Friend
- Friend is a mechanism provided by C + + to destroy data encapsulation and data hiding.
- By declaring a module as a friend of another module, one module can refer to the hidden information in another module.
- You can use friend functions and friend classes.
- In order to ensure the integrity of data and the principle of data encapsulation and hiding, it is recommended to use as few friends as possible.
friend function
- If you define a friend function (it can be a member function of another class or a non member function that doesn't belong to any class) elsewhere in this class, you can declare it with friend in the body of this class, and this function will become a friend function of this class, and you can access the private members of this class.
- Friend function is a non class member function described by the keyword friend in class declaration. In its function body, it can access private member, protected member and public member by object name.
- Function: increase flexibility, so that programmers can make reasonable choices in encapsulation and rapidity.
- Members in an access object must pass through the object name.
-
Declare a normal function as a friend function of this type:
#include <iostream> using namespace std; class Box{ public: Box(){} Box(int h ,int w):height(h),width(w){} void volume(); static void show(); friend void display(Box &b); static int length; private: int height; int width; static int c; }; void Box::volume() { cout<<"The volume is:"<<height<<"*"<<width<<"*"<<length<<"="<<height * width*length<<endl; } void Box::show() { cout << "Static private member c: " << c << " Static public member length: " <<length<< endl; } int Box::length = 5; int Box::c = 6; void display(Box &b) { b.width = 3; b.height = 3; b.c = 3; b.length = 3; b.volume(); b.show(); } void main() { Box b; //Call normal constructor display(b); /* Volume: 3 * 3 * 3 = 27 Static private member c: 3 static public member length: 3 */ } -
Friend member functions (member functions of other classes)
#include <iostream> using namespace std; class Display; //Declaration of Box class class Box { public: Box() {} Box(int h, int w) :height(h), width(w) {} void volume(Display &); //Member arguments must be Display class objects static int length; private: int height; int width; static int c; }; class Display { public: Display() { a = 10; b = 5; } void display(); friend void Box::volume(Display &);//Take volume in the Box class as the friend function of this class private: int a; int b; }; void Display::display() { cout << "a=" << a << " b=" << b << endl; } void Box::volume(Display &d) { d.display(); //Reference to Display private variable must be added with object name d.a = 20; d.b = 20; d.display(); cout << "The volume is:" << height << "*" << width << "*" << length << "=" << height * width*length << endl; } int Box::length = 5; int Box::c = 6; void main() { Display d; Box b(7,7); b.volume(d); /* a=10 b=5 a=20 b=20 Volume: 7 * 7 * 5 = 245 */ }
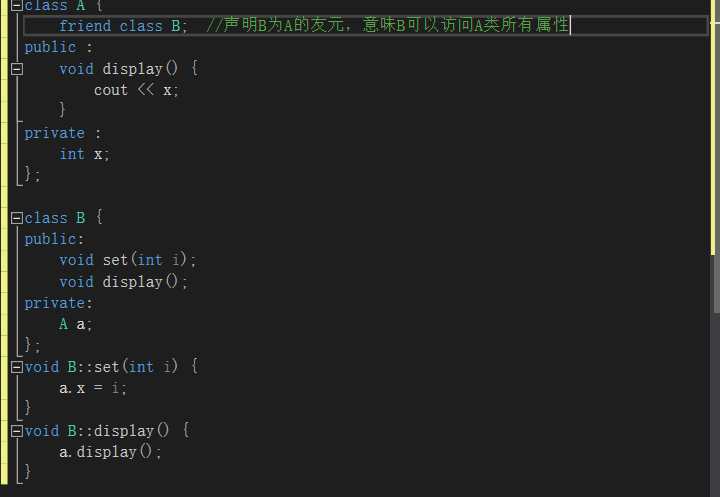
Friends
- Class is a friend of another class, all members of this class can access private members of the other class.
- Declaration syntax: use friend modifier to describe friend class name in another class
- If class B is declared as a friend of class A, the member functions of class B can access the private and protected data of class A, but the member functions of class a cannot access the private and protected data of class B.