Big data concept
Big Data: refers to a data set that cannot be captured, managed and processed by conventional software tools within a certain time range. It is a massive, high growth rate and diversified information asset that requires a new processing mode to have stronger decision-making power, insight and discovery power and process optimization ability
Big data mainly solves the problems of massive data collection, storage, analysis and calculation
Through the analysis and mining of massive data, we can find the internal laws of data, so as to create value for enterprises or countries
Big data features (4V)
Volume (large)
The capacity of typical personal computer hard disk is TB, while the data volume of some large enterprises is close to EB
Velocity
Double 11 one second trading volume of more than 10 billion
Variety
This type of diversity also allows data to be divided into structured data and unstructured data. Compared with the structured data based on database / text, which is easy to store in the past, there are more and more unstructured data, including network log, audio, video, picture, geographic location information, etc. these multiple types of data put forward higher requirements for data processing ability.
Value (low value density)
The value density is inversely proportional to the total amount of data
Hadoop
What is Hadoop
- Hadoop is a distributed system infrastructure developed by the Apache foundation.
- It mainly solves the problems of massive data storage and massive data analysis and calculation.
- In a broad sense, Hadoop usually refers to a broader concept - Hadoop ecosystem.
Three major releases of Hadoop
Hadoop has three major distributions: Apache, Cloudera and Hortonworks.
The most original (basic) version of Apache is the best for getting started. two thousand and six
Cloudera integrates many big data frameworks internally, corresponding to the product CDH. two thousand and eight
Hortonworks documents are good, corresponding to the product HDP. two thousand and eleven
Hortonworks has now been acquired by Cloudera to launch a new brand CDP.
Hadoop advantages
- High reliability: Hadoop bottom layer maintains multiple data copies, so even if a Hadoop computing element or storage fails, it will not cause data loss
- High scalability: allocating task data among clusters can easily expand thousands of nodes.
- Efficiency: under the idea of MapReduce, Hadoop works in parallel to speed up task processing.
- High fault tolerance: it can automatically reassign failed tasks
Hadoop composition
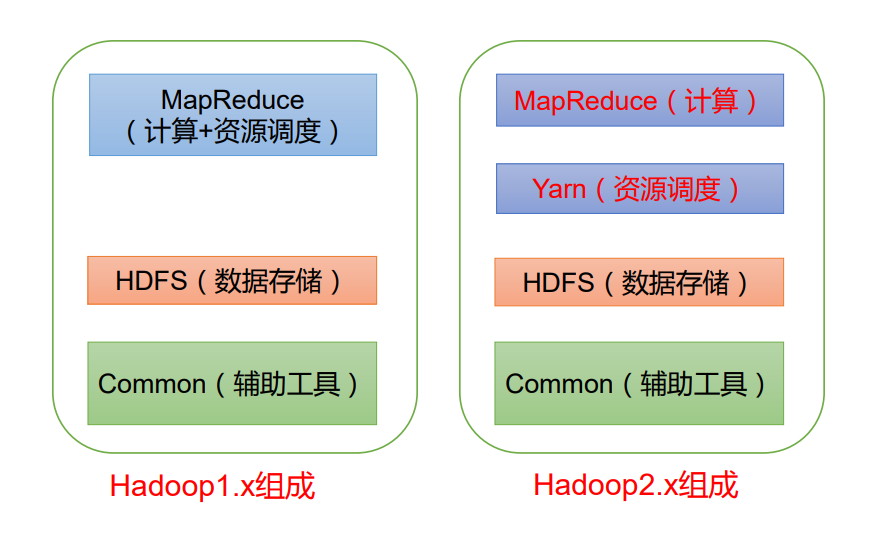
In the era of Hadoop 1. X, MapReduce in Hadoop handles business logic operation and resource scheduling at the same time, with great coupling.
In the Hadoop 2. X era, Yan was added. Yarn is only responsible for resource scheduling, and MapReduce is only responsible for computing.
Hadoop 3. X has no change in composition
HDFS
Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS for short) is a distributed file system.
HDFS Architecture Overview
NameNode(nn)
Store the metadata of the file, such as file name, file directory structure, file attributes (generation time, number of copies, file permissions), block list of each file, DataNode where the block is located, etc.
DataNode(dn)
Store the file block data and the checksum of the block data in the local file system
Secondary NameNode(2nn)
Backup the NameNode metadata at regular intervals
Block
Data block. In order to save large data sets through multiple nodes, HDFS divides large data set files into data blocks. In the existing Hadoop 2 version, the default block size is 128M
Overview of YARN architecture
YT another resource Negotiator (YARN for short), another resource coordinator, is the resource manager of Hadoop
- Resource Manager (RM): the leader of the entire cluster resources (memory, CPU, etc.)
- Application master (AM): the master of a single task run
- NodeManager (N M): single node server resource manager
- Container: container, which is equivalent to an independent server and is encapsulated inside
Resources required for task operation, such as memory, CPU, disk, network, etc.
There can be multiple clients
Multiple applicationmasters can run on a cluster
There can be multiple containers on each NodeManager
MapReduce Architecture Overview
- MapReduce divides the calculation process into two stages: Map and Reduce
- The Map phase processes the input data in parallel
- In the Reduce phase, the Map results are summarized
Construction of Hadoop running environment
Create three virtual machines
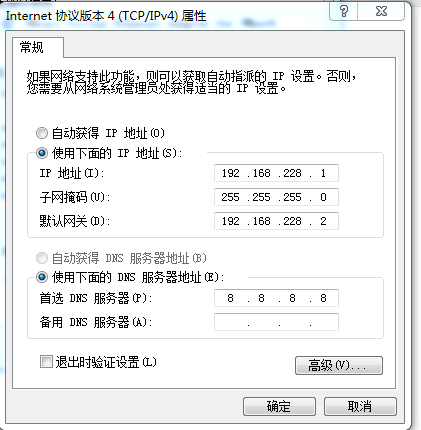
1. Virtual network card IP settings
ip 192.168.228.1 gw 192.168.228.2 netmask 255.255.255.0 dns 8.8.8.8
2. Modify the static IP of the virtual machine
First bigdata login
su root vi /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-ens33 BOOTPROTO=static ###modify ONBOOT=yes ###modify IPADDR=192.168.228.161 ###add to NETMASK=255.255.255.0 ###add to GATEWAY=192.168.228.2 ###add to DNS1=8.8.8.8 ###add to
screenshot
Restart the network card
service network restart
View IP
ip addr
screenshot
3. Modify host name
su root vi /etc/hostname hadoop102
Configure the Linux clone host name mapping hosts file and open / etc/hosts
vi /etc/hosts 192.168.228.161 hadoop102 192.168.228.162 hadoop103 192.168.228.163 hadoop104
reboot restart
The other two hosts are configured as follows
Second set bigdata Sign in su root vi /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-ens33 BOOTPROTO=static ### ONBOOT=yes ### IPADDR=192.168.228.162 ### NETMASK=255.255.255.0 ### GATEWAY=192.168.228.2 ### DNS1=8.8.8.8 Restart the network card service network restart see IP ip addr srt Software su root vi /etc/hostname hadoop103 vi /etc/hosts 192.168.228.161 hadoop102 192.168.228.162 hadoop103 192.168.228.163 hadoop104 Third set bigdata Sign in su root vi /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-ens33 BOOTPROTO=static ### ONBOOT=yes ### IPADDR=192.168.228.163 ### NETMASK=255.255.255.0 ### GATEWAY=192.168.228.2 ### DNS1=8.8.8.8 Restart the network card service network restart see IP ip addr srt Software su root vi /etc/hostname hadoop104 vi /etc/hosts 192.168.228.161 hadoop102 192.168.228.162 hadoop103 192.168.228.163 hadoop104
4. Turn off the firewall
su root 123456 #Turn off firewall systemctl stop firewalld #Turn off firewall and start systemctl disable firewalld #View firewall status systemctl status firewalld
5. Configure SSH login free
1. bigdata Sign in hadoop102
su bigdata
cd ~/(#Go to my home directory)
cd .ssh(If an error is reported, perform the following operations)
ssh hadoop102(own-Purpose generation.ssh (file)
yes
123456
exit
cd .ssh
ssh-keygen -t rsa((three carriage returns)
# Execute the following three commands respectively
ssh-copy-id hadoop102
ssh-copy-id hadoop103
ssh-copy-id hadoop104
6. Create directory and modify permissions
su root mkdir /opt/software mkdir /opt/module chmod 777 /opt/software chmod 777 /opt/module
7. Install JDK
Uninstall existing JDK
To query whether Java software is installed:
rpm -qa | grep java
If the installed version is lower than 1.7, uninstall the JDK
sudo rpm -e software package
View JDK installation path:
which java
Use the XShell transport tool to import the JDK into the software folder under the opt directory
Check whether the software package is successfully imported in the opt directory under the Linux system
ls /opt/software/
Unzip the JDK to the / opt/module directory
tar -zxvf jdk-8u251-linux-x64.tar.gz -C /opt/module
Configure JDK environment variables
su root 123456 vi /etc/profile #JAVA_HOME export JAVA_HOME=/opt/module/jdk1.8.0_251 export PATH=$PATH:$JAVA_HOME/bin
:wq
source /etc/profile
Test whether the JDK is installed successfully
java -version
Configuration of the other two machines
su bigdata cd /opt scp -r /opt/module hadoop103:/opt scp -r /opt/module hadoop104:/opt Respectively in hadoop103,hadoop104 modify/etc/profile su root 123456 vi /etc/profile export JAVA_HOME=/opt/module/jdk1.8.0_251 export PATH=$PATH:$JAVA_HOME/bin source /etc/profile su bigdata
Installing hadoop
Upload hadoop
Upload hadoop to / opt/software
Unzip / opt/module
cd /opt/software tar -zxvf hadoop-2.7.2.tar.gz -C /opt/module
Configure hadoop
First: hadoop-env.sh
cd /opt/module/hadoop-2.7.2/etc/hadoop vi hadoop-env.sh #Around line 27 export JAVA_HOME=/opt/module/jdk1.8.0_251
Second: core-site.xml
vi core-site.xml
<configuration>
<!--to configure hdfs File system default name-->
<property>
<name>fs.defaultFS</name>
<value>hdfs://Hadoop (hostname): 9000 < / value >
</property>
</configuration>
Note: the name is an HDFS URL
Configure it in the configuration tab
<!-- appoint HADOOP File system used schema(URI),HDFS My boss( NameNode)Address of --> <property> <name>fs.defaultFS</name> <value>hdfs://hadoop102:9000</value> </property> <!-- appoint hadoop The storage directory where files are generated at run time --> <property> <name>hadoop.tmp.dir</name> <value>/opt/module/hadoop-2.7.2/data/tmp</value> </property>
mkdir -p /opt/module/hadoop-2.7.2/data/tmp
Third: hdfs-site.xml
vi hdfs-site.xml
<!-- appoint HDFS Number of copies --> <property> <name>dfs.replication</name> <value>3</value> </property> <property> <name>dfs.permissions.enabled</name> <value>false</value> </property>
Fourth: mapred-site.xml
mv mapred-site.xml.template mapred-site.xml vi mapred-site.xml
<!-- appoint mr Run in yarn upper --> <property> <name>mapreduce.framework.name</name> <value>yarn</value> </property>
Fifth: yarn-site.xml
vi yarn-site.xml
<!-- appoint YARN My boss( ResourceManager)Address of --> <property> <name>yarn.resourcemanager.hostname</name> <value>hadoop102</value> </property> <!-- reducer How to get data --> <property> <name>yarn.nodemanager.aux-services</name> <value>mapreduce_shuffle</value> </property>
Sixth: slaves
vi slaves
add to
hadoop102 hadoop103 hadoop104
Copy to two other machines
cd /opt/module
scp -r /opt/module/hadoop-2.7.2 hadoop103:/opt/module scp -r /opt/module/hadoop-2.7.2 hadoop104:/opt/module
Add environment variable
Add hadoop to the environment variable (three machines)
su root vi /etc/profile
export HADOOP_HOME=/opt/module/hadoop-2.7.2 export PATH=$PATH:$JAVA_HOME/bin:$HADOOP_HOME/bin:$HADOOP_HOME/sbin source /etc/profile su bigdata
Format hdfs
Format namenode (Hadoop 102) (only the first use requires formatting)
hdfs namenode -format
Note: the format here is a file system recognized by hadoop. For example, if we buy a hard disk, we need to format it into a file system recognized by windows or Mac and Linux system to use this file system.
Start hadoop (hadoop 102)
# Start HDFS first start-dfs.sh Restart YARN start-yarn.sh Turn off safe mode hdfs dfsadmin -safemode leave
Verify successful startup
use jps Command validation
# 12. Check whether hadoop is started successfully
jps The presence of the following process name indicates successful startup
5876 SecondaryNameNode
5702 DataNode
5995 Jps
5612 NameNode
Visual management interface
http://hadoop102:50070 (HDFS management interface)
http://hadoop102:8088 (MR management interface)
screenshot
Hadoop directory structure
- bin directory: stores scripts for operating Hadoop related services (hdfs, yarn, mapred)
- etc Directory: Hadoop configuration file directory, which stores Hadoop configuration files
- lib Directory: local library for storing Hadoop (function of compressing and decompressing data)
- sbin Directory: stores scripts for starting or stopping Hadoop related services
- share Directory: stores the dependent jar packages, documents, and official cases of Hadoop
Hadoop running mode
Hadoop operation modes include: local mode, pseudo distributed mode and fully distributed mode.
- Local mode: stand-alone operation, just to demonstrate the official case. Not used in production environment
- Pseudo distributed mode: it is also a stand-alone operation, but it has all the functions of Hadoop cluster. One server simulates a distributed environment. Individual companies that are short of money are used for testing, and the production environment is not used
- Fully distributed mode: multiple servers form a distributed environment. Production environment usage
Word count
- Create a wcinput folder under the hadoop-3.1.3 file
mkdir wcinput
- Create a word.txt file under the wcinput file
cd wcinput
- Edit word.txt file
vim word.txt
Enter the following in the file
hadoop yarn hadoop mapreduce dyk dyk
Save exit:: wq
- Go back to Hadoop directory / opt/module/hadoop-3.1.3
hadoop jar share/hadoop/mapreduce/hadoop-mapreduce-examples-3.1.3.jar wordcount wcinput wcoutput
- View results
cat wcoutput/part-r-00000