/* *Copyright(c)2017, School of computer science, Yantai University *All right reserved. *File name: main.cpp list.h list.cpp *Author: Huang Shisheng *Completion date: September 21, 2017 *Version number: v1.0 * *Problem Description: intersection of two sets *Enter Description: None *Program output: see window */
Or multi file organization is used to realize the operation of the project.
Code:
Code: list.h#include "../list.h" #include "stdio.h" void unionList(SqList *LA, SqList *LB, SqList *&LC) { int lena,i; ElemType e; InitList(LC); for (i=1; i<=ListLength(LA); i++) //Insert all elements of LA into Lc { GetElem(LA,i,e); ListInsert(LC,i,e); } lena=ListLength(LA); //Find the length of linear table LA for (i=1; i<=ListLength(LB); i++) { GetElem(LB,i,e); //Assign the ith data element in LB to e if (!LocateElem(LA,e)) //LA does not exist the same as e, insert into LC ListInsert(LC,++lena,e); } } int main() { SqList *sq_a, *sq_b, *sq_c; ElemType a[6]= {5,8,7,2,4,9}; CreateList(sq_a, a, 6); printf("LA: "); DispList(sq_a); ElemType b[6]= {2,3,8,6,0}; CreateList(sq_b, b, 5); printf("LB: "); DispList(sq_b); unionList(sq_a, sq_b, sq_c); printf("LC: "); DispList(sq_c); return 0; }
Code: list.cpp#ifndef LIST_H_INCLUDED #define LIST_H_INCLUDED #define MaxSize 50 typedef int ElemType; typedef struct { ElemType data[MaxSize]; int length; } SqList; void CreateList(SqList *&L, ElemType a[], int n);//Creating linear tables with arrays void InitList(SqList *&L);//Initialize linear table initlist void DestroyList(SqList *&L);//Destroy linear table destroylist bool ListEmpty(SqList *L);//Determine whether it is an empty table listempty int ListLength(SqList *L);//Find the length of linear table listlength void DispList(SqList *L);//Output linear table displist bool GetElem(SqList *L,int i,ElemType &e);//Get a data element value GetElem(L,i,e) int LocateElem(SqList *L, ElemType e);//Find locateelem by element value (L, e) bool ListInsert(SqList *&L,int i,ElemType e);//Insert data element ListInsert(L,i,e) bool ListDelete(SqList *&L,int i,ElemType &e);//Delete the data element ListDelete (L, I, e) settings #endif
#include <stdio.h> #include <malloc.h> #include "list.h" //Creating linear tables with arrays void CreateList(SqList *&L, ElemType a[], int n) { int i; L=(SqList *)malloc(sizeof(SqList)); for (i=0; i<n; i++) L->data[i]=a[i]; L->length=n; } //Initialize linear table initlist void InitList(SqList *&L) //Referential pointer { L=(SqList *)malloc(sizeof(SqList)); //Allocate space for linear tables L->length=0; } //Destroy linear table destroylist void DestroyList(SqList *&L) { free(L); } //Determine whether it is an empty table listempty bool ListEmpty(SqList *L) { return(L->length==0); } //Find the length of linear table listlength int ListLength(SqList *L) { return(L->length); } //Output linear table displist void DispList(SqList *L) { int i; if (ListEmpty(L)) return; for (i=0; i<L->length; i++) printf("%d ",L->data[i]); printf("\n"); } //Get a data element value GetElem(L,i,e) bool GetElem(SqList *L,int i,ElemType &e) { if (i<1 || i>L->length) return false; e=L->data[i-1]; return true; } //Find locateelem by element value (L, e) int LocateElem(SqList *L, ElemType e) { int i=0; while (i<L->length && L->data[i]!=e) i++; if (i>=L->length) return 0; else return i+1; } //Insert data element ListInsert(L,i,e) bool ListInsert(SqList *&L,int i,ElemType e) { int j; if (i<1 || i>L->length+1) return false; //Return false when parameter error i--; //Convert logical sequence number of sequence table to physical sequence number for (j=L->length; j>i; j--) //Move the data[i..n] element back one position L->data[j]=L->data[j-1]; L->data[i]=e; //Insert element e L->length++; //Sequence table length increased by 1 return true; //Insert successfully returns true } //Delete data element ListDelete(L,i,e) bool ListDelete(SqList *&L,int i,ElemType &e) { int j; if (i<1 || i>L->length) //Return false when parameter error return false; i--; //Convert logical sequence number of sequence table to physical sequence number e=L->data[i]; for (j=i; j<L->length-1; j++) //Move the data[i..n-1] element forward L->data[j]=L->data[j+1]; L->length--; //Sequence table length minus 1 return true; //Delete successfully return true }
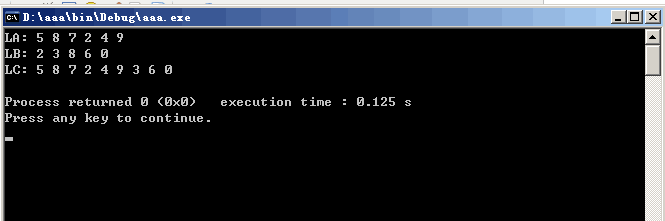
Running screenshot:
Learning experience:
Through this small design, it can be seen that after the implementation of the linear table LIST, it can be used as a container to store the set data, or it can use its basic operations to complete more complex set operations, how to find the union of two sets and so on
Published 34 original articles·
Zan Zan 9.
10000 visitors+

