Using Dev CPP as the programming environment
Note that dev cpp5.4.0 does not have the function of formatting code, so do not set it again
Set common shortcuts for
Ctr+E: multiline comment
Ctrl+Shift+E: uncomment multiline
Ctrl+Z: undo
Ctrl+Shift+Z: cancel undo
Ctrl+L: collapse function
Ctrl+Shif+L: unfold function
Set Dev Cpp
Dev C + + initialization (default) code modification method
C + + Basics
C + + is a static, compiled, general, case sensitive and irregular programming language. It supports procedural programming, object-oriented programming and generic programming. [object oriented and process oriented]
C + + is considered as an intermediate language, which combines the characteristics of high-level language and low-level language.
C + + is a superset of C. in fact, any legal C program is a legal C + + program.
The first C + + program
Starting with # tells the compiler that this line of code needs preprocessing. include tells the compiler that the header file iostream needs to be introduced. The iostream file defines the input / output stream objects.
using namespace std;// Use a namespace named STD, which contains the functions of the C + + standard library.
Cout < < "Hello World!" is used to output "Hello World!" to the screen.
return is the last instruction statement in the program. It terminates the main() function and returns 0 to the calling process. A non-zero value (usually 1) indicates abnormal termination.
The cout operator does not insert a newline character at the end, so if you want to print two lines, you can use the endl manipulator; Endl is only a way of line feed operation. We can also use the escape character "\ n" for line feed
#include<iostream>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
//#include<stdlib.h>
cout<<"hello world"<<endl;
//#Include < stdlib. H > standard library
system("pause");
return 0;
}
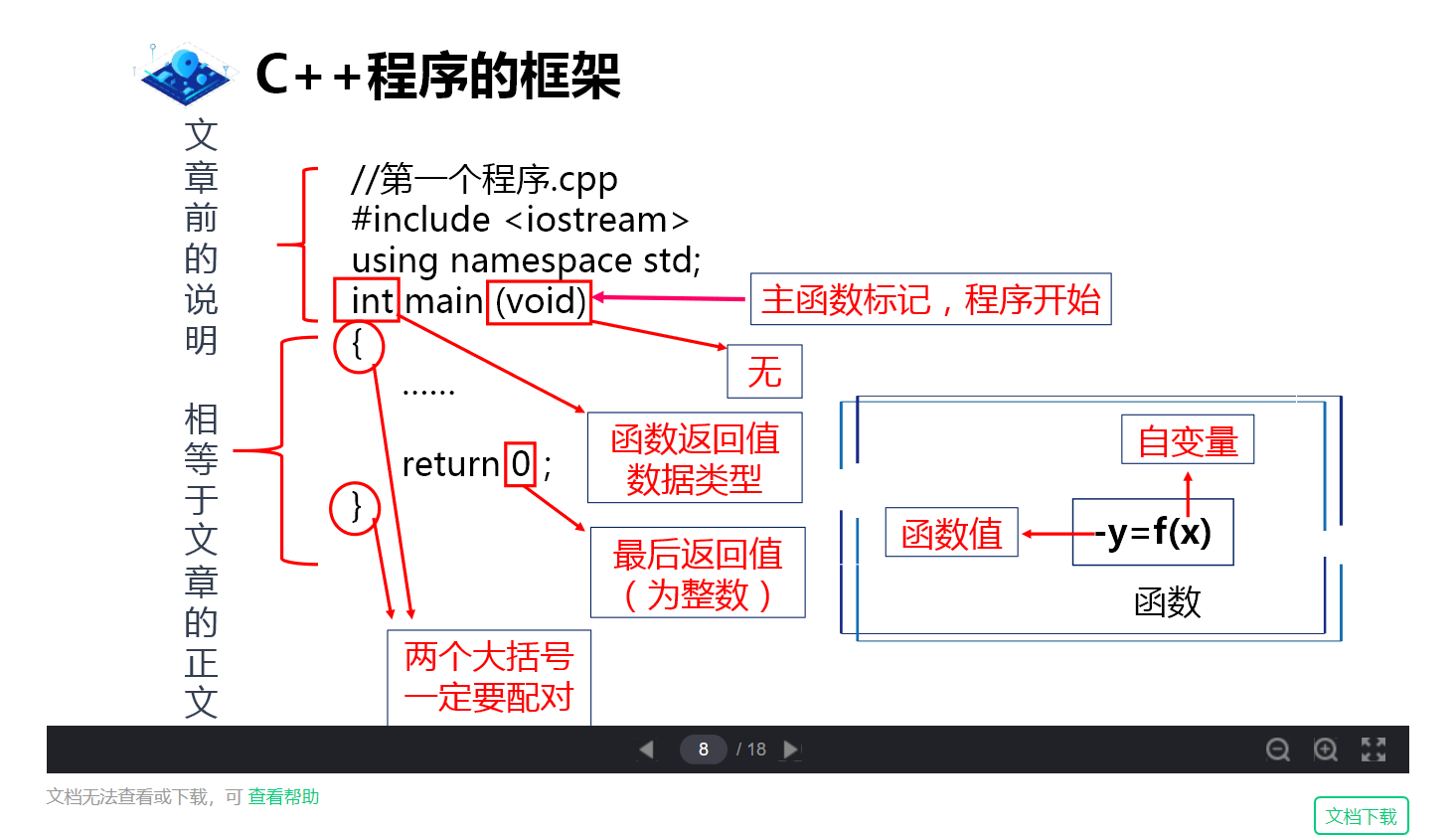
Framework of C + + program

Keywords, identifiers, constants
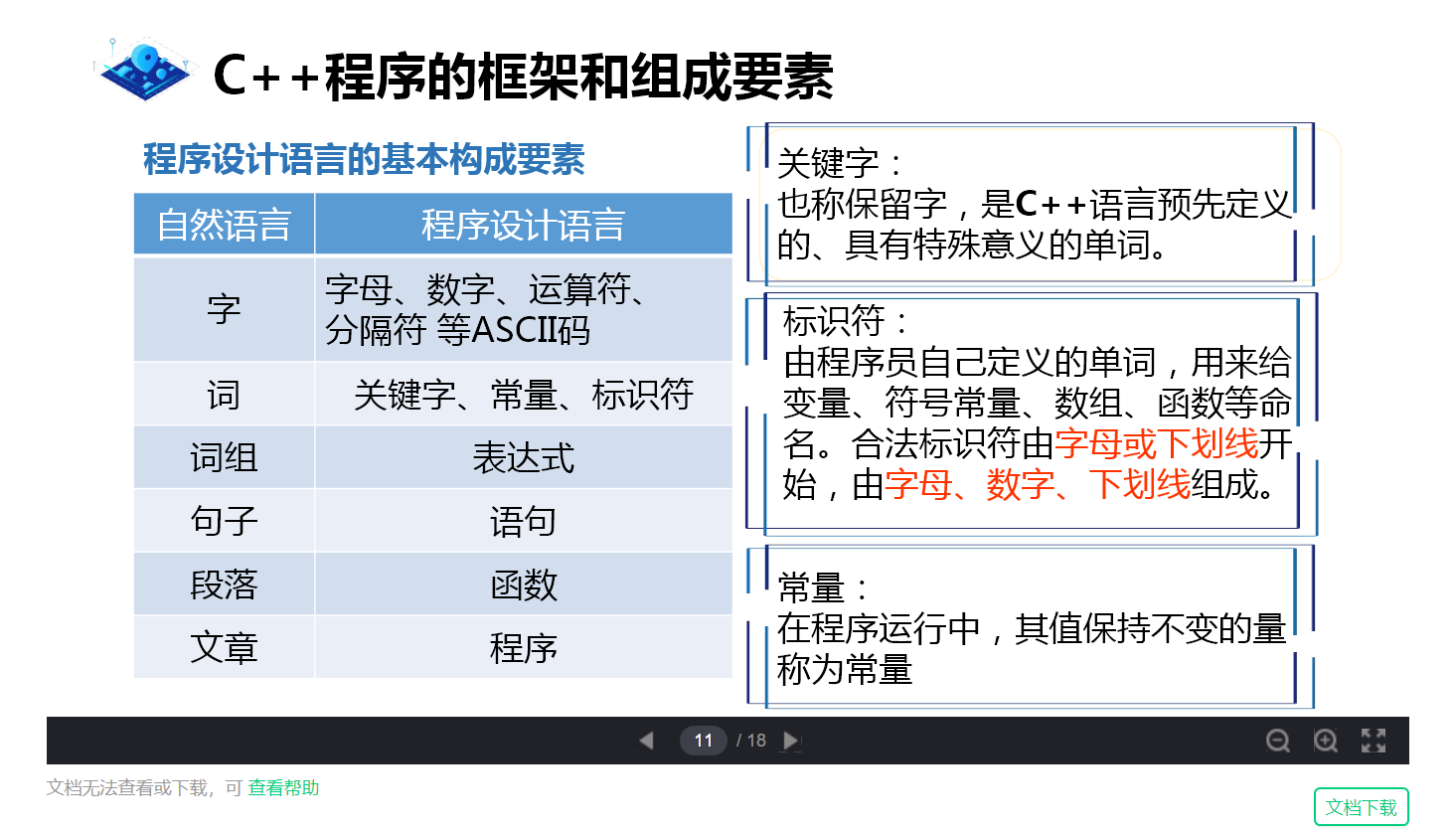
C + + identifier:
Starts with a letter or underscore and contains numbers, letters, and underscores
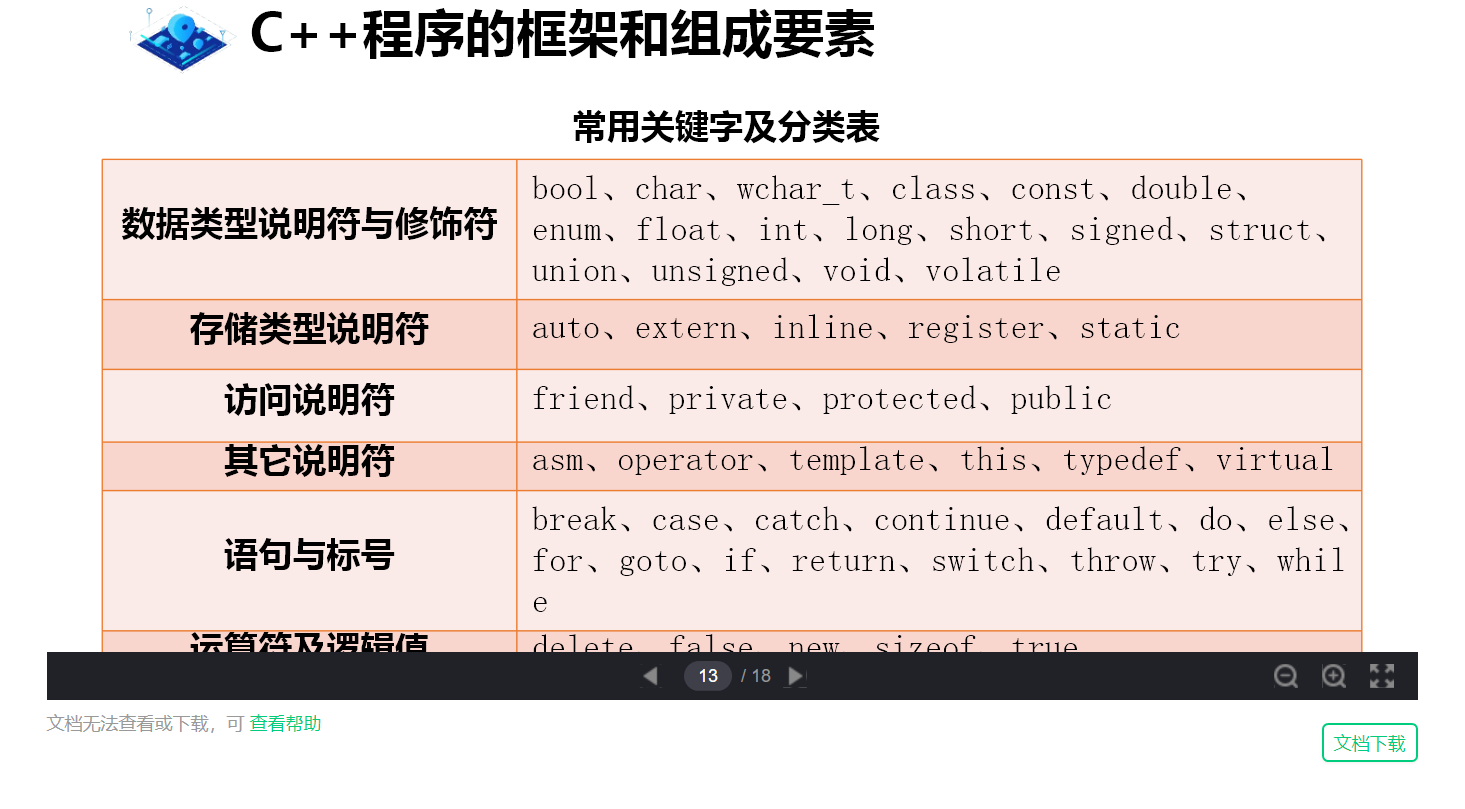
keyword

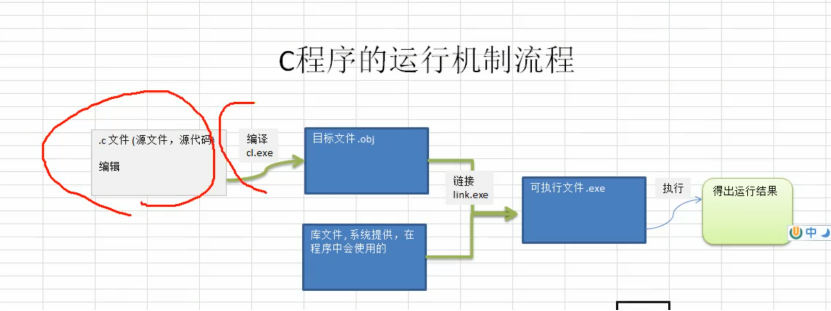
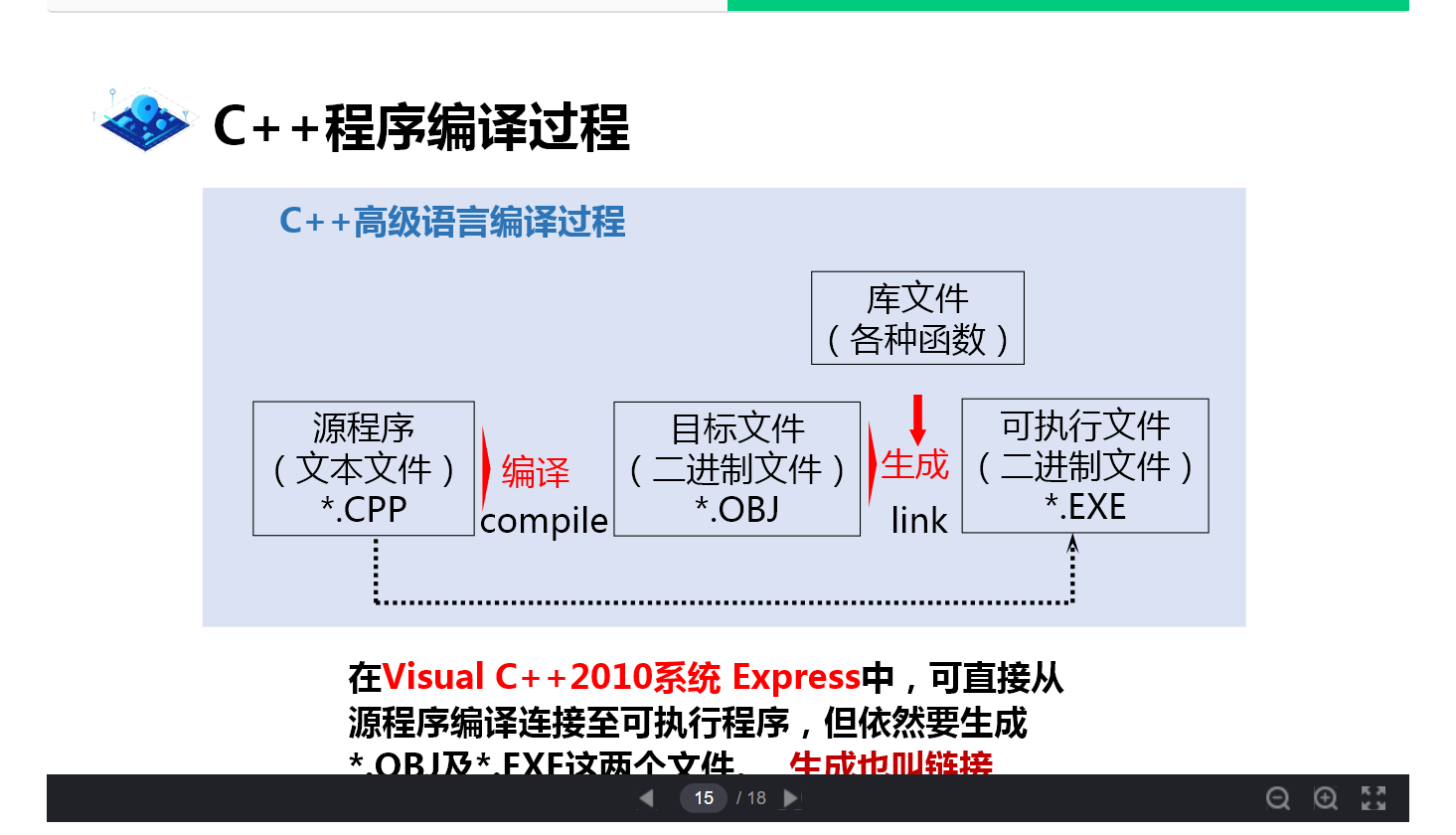
C + + compilation process
Edit hello.cpp – > compile hello.obj – > link (project. exe) - > run (run. exe file)
Note. cpp is the source code of C + +, and. C is the source code of C language

Single line and multiline notes
Comments are explanatory statements that can be included in C + + code to explain the functions of the code.
The compiler ignores everything that appears in the comment, so no information is displayed in the result.
Single line note:
Comments that begin with two slashes (/ /) are called single line comments. Slashes tell the compiler to ignore everything that follows until the end of the line.
Multiline comment:
Multiline comments start with * * / * * * and end with * * * / * *. You can put them on the same line or insert one or more lines of code between them.

C + + programming summary
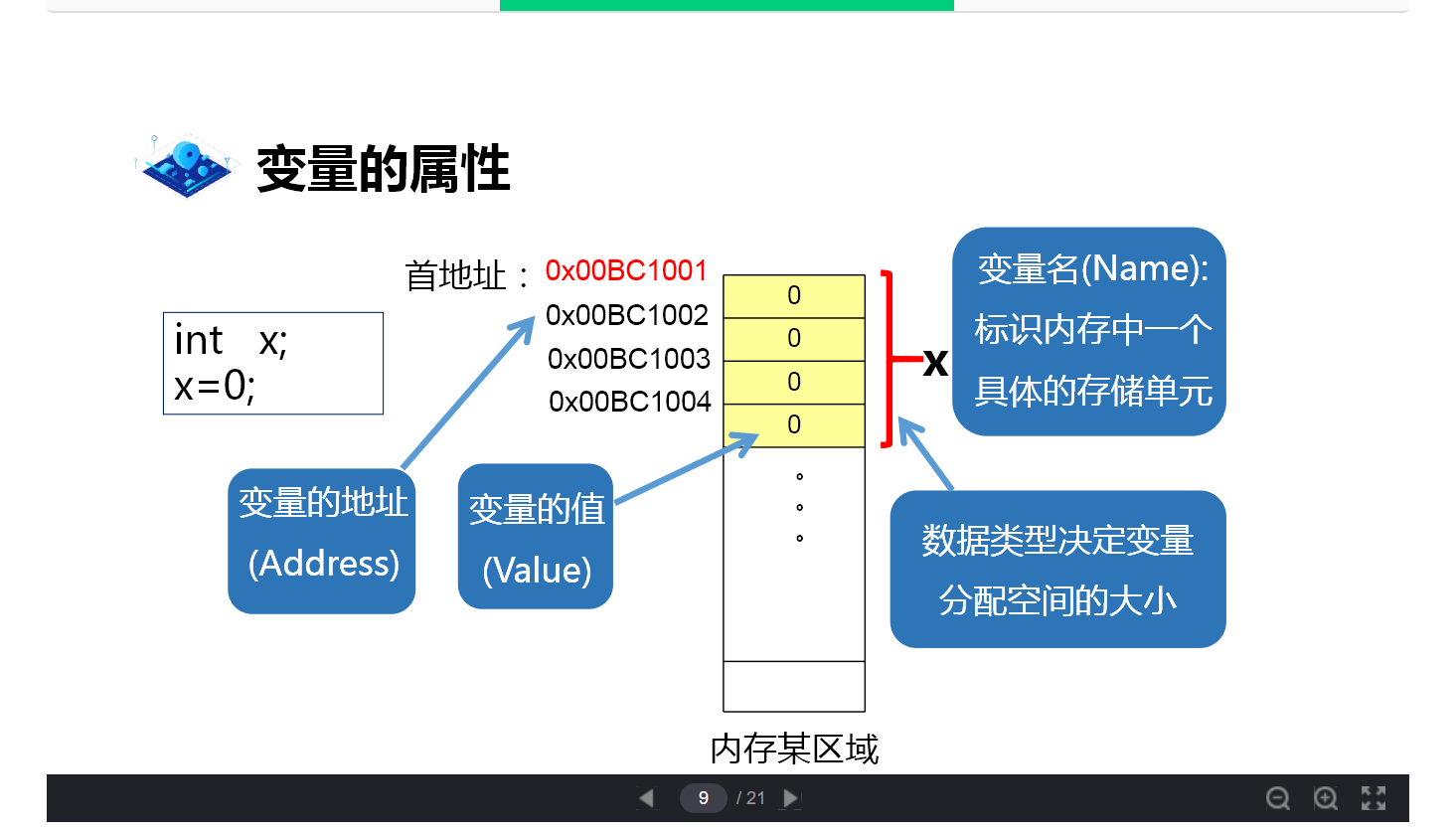
variable and constant

Literal constant and Symbolic Constant

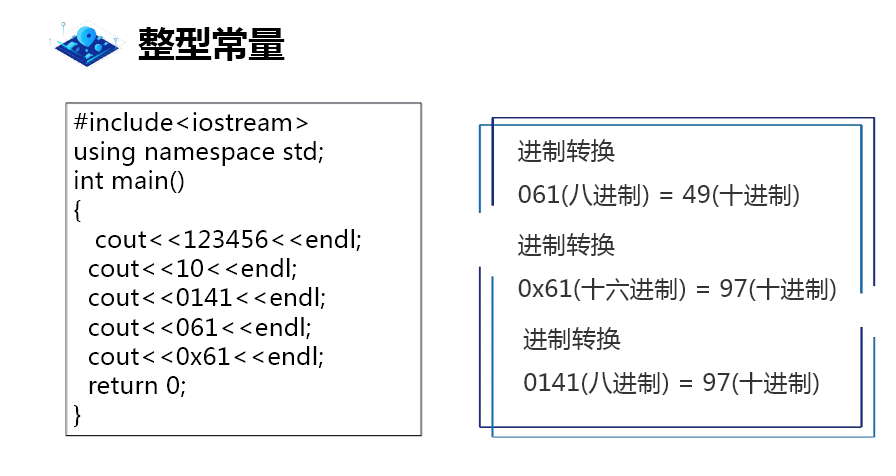
Literal constants: integer constants

Octal and hexadecimal in C + + will be converted to decimal output
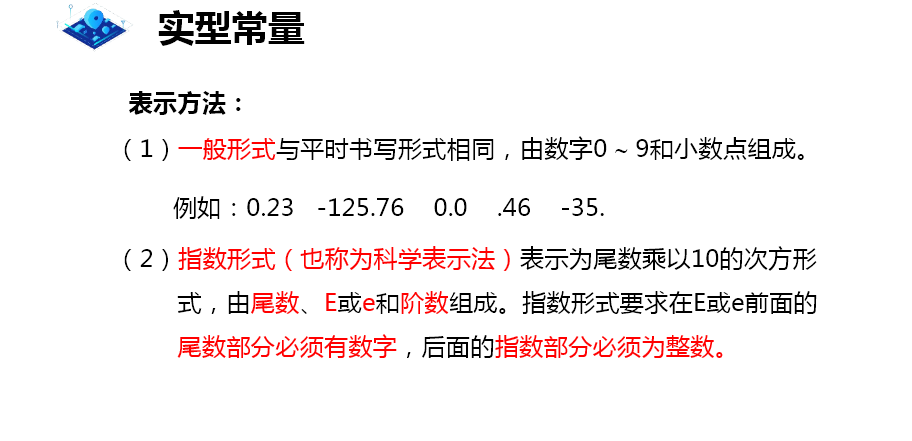
Literal constants: real constants
cout in C + + outputs six significant digits by default. If it exceeds 6 digits, it will be rounded to output six digits
C language:
float-4byte - keep 6 decimal places - add f or F when using
double-8byte-15 decimal places reserved
The output decimal 37.0 will output integer by default: 37
Scientific counting method:
1.2E-38=1.2*10^-38
Index bit: - 38
Mantissa: decimal
5.12e2=5.1210^2=512
5.12E2=5.1210^2=512
Dev Cpp output: 1.2e+002 means 1.2 * 10 ^ 2
+Or - 002: positive or negative
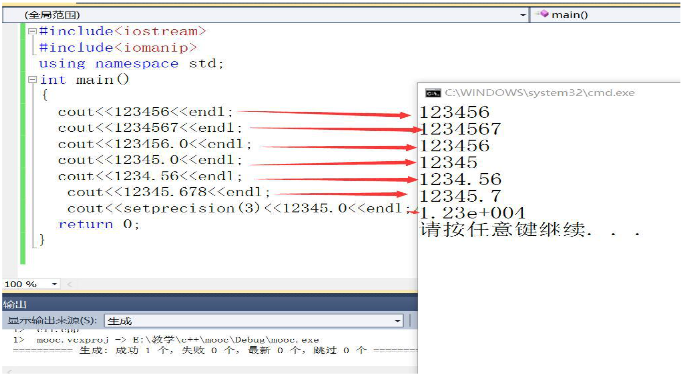
Case:
#include<iostream>
#include<iomanip>
#include<stdio.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
// 67: decimal 077: octal 0x78: hexadecimal
cout<<67<<"\t"<<077<<"\t"<<0x78<<"\n"<<endl;
//Output: 67 63 120
//General form
cout<<11<<"\t"<<0.12<<"\t"<<-9.8<<"\t"<<.9<<"\t"<<-39.<<"\n"<<endl;
//Output: 11 0.12 - 9.8 0.9 - 39
//Note: cout in C + + outputs six significant digits by default. If it exceeds 6 digits, it will be rounded to output six digits
cout<<7.793456<<"\n"<<endl; //7.79346
//The output of C is simpler
printf("%.4f\n",234.4678);//234.4678
//Note: the output decimal 37.0 will output integer 37 by default
cout<<37.0<<"\n"<<endl;//37
//Scientific counting method: setprecision(n): note that after setting it once, the subsequent output will be limited to 2 significant digits
cout<< setprecision(2)<<123.444546<<"\n"<<endl;//1.2e+002
return 0;
}
Text constant: character constant

Escape character

Difference between string constant and character constant:
//c + + string string x="xwer";

\Is an escape character. If it is followed by a number, it represents the character corresponding to the ASCII value. The number here is usually a 1-3-digit octal number, and it can also be represented by hexadecimal in the form of \ xNN.
For example '\ 141': the ASCII code representing \ 0141 octal 141 is' a '
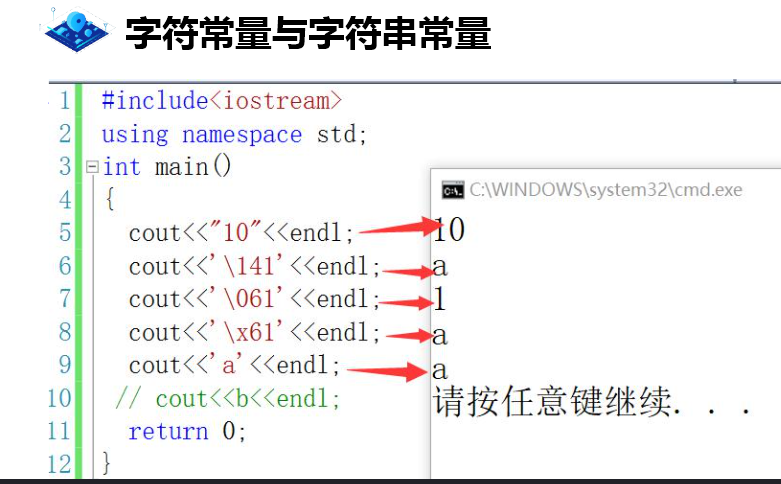
Case:
//auther:dq
//function: literal constant: integer constant real constant character constant string constant 2
#include<iostream>
#include<stdio.h>
using namespace std;
int main() {
//'a': character 'aa': a string consisting of two 'a' and string end tag '\ 0'
cout<<'a'<<"\t"<<"aa"<<"\n"<<endl;
//\Is an escape character. If it is followed by a number, it represents the character corresponding to the ASCII value
//The numbers here are usually 1-3-digit octal numbers, which can also be expressed in hexadecimal in the form of \ xNN.
//For example '\ 141': the ASCII code representing \ 0141 octal 141 is' a '
cout<<0141<<"\t"<<'\141'<<"\t"<<'\061'<<"\n"<<endl;//97 a 1
cout<<0x60<<"\t"<<'\x60'<<"\n"<<endl;//96 `
//c + + string
string x="xwer";
cout<<x<<endl;
return 0;
}
Symbolic constants: identifier constants



Case:
//auther:dq
//function: symbol constant: identifier constant const
#include<iostream>
#include<iomanip>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
const char x='a';
const int y=8;
const double z=8.2345;
cout<<x<<"\t"<<y<<"\t"<<fixed<<setprecision(2)<<z<<"\n"<<endl;
return 0;
}
Constant summary

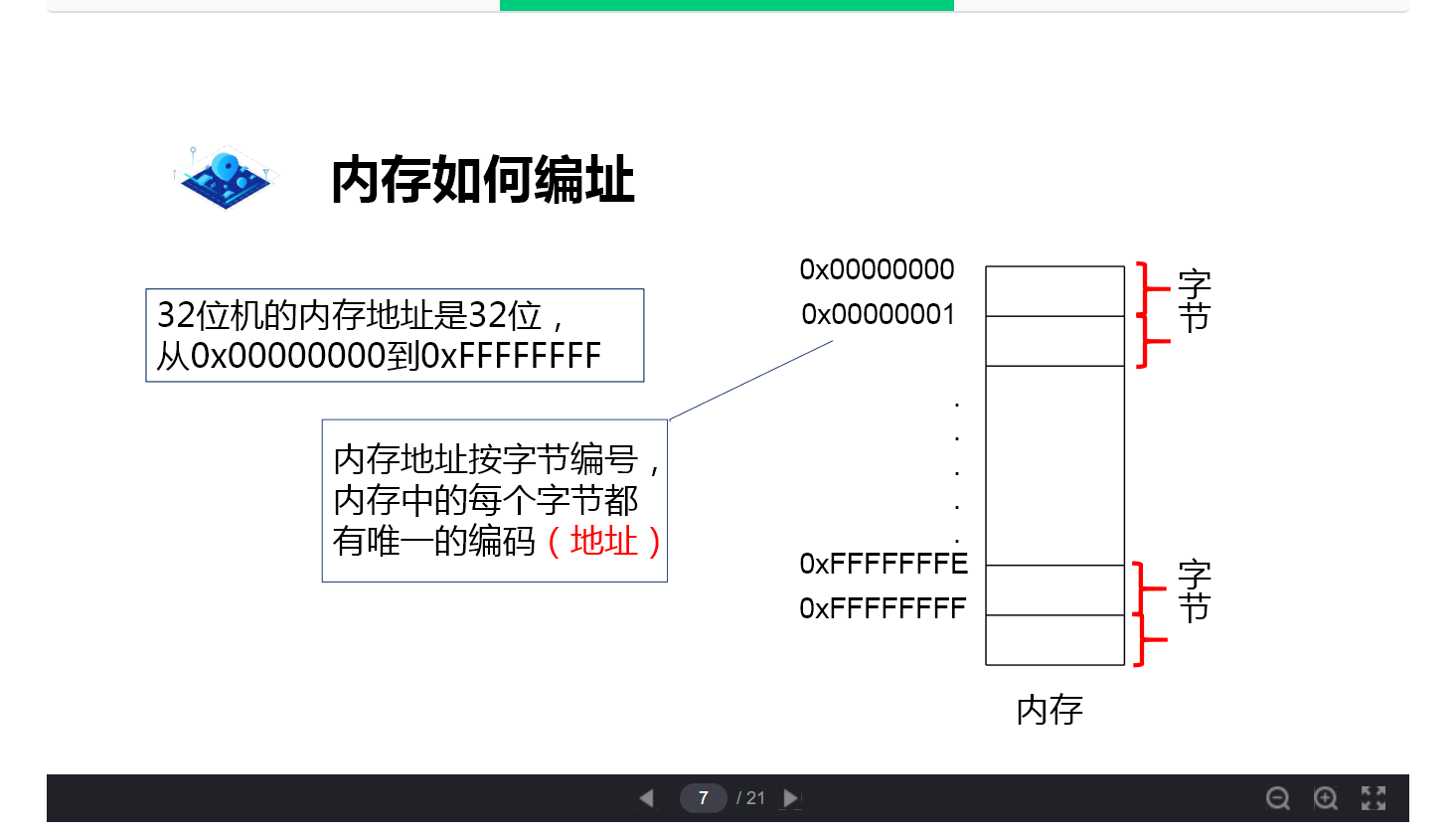
Memory addressing
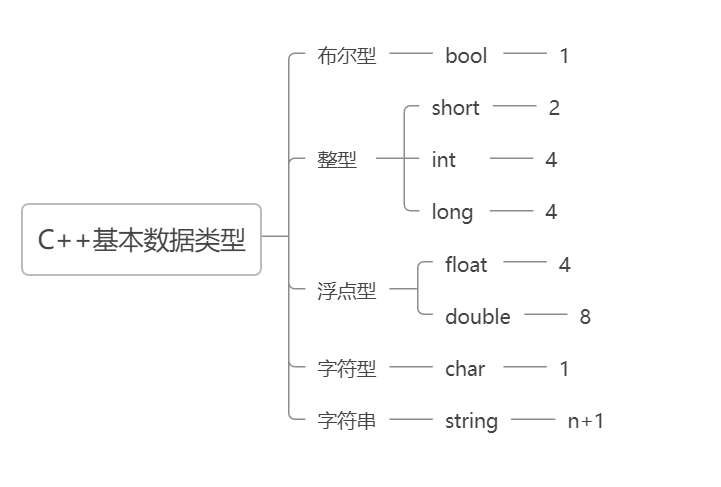
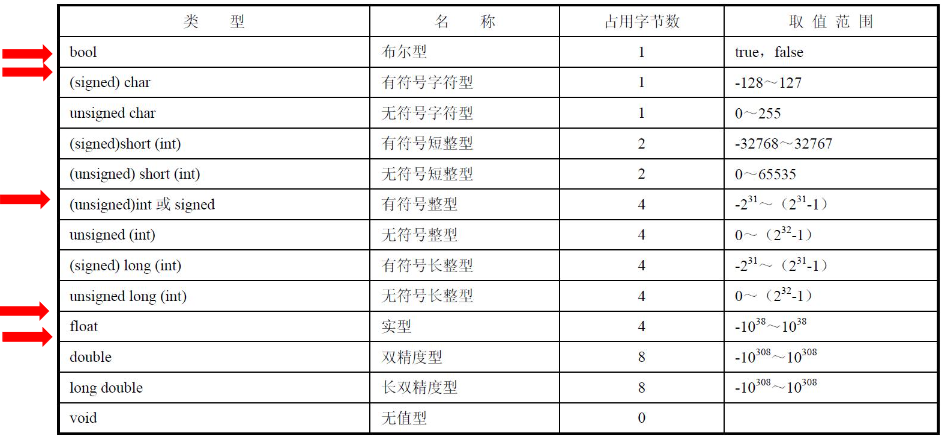
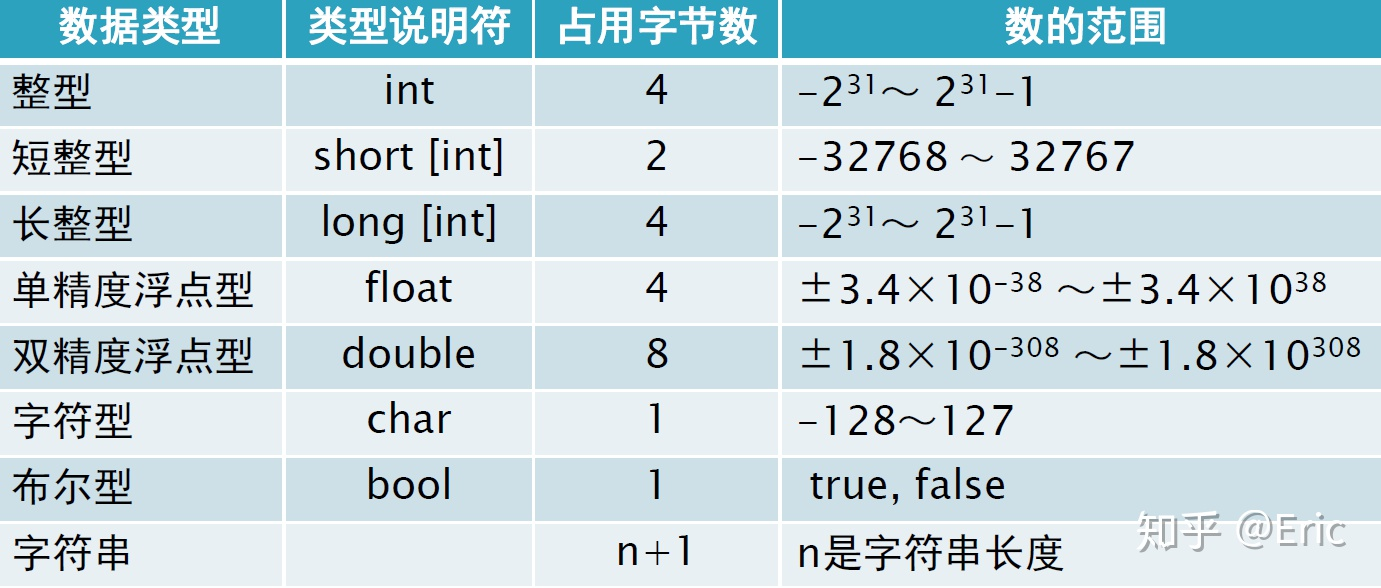
Basic data type
bool char 1 1
short int long 2 4 4
float double long double 4 8 8
Case: output the value of x+y

//Header file
#include<iostream>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
// Namespace identifier
using namespace std;
//Main function
int main()
{
//Declarative variable
int x,y,z;
//Variable assignment
x=1;
y=9;
z=x+y;
//cout: output stream object < <: output stream operator
cout<<"The result is:"<<"\n";
cout<<"x+y="<<z<<endl;
return 0;
}
Summary of variables

Input stream and output stream Cin Cout
CIN > > r: enter a value from the keyboard to r
Cout < < R: output r to the screen
Note: when writing a floating point constant, add a decimal point
double r;
cout<<"input:r"<<endl;//Prompt statement
cin>>r;
cout<<"r="<<r<<endl;
Keep several significant digits
setprecision(n): n significant digits are reserved
//Scientific counting method: setprecision(n): note that after setting it once, the subsequent output will be limited to n significant digits cout<< setprecision(2)<<123.444546<<"\n"<<endl;//1.2e+002
123.444546 exceeds 2 digits, and the decimal point moves to the left until it is 2 digits
Move right: + 002
Keep several decimal places
Fixed < < setprecision (n): keep N decimal places
#include<iomanip> cout<<fixed<<setprecision(2)<<s<<endl;
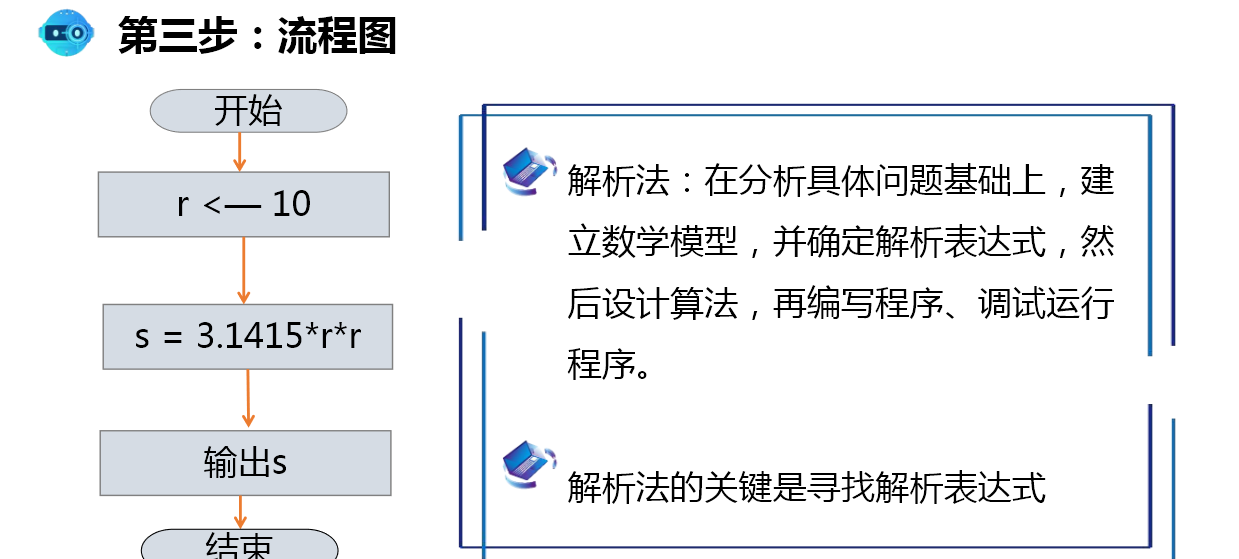
Case: finding the area of a circle


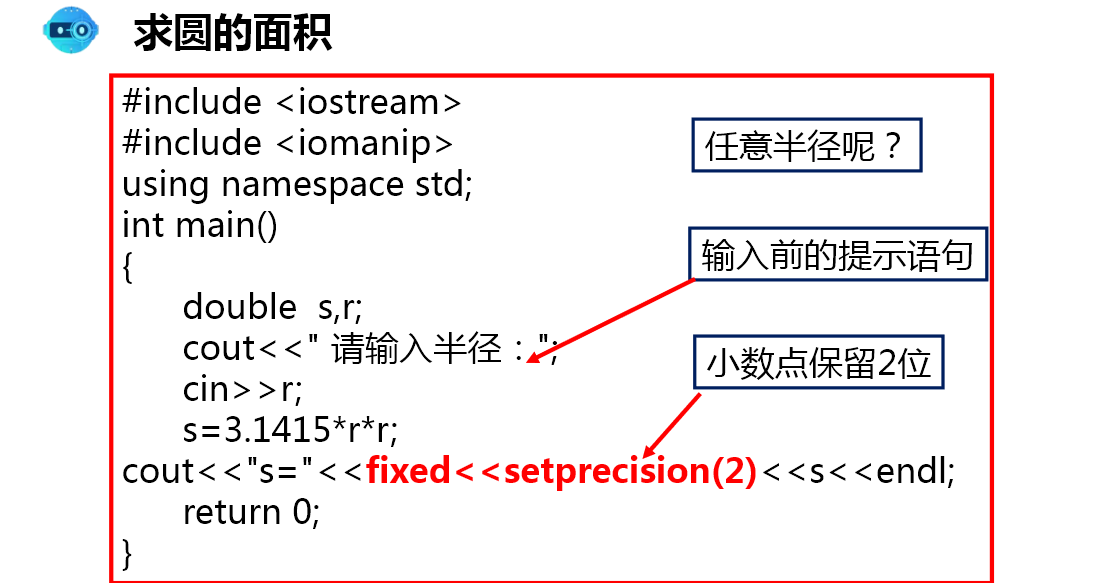
#include <iostream>
#include<iomanip>
using namespace std;
void circle(double r)
{
double pi=3.1415;
double s=pi*r*r;
double c=pi*2.0*r;
cout<<"s="<<s<<"\n"<<"c="<<c<<endl;
//cout<<"s="<<fixed<<setprecision(2)<<s; Keep two digits after the decimal point
cout<<"s="<<fixed<<setprecision(4)<<s<<"\n"<<"c="<<fixed<<setprecision(4)<<c<<"\n"<<endl;
}
int main()
{
double r;
cout<<"input:r"<<endl;//Prompt statement
cin>>r;
circle(r);
cout<<"end"<<endl;
return 0;
}