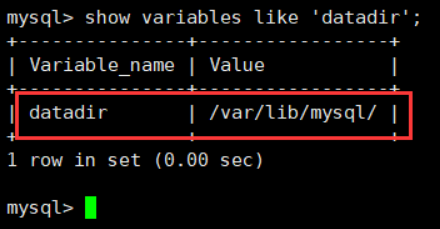
1. View the MySQL source data storage path command:
show variables like 'datadir';
After query, the results are shown as follows:
2. Stop Mysql service:
service mysql stop //Or if service mysqld stop is not added to the service, execute the next sentence ps -ef|grep mysql kill -9 pid //pid = obtained after querying the previous command
3. Create a new directory: / home/mysql/data, and ensure that the permission is granted
//Create user groupadd mysql useradd mysql -g mysql //Create directory mkdir -p /home/mysql/data //To grant authorization chmod -R 777 /home/mysql chown -R mysql:mysql /home/mysql
4. Copy the previous data files to the new data directory:
cp -rf /usr/local/mysql/data/* /home/mysql/data/ chown -R mysql:mysql /home/mysql/data/* //Swipe the permission again
5. Change profile:
①/etc/my.cnf
[client] socket = /home/mysql/data/mysql.sock [mysqld] datadir = /home/mysql/data socket = /home/mysql/data/mysql.sock
② / etc/init.d/mysql [or mysqld]
datadir = /home/mysql/data
6. Refresh directory permission:
chown -R mysql:mysql /home/mysql/data service iptables restart service iptables stop setenforce 0
7. Restart mysql service
service mysql start/restart //service mysqld start/restart //If no service is added cd /usr/local/mysql/support-files ./mysql.server start
8. Enter mysql command line
mysql perhaps mysql -uroot -p perhaps mysql -hlocalhost -uroot -p etc. show databases; show variables like 'datadir' //Check whether the directory has been modified successfully / home/mysql/data
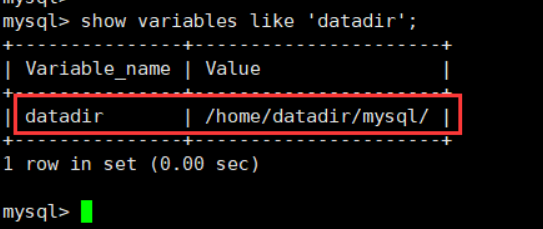
At this time, the data file directory has been modified successfully, followed by the permission table permission problem.
The second step:
1. Enter the data file directory to view the properties:
//To grant authorization cd /home/mysql/data ll -lah //To grant authorization chmod -R 777 /home/mysql/data/* chown -R mysql:mysql /home/mysql //View the properties of the moved data file, such as MySQL and test.~~~~~ //Make sure the attribute is mysql. If necessary, you can enter the lower directory to view the attribute. If it is root, you need to modify it to MySQL.
2. Refresh mysql.server table
//Connect mysql mysql -uroot -p //Connect to mysql database use mysql; //Refresh flush privileges; //ERROR 1146(42S02):Table 'mysql.servers' doesn't exist //Delete servers table drop table if exists mysql.servers;
3. Run the database creation script
CREATE TABLE `servers` (
`Server_name` char(64) NOT NULL,
`Host` char(64) NOT NULL,`Db` char(64) NOT NULL,
`Username` char(64) NOT NULL,
`Password` char(64) NOT NULL,
`Port` int(4) DEFAULT NULL,
`Socket` char(64) DEFAULT NULL,
`Wrapper` char(64) NOT NULL,
`Owner` char(64) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`Server_name`)
) ENGINE=MyISAM DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 COMMENT='MySQL Foreign Servers table';4. Refresh permissions again
flush privileges; //If the error is still reported, restart and execute again
5. Finish. Now open Navicat connection.
List of error reporting problems:
1. reference https://www.cnblogs.com/Mchn/p/9984186.html

2. Prompt pid or localadmin.locaadmin after installation.
A: it is usually caused by the sock file or the wrong directory modification.