Python xlwt module Excel table foundation 3: cell format, font format, alignment, border and fill, etc
preface:
The first two sections of the blog introduce some basic operations of xlwt on Excel tables. The last two sections are as follows:
1: Cell write, merge, insert bitmap, etc
2: Freezing windows, setting encryption protection, printing settings, etc
This blog mainly introduces cell format settings, including:
1. Cell data type;
2. Font setting;
3. Alignment;
4. Border setting;
5. Filling setting;
6. Cell protection.
1. Data type settings
Here we still use the method of the previous section. First, we create two sheet tables, write data, and then set a custom cell format for the Tset sheet table, and the T2 sheet table is written in the default cell format.
# Import module import xlwt work_book = xlwt.Workbook() work_sheet = work_book.add_sheet('Test') w2 = work_book.add_sheet('T2') # Create data z = [[r,c] for r in range(20) for c in range(20)] [l.append(str(i)) for i,l in enumerate(z)]
Cell formatting method:
# Style my_style_1 = xlwt.XFStyle() # Create cell data type, numeric type, default: 'General' my_style_1.num_format_str = '0' # Write data, Test sheet object in custom format, T2 sheet object in default format for info in z: # Write data and Format Cells work_sheet.write(info[0],info[1],info[2],my_style_1) w2.write(info[0],info[1],info[2]) # Save file work_book.save('Test3.xls')
The data formats that can be set are:
# Cell data type ####################################################### ''' 'general', '0', '0.00', '#,##0', '#,##0.00', '"$"#,##0_);("$"#,##0)', '"$"#,##0_);[Red]("$"#,##0)', '"$"#,##0.00_);("$"#,##0.00)', '"$"#,##0.00_);[Red]("$"#,##0.00)', '0%', '0.00%', '0.00E+00', '# ?/?', '# ??/??', 'M/D/YY', 'D-MMM-YY', 'D-MMM', 'MMM-YY', 'h:mm AM/PM', 'h:mm:ss AM/PM', 'h:mm', 'h:mm:ss', 'M/D/YY h:mm', '_(#,##0_);(#,##0)', '_(#,##0_);[Red](#,##0)', '_(#,##0.00_);(#,##0.00)', '_(#,##0.00_);[Red](#,##0.00)', '_("$"* #,##0_);_("$"* (#,##0);_("$"* "-"_);_(@_)', '_(* #,##0_);_(* (#,##0);_(* "-"_);_(@_)', '_("$"* #,##0.00_);_("$"* (#,##0.00);_("$"* "-"??_);_(@_)', '_(* #,##0.00_);_(* (#,##0.00);_(* "-"??_);_(@_)', 'mm:ss', '[h]:mm:ss', 'mm:ss.0', '##0.0E+0', '@' '''
2. Font settings
First create a font object:
# Create font font = my_style_1.font
Then set the font name, font height, bold and other aspects:
Settable (default):
# self.height = 0x00C8 # 200: this is font with height 10 points # self.italic = False # self.struck_out = False # self.outline = False # self.shadow = False # self.colour_index = 0x7FFF # self.bold = False # self._weight = 0x0190 # 0x02BC gives bold font # self.escapement = self.ESCAPEMENT_NONE # self.underline = self.UNDERLINE_NONE # self.family = self.FAMILY_NONE # self.charset = self.CHARSET_SYS_DEFAULT # self.name = 'Arial'
example:
# Set font name font.name = 'Times New Roman ' # Set font height font.height = 400 # Set italics font.italic = True # Set strikethrough font.struck_out = True # Set profile font.outline = True # Set shadow font.shadow = True # Set font color, blue font.colour_index = 0x0C # Set bold font.bold = True # Set font superscript and superscript # font.escapement = 1 # Set underline, double underline font.underline = 2 # Set character set, GBK font.charset = 0x86
Set up renderings:
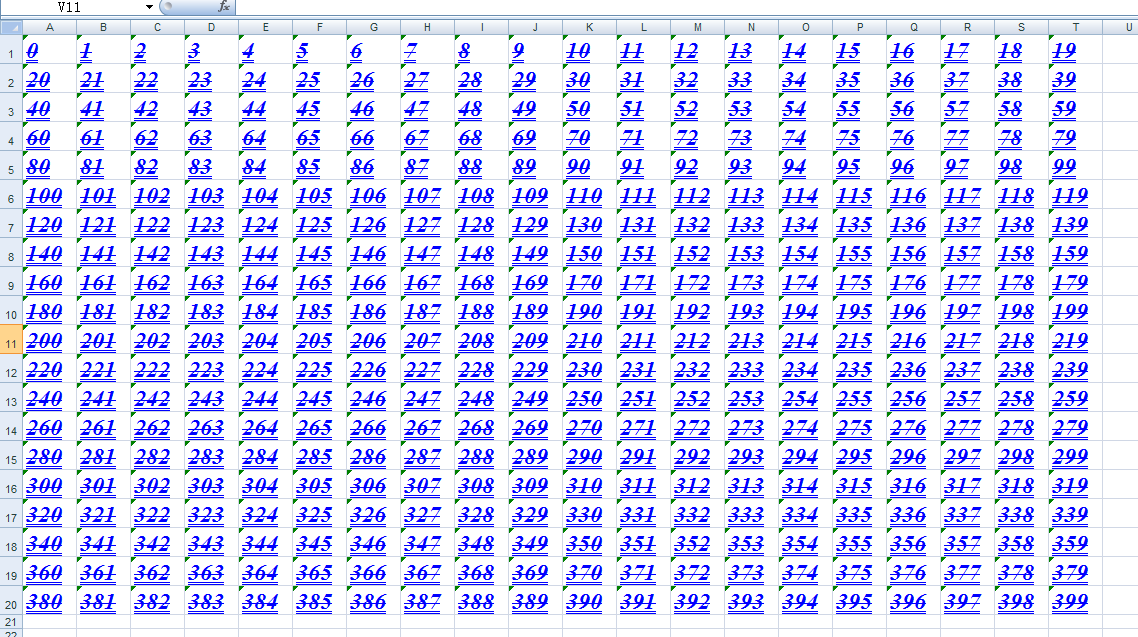
Get font format information:
font_info = font._search_key() print(font_info) # Print results: # (400, True, True, True, True, 12, True, 400, 0, 2, 0, 134, 'Times New Roman ')
Setting Description:
The above settings set the font color to blue:
font.colour_index = 0x0C
Font color options:
# Color index ####################################################### """ aqua 0x31 black 0x08 blue 0x0C blue_gray 0x36 bright_green 0x0B brown 0x3C coral 0x1D cyan_ega 0x0F dark_blue 0x12 dark_blue_ega 0x12 dark_green 0x3A dark_green_ega 0x11 dark_purple 0x1C dark_red 0x10 dark_red_ega 0x10 dark_teal 0x38 dark_yellow 0x13 gold 0x33 gray_ega 0x17 gray25 0x16 gray40 0x37 gray50 0x17 gray80 0x3F green 0x11 ice_blue 0x1F indigo 0x3E ivory 0x1A lavender 0x2E light_blue 0x30 light_green 0x2A light_orange 0x34 light_turquoise 0x29 light_yellow 0x2B lime 0x32 magenta_ega 0x0E ocean_blue 0x1E olive_ega 0x13 olive_green 0x3B orange 0x35 pale_blue 0x2C periwinkle 0x18 pink 0x0E plum 0x3D purple_ega 0x14 red 0x0A rose 0x2D sea_green 0x39 silver_ega 0x16 sky_blue 0x28 tan 0x2F teal 0x15 teal_ega 0x15 turquoise 0x0F violet 0x14 white 0x09 yellow 0x0D """
Font superscript setting, underline setting, character set setting:
# Font superscript font.escapement = 1 # Set underline, double underline font.underline = 2 # Set character set, GBK font.charset = 0x86
Resolution:
Here, the default font superscript and subscript settings of cells are:
self.escapement = self.ESCAPEMENT_NONE
Look up the following index: Escape element_ NONE = 0x00
If we want to set cell as superscript, superscript is: Escape element_ Superscript, corresponding value: 0x01 (16 digits)
And cell format:
font.escapement = 0x01
//Or:
font.escapement = 1
The other settings that appear below are similar in principle. If they appear again, they will not be explained.
Superscript, underscore, character set index:
ESCAPEMENT_NONE = 0x00 # Superscript ESCAPEMENT_SUPERSCRIPT = 0x01 # subscript ESCAPEMENT_SUBSCRIPT = 0x02 # Underline optional UNDERLINE_NONE = 0x00 UNDERLINE_SINGLE = 0x01 UNDERLINE_SINGLE_ACC = 0x21 UNDERLINE_DOUBLE = 0x02 UNDERLINE_DOUBLE_ACC = 0x22 # Character set optional CHARSET_ANSI_LATIN = 0x00 CHARSET_SYS_DEFAULT = 0x01 CHARSET_SYMBOL = 0x02 CHARSET_APPLE_ROMAN = 0x4D CHARSET_ANSI_JAP_SHIFT_JIS = 0x80 CHARSET_ANSI_KOR_HANGUL = 0x81 CHARSET_ANSI_KOR_JOHAB = 0x82 CHARSET_ANSI_CHINESE_GBK = 0x86 CHARSET_ANSI_CHINESE_BIG5 = 0x88 CHARSET_ANSI_GREEK = 0xA1 CHARSET_ANSI_TURKISH = 0xA2 CHARSET_ANSI_VIETNAMESE = 0xA3 CHARSET_ANSI_HEBREW = 0xB1 CHARSET_ANSI_ARABIC = 0xB2 CHARSET_ANSI_BALTIC = 0xBA CHARSET_ANSI_CYRILLIC = 0xCC CHARSET_ANSI_THAI = 0xDE CHARSET_ANSI_LATIN_II = 0xEE CHARSET_OEM_LATIN_I = 0xFF
3. Cell alignment
Establish alignment objects and set alignment properties:
Settable (default):
# self.horz = self.HORZ_GENERAL # self.vert = self.VERT_BOTTOM # self.dire = self.DIRECTION_GENERAL # self.orie = self.ORIENTATION_NOT_ROTATED # self.rota = self.ROTATION_0_ANGLE # self.wrap = self.NOT_WRAP_AT_RIGHT # self.shri = self.NOT_SHRINK_TO_FIT # self.inde = 0 # self.merg = 0
example:
# Establish a way to: alignment = my_style_1.alignment # Horizontal alignment, horizontal center alignment.horz = 2 # Vertical alignment, vertical center alignment.vert = 1 # Rotation direction, set rotation direction 45 alignment.rota = 45 # Auto indent settings alignment.shri = 1
Set up renderings:
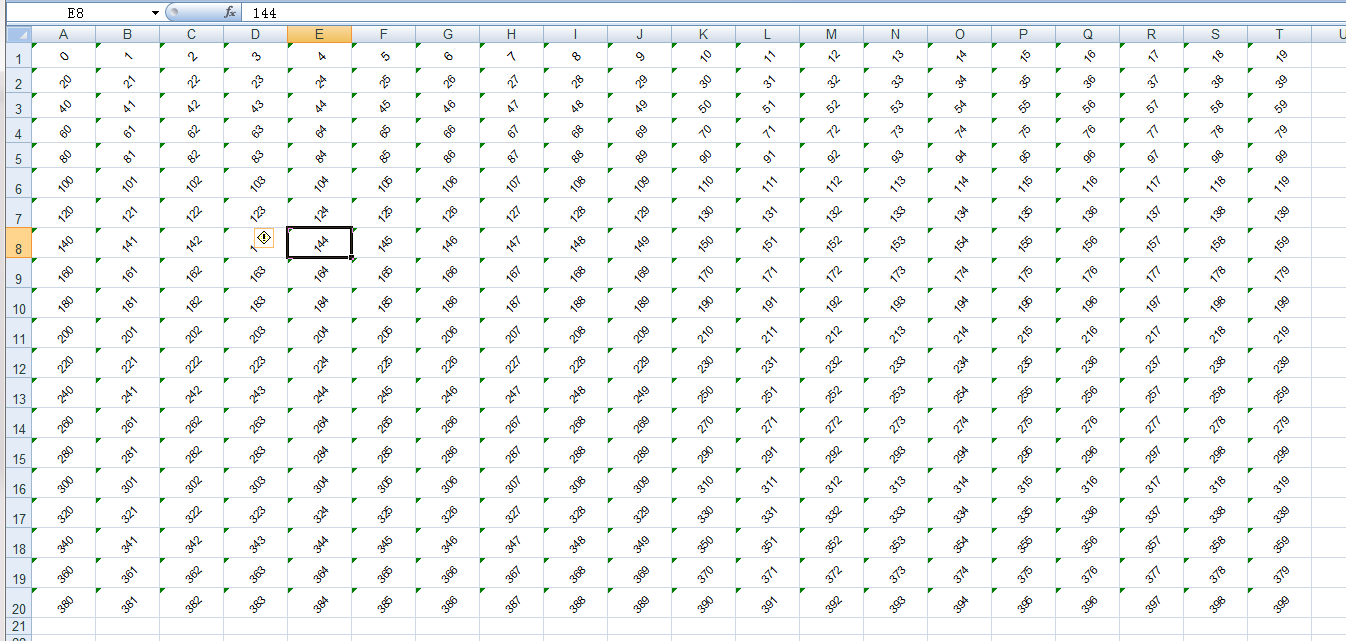
Get alignment information:
# Get current alignment alignment_info = alignment._search_key() print(alignment_info) # Print results: # (2, 1, 0, 0, 45, 0, 1, 0, 0)
Other alignment indexes:
# Horizontal alignment HORZ_GENERAL = 0x00 HORZ_LEFT = 0x01 HORZ_CENTER = 0x02 HORZ_RIGHT = 0x03 HORZ_FILLED = 0x04 HORZ_JUSTIFIED = 0x05 # BIFF4-BIFF8X HORZ_CENTER_ACROSS_SEL = 0x06 # Centred across selection (BIFF4-BIFF8X) HORZ_DISTRIBUTED = 0x07 # Distributed (BIFF8X) # Vertical alignment VERT_TOP = 0x00 VERT_CENTER = 0x01 VERT_BOTTOM = 0x02 VERT_JUSTIFIED = 0x03 # Justified (BIFF5-BIFF8X) VERT_DISTRIBUTED = 0x04 # Distributed (BIFF8X) # Rotation angle ROTATION_0_ANGLE = 0x00 ROTATION_STACKED = 0xFF # Auto indent settings SHRINK_TO_FIT = 0x01 NOT_SHRINK_TO_FIT = 0x00
4. Cell border settings
To create a cell border object, set the property value:
Settable (default):
# self.left = self.NO_LINE # self.right = self.NO_LINE # self.top = self.NO_LINE # self.bottom = self.NO_LINE # self.diag = self.NO_LINE # self.left_colour = 0x40 # self.right_colour = 0x40 # self.top_colour = 0x40 # self.bottom_colour = 0x40 # self.diag_colour = 0x40 # self.need_diag1 = self.NO_NEED_DIAG1 # self.need_diag2 = self.NO_NEED_DIAG2
example:
borders = my_style_1.borders # Left border thin line borders.left = 1 # Center thin line of right border borders.right = 2 # Dashed top border borders.top = 3 # Bottom border dotted line borders.bottom = 4 # Thick line of inner border borders.diag = 5 # Left border color blue borders.left_colour = 0x0C # Right border color gold borders.right_colour = 0x33 # Top border color green borders.top_colour = 0x11 # Bottom border color red borders.bottom_colour = 0x0A # Yellow inner border borders.diag_colour = 0x0D
Setting effect:
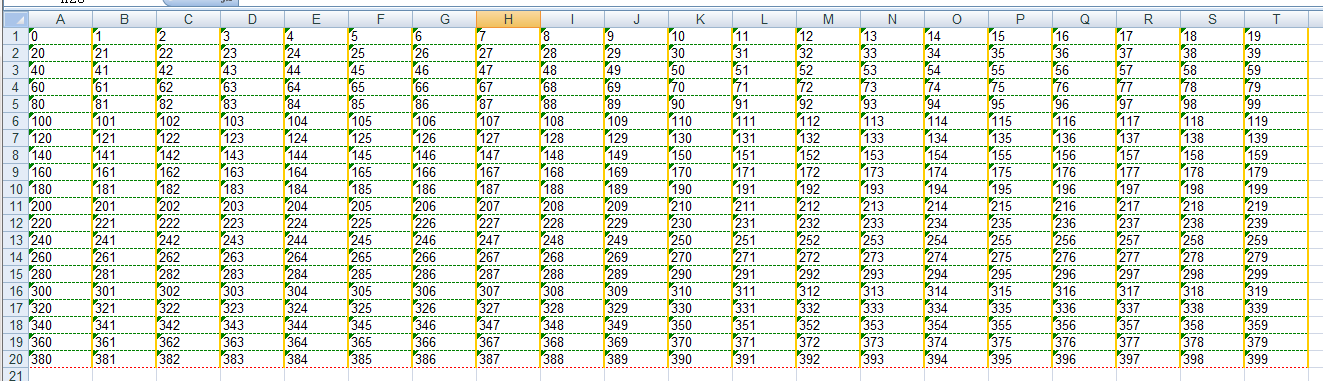
Get border setting information:
borders_info = borders._search_key() print(borders_info) # Print results # (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 12, 51, 17, 10, 13, 0, 0)
Border line index:
NO_LINE = 0x00 THIN = 0x01 MEDIUM = 0x02 DASHED = 0x03 DOTTED = 0x04 THICK = 0x05 DOUBLE = 0x06 HAIR = 0x07 #The following for BIFF8 MEDIUM_DASHED = 0x08 THIN_DASH_DOTTED = 0x09 MEDIUM_DASH_DOTTED = 0x0A THIN_DASH_DOT_DOTTED = 0x0B MEDIUM_DASH_DOT_DOTTED = 0x0C SLANTED_MEDIUM_DASH_DOTTED = 0x0D
Note: for border color setting, please refer to font color setting index.
5. Fill settings
To create a fill object, set properties:
Settable (default):
# self.pattern = self.NO_PATTERN # self.pattern_fore_colour = 0x40 # self.pattern_back_colour = 0x41
example:
# Fill settings pat = my_style_1.pattern # Open fill pat.pattern = 1 # Fill foreground, purple pat.pattern_fore_colour = 0x14 # Fill background color, purple pat.pattern_back_colour = 0x14
design sketch:
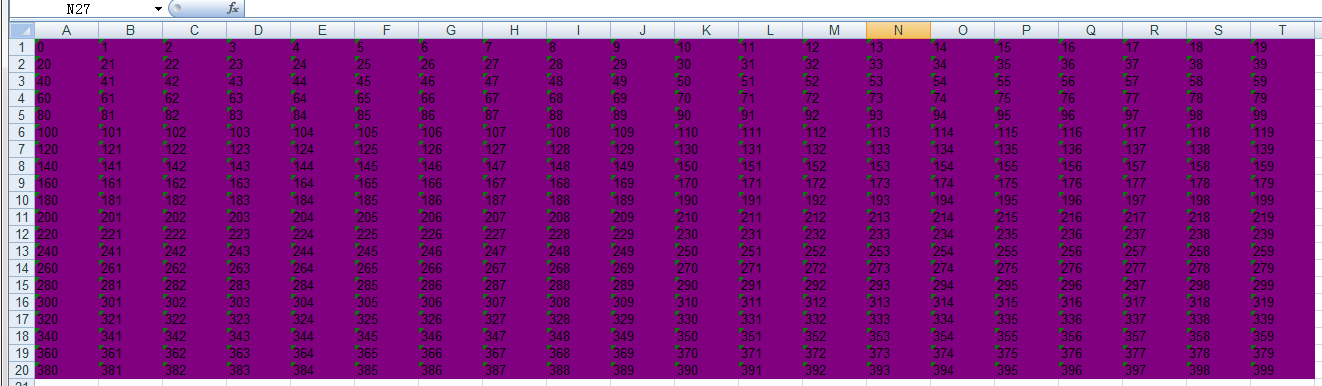
Note: it seems that the xlwt module only provides color fill setting method, while the hatch method is not provided. Color index see font color index.
6. Cell protection
Establish the protection object and set the properties:
Settable (default):
# self.cell_locked = 1 # self.formula_hidden = 0
example:
# Set cell lock protection.cell_locked = 1 # Set hidden formula in cell protection.formula_hidden = 1 # Only valid if sheet table is set to protected work_sheet.set_protect(1)
Note: it is only valid when the sheet table is set as protected (for the effect, please refer to the table protection content in Section 2).
last:
Thank you for reading.
[Python and Office software] a series of articles will explain the use of common Office software processing modules in Python. Interested friends can pay attention to and collect them.