Categorizing dogs and cats, this paper describes the classification algorithm of deep learning.

Part 1, Data Set, including:
- Download data sets: use Kaggle API to download data sets;
- Preprocessing data sets: The data sets are divided into two parts: training and testing.
- Display data sets: use Pillow to draw a combination of multiple pictures;
download
Data set: https://www.kaggle.com/c/dogs-vs-cats/data

Download using the Kaggle API. GitHub The order is as follows:
kaggle competitions download -c dogs-vs-cats
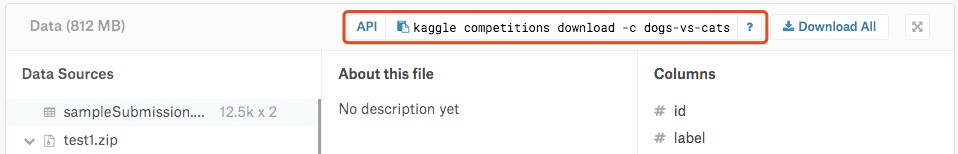
Download data sets:
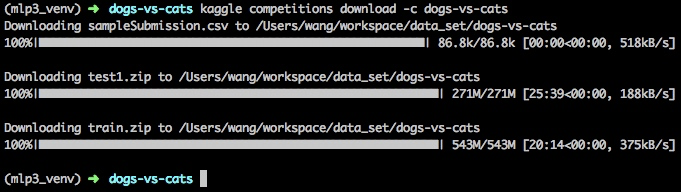
Training set: 25,000 pictures, 12,500 cats and 12,500 dogs;
Test Set: 12,500 pictures, no distinction between categories;
About the configuration of Kaggle API:
- Log in. In the API project on the MyAccount page, click Create New API Token to download kaggle.json, which contains username and key.
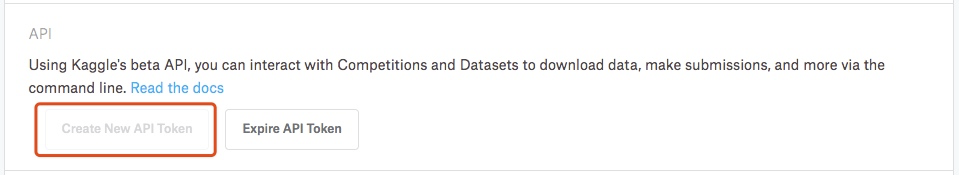
Place kaggle.json in the. kaggle folder. If it does not exist, you need to create a folder.
Modify kaggle.json as a readable permission, Chmod 600.kaggle/kaggle.json.
Install the Kaggle API, pip install kaggle.
Execute download commands, such as kaggle competitions download-c dogs-vs-cats.
Preprocessing
1000 cats and 1000 dogs were used as training set, 400 cats and 400 dogs as test set.
Step 1: Read the data into memory and distinguish between cat and dog.
def list_dataset(dataset_dir): """ //The training data set is read into memory and divided into two parts: cat and dog. """ paths_list, names_list = traverse_dir_files(dataset_dir) cats_dict, dogs_dict = dict(), dict() for path, name in zip(paths_list, names_list): [clz, num, _] = name.split('.') num = int(num) if clz == 'cat': cats_dict[num] = path elif clz == 'dog': dogs_dict[num] = path else: continue # print('cat: {}, dog: {}'.format(len(cats_dict.keys()), len(dogs_dict.keys()))) return cats_dict, dogs_dict
Step 2: Copy the dataset, and copy several cats or dogs to a new folder.
def copy_files(target_folder, clz_name, n_start, n_end): cats_dict, dogs_dict = list_dataset(O_DATASET_DIR) new_train = os.path.join(DATASET_DIR, 'train') new_test = os.path.join(DATASET_DIR, 'test') mkdir_if_not_exist(DATASET_DIR) mkdir_if_not_exist(new_train) mkdir_if_not_exist(new_test) # test data # target_folder = 'train' # clz_name = 'cat' # n_start = 0 # n_end = 10 for i in range(n_start, n_end): data_dict = cats_dict if clz_name == 'cat' else dogs_dict folder = new_train if target_folder == 'train' else new_test shutil.copy(data_dict[i], folder) print("[complete]Target folder: {}, category: {}, Start stop: {} ~ {}".format( target_folder, clz_name, n_start, n_end))
Step 3: Construct 1000 cats + 1000 dogs training set and 400 cats + 400 dogs testing set.
def main(): # 1000 cats + 1000 dogs training set; 400 cats + 400 dogs testing set copy_files('train', 'cat', 0, 1000) copy_files('train', 'dog', 0, 1000) copy_files('test', 'cat', 0, 400) copy_files('test', 'dog', 0, 400)
Exhibition
Pillow's Image Library is used to compose multiple images into one picture, each of which is proportioned to 416 longest edges.
def draw_multi_imgs(path_list, file_name): """ //Draw similar picture groups :param path_list: Picture Path List :param file_name: Output file name :return: None """ img_w, img_h = 4, 3 img_size = 416 try: o_images = [Image.open(p) for p in path_list] images = [] for img in o_images: wp = img_size / float(img.size[0]) hsize = int(float(img.size[1]) * float(wp)) img = img.resize((img_size, hsize), Image.ANTIALIAS) images.append(img) except Exception as e: print('Exception: {}'.format(e)) return new_im = Image.new('RGB', (img_size * img_w, img_size * img_h), color=(255, 255, 255)) x_offset, y_offset = 0, 0 for i in range(img_h): for j in range(img_w): im = images[i * img_w + j] new_im.paste(im, (x_offset, y_offset)) x_offset += 416 y_offset += 416 x_offset = 0 new_im.save(file_name) # Save pictures
Show 12 random cat pictures and 12 dog pictures in the training set.
def main(): new_train = os.path.join(DATASET_DIR, 'train') new_test = os.path.join(DATASET_DIR, 'test') cats_dict, dogs_dict = list_dataset(new_train) cats_list = list(cats_dict.values()) dogs_list = list(dogs_dict.values()) random.shuffle(cats_list) random.shuffle(dogs_list) draw_multi_imgs(cats_list[:12], os.path.join(DATA_DIR, 'train_cat.jpg')) draw_multi_imgs(dogs_list[:12], os.path.join(DATA_DIR, 'train_dog.jpg'))
Data set:
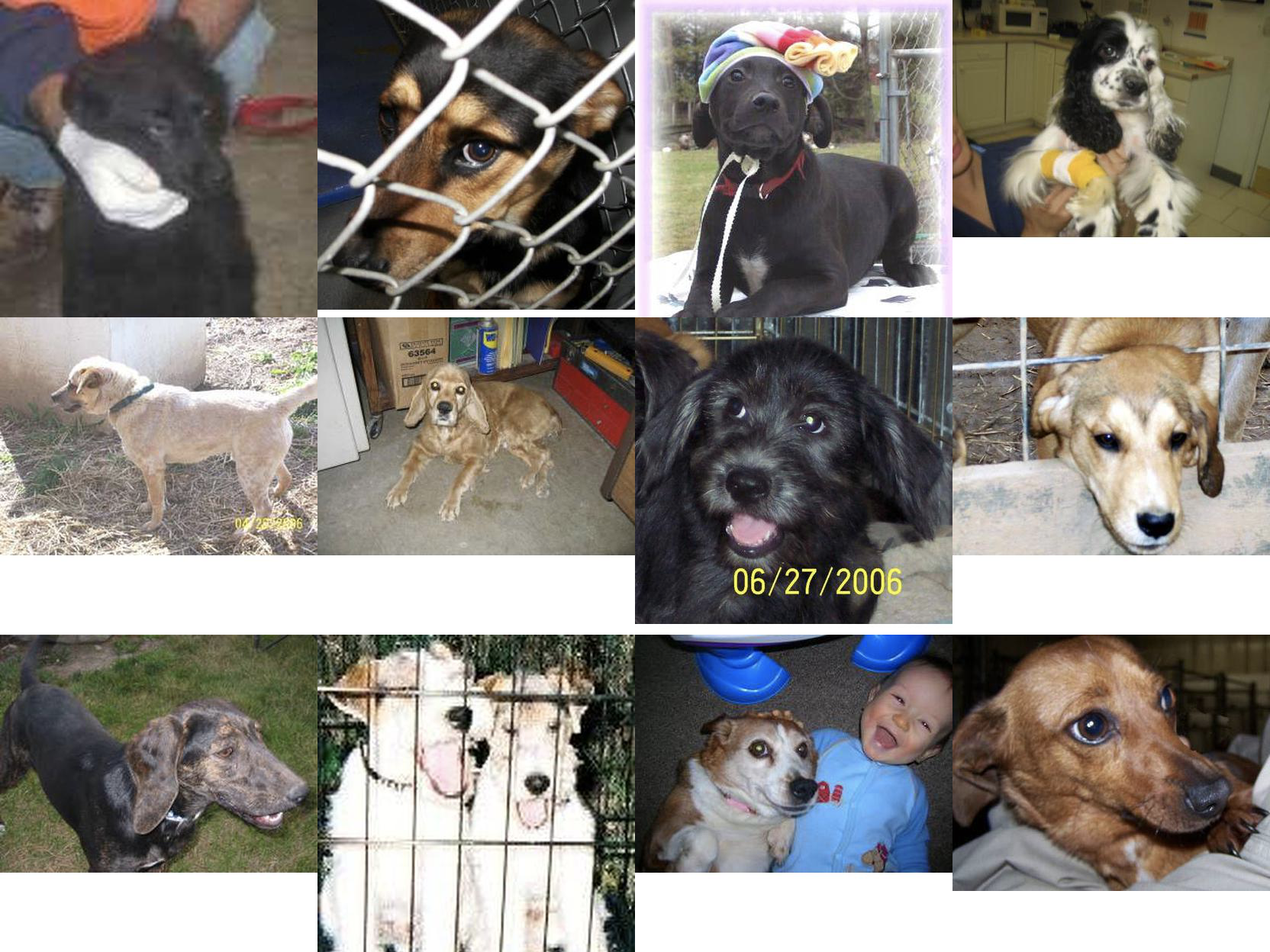


At this point, complete the construction of the data set.