10 port management of switch background management
Project requirements
Switch

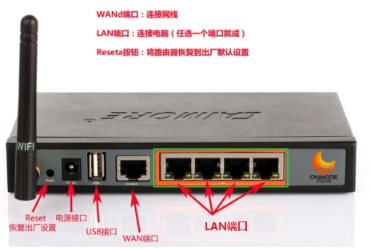
Port:
1) Port name
2) Port status
3) IP address of the port
4) Port type
WAN
LAN
Project realization
1. Add menu frame
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
FILE *file;
void init(void) {
//Open file
file = fopen("users.txt", "r");
if (!file) { //Equivalent to file == NULL
printf("File open failed");
//return 1;
exit(1);
}
}
void login(void) {
char name[32];
char password[16];
char line[128];
char name_tmp[32];
char password_tmp[16];
char *ret;
//Enter user name and password
while (1) {
system("cls");
// Enter user name and password
printf("Please enter the user name:");
scanf("%s", name);
printf("Please input a password:");
scanf("%s", password);
//Read the account from the file and judge!
while (1) {
//Read a row
ret = fgets(line, sizeof(line), file); //line: "admin 123456\n"
if (!ret) {
break;
}
sscanf(line, "%s %s", name_tmp, password_tmp);
if (!strcmp(name, name_tmp) && !strcmp(password, password_tmp)) {
break;
}
}
if (ret) { //User name and password match successfully
break;
} else {
printf("Wrong user name or password!\n");
system("pause");
system("cls");
fseek(file, 0, SEEK_SET); //Set the location pointer inside the file to the file header
}
}
}
void create_user(void) {
system("cls");
printf("\n\n---Create account---\n\n");
printf("To be realized...\n\n");
printf("\n\n Press any key to return to the main menu");
fflush(stdin);
getchar();
}
void ip_admin(void) {
system("cls");
printf("\n\n---IP Administration---\n\n");
printf("To be realized...\n\n");
printf("\n\n Press any key to return to the main menu");
fflush(stdin);
getchar();
}
void logout(void) {
system("cls");
fclose(file);
exit(0);
}
void input_error(void) {
system("cls");
printf("\n\n Input error!\n\n");
printf("\n\n After pressing any key, please re-enter\n\n");
fflush(stdin);
getchar();
}
void show_memu(void) {
system("cls");
// Print function menu
printf("---Switch background management---\n");
printf("1. Create account\n");
printf("2. IP Administration\n");
printf("3. Sign out\n");
printf("4. Port management\n");
printf("Please choose: ");
}
void show_ports(void) {
system("cls");
printf("---port status---\n");
printf("To be realized.\n");
system("pause");
}
void set_ports(void) {
system("cls");
printf("---port settings---\n");
printf("To be realized.\n");
system("pause");
}
void port_admin(void) {
char n;
while(1) {
system("cls");
printf("1. View port\n");
printf("2. Set port\n");
printf("3. Back to main menu\n");
printf("Please choose: ");
fflush(stdin);
scanf("%c", &n);
if (n == '1') {
show_ports();
} else if (n == '2') {
set_ports();
} else if (n == '3') {
break;
} else {
input_error();
}
}
}
int main(void) {
char n; //User selected menu number
init(); //Initialization
login(); //Sign in
while (1) {
show_memu();
fflush(stdin);
scanf("%c", &n);
switch (n) {
case '1':
create_user();
break;
case '2':
ip_admin();
break;
case '3':
logout();
break;
case '4':
port_admin();
break;
default:
input_error();
break;
}
}
return 0;
}2. Representation of port information
Add type definition and port variables
struct port {
char name[16]; //Name of the port
int status; //1: Activate 0: Disable
char ip[16]; //192.168.1.5
char type[4]; //Port type LAN WAN
};
//Five port variables are defined
struct port port1;
struct port port2;
struct port port3;
struct port port4;
struct port port5;Project realization
void show_port(struct port port) {
printf("Name[%s]\t state[%s]\tIP[%s]\t type[%s]\n",
port.name,
port.status == 0 ? "Prohibit":"activation",
port.ip,
port.type);
}
void show_ports(void) {
system("cls");
printf("---port status---\n");
printf("PORT1:\t");
show_port(port1);
printf("PORT2:\t");
show_port(port2);
printf("PORT3:\t");
show_port(port3);
printf("PORT4:\t");
show_port(port4);
system("pause");
}
void set_port1(void) {
system("cls");
printf("---Set up PORT1 port---\n");
printf("Please enter the port name: ");
scanf("%s", port1.name);
printf("Please enter the status of the port:[0:prohibit] [1:activation] ");
scanf("%d", &port1.status);
printf("Please enter the type of port:[LAN or WAN] ");
scanf("%s", port1.type);
printf("Please enter the IP address: ");
scanf("%s", port1.ip);
system("pause");
}
void set_port2(void) {
system("cls");
printf("---Set up PORT2 port---\n");
printf("Please enter the port name: ");
scanf("%s", port2.name);
printf("Please enter the status of the port:[0:prohibit] [1:activation] ");
scanf("%d", &port2.status);
printf("Please enter the type of port:[LAN or WAN] ");
scanf("%s", port2.type);
printf("Please enter the IP address: ");
scanf("%s", port2.ip);
}
void set_port3(void) {
system("cls");
printf("---Set up PORT3 port---\n");
printf("Please enter the port name: ");
scanf("%s", port3.name);
printf("Please enter the status of the port:[0:prohibit] [1:activation] ");
scanf("%d", &port3.status);
printf("Please enter the type of port:[LAN or WAN] ");
scanf("%s", port3.type);
printf("Please enter the IP address: ");
scanf("%s", port3.ip);
}
void set_port4(void) {
system("cls");
printf("---Set up PORT4 port---\n");
printf("Please enter the port name: ");
scanf("%s", port4.name);
printf("Please enter the status of the port:[0:prohibit] [1:activation] ");
scanf("%d", &port4.status);
printf("Please enter the type of port:[LAN or WAN] ");
scanf("%s", port4.type);
printf("Please enter the IP address: ");
scanf("%s", port4.ip);
}
void set_port5(void) {
system("cls");
printf("---Set up PORT5 port---\n");
printf("Please enter the port name: ");
scanf("%s", port5.name);
printf("Please enter the status of the port:[0:prohibit] [1:activation] ");
scanf("%d", &port5.status);
printf("Please enter the type of port:[LAN or WAN] ");
scanf("%s", port5.type);
printf("Please enter the IP address: ");
scanf("%s", port5.ip);
}
void set_ports(void) {
char n;
while(1) {
system("cls");
printf("---port settings---\n");
printf("1. PORT1\n");
printf("2. PORT2\n");
printf("3. PORT3\n");
printf("4. PORT4\n");
printf("5. PORT5\n");
printf("6. Return\n");
printf("Please choose: ");
fflush(stdin);
scanf("%c", &n);
switch (n) {
case '1':
set_port1();
break;
case '2':
set_port2();
break;
case '3':
set_port3();
break;
case '4':
set_port4();
break;
case '5':
set_port5();
break;
case '6':
return;
default:
input_error();
break;
}
}
}Project presentation
1. Why use structure (structure)
However, it is not convenient to use a simple data type when you need to represent some replication information.
For example: student information (student number, name, class, phone number, age)
2. What is "structure"
Structure is a kind of "data type" defined by programmers
It is a new "data type" composed of several basic data types or other structures.
3. Definition of structure
struct structure name{
Member type member name;
Member type member name;
};
Example:
struct student {
char name[16];
int age;
char tel[12];
};Special attention:
1) Start with struct
2) Last use semicolon
3) Members are separated by semicolons
4. Initialization of structure
demo
#include <stdio.h>
struct student {
char name[16];
int age;
};
int main(void) {
struct student s1 = {
"Rock", 38
};
struct student s2 = {
.age = 100,
.name = "Zhang Sanfeng"
};
struct student s3;
s3.age = 40;
strcpy(s3.name, "Yang Guo");
printf("%s, %d\n", s1.name, s1.age);
printf("%s, %d\n", s2.name, s2.age);
printf("%s, %d\n", s3.name, s3.age);
return 0;
}5. Use of structure
// Defining structural variables
// Note: the full type name is struct student
// Not just student s
struct student s1,s2;
struct student s3;
scanf("%s", s1.name);
s1.name = 25;
s2 = s1; //Direct assignment between structural variablesUsage:
Structural variables. Member variables
Separated by
6. Use structure as function parameter
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
struct student {
char name[16];
int age;
char tel[12];
};
void work(struct student stu) {
stu.age++;
printf("%s,%d\n", stu.name, stu.age);
}
int main(void) {
struct student s;
strcpy(s.name, "Rock");
s.age = 38;
work(s); //Structure variable s as a function parameter does not change the value of S itself
printf("%s,%d\n", s.name, s.age);
return 0;
}Be careful:
It is generally not recommended to take the structure as a function parameter directly.
Because the size of the structure is relatively large, it can directly transfer and consume performance!
Solution (using pointers)
7. Global variable, local variable
test1.c
#include <stdio.h>
void east_travel(void);
char master[16] = "Nu Wa";
void west_travel(void) {
char master[16] = "Tang Seng";
printf("[Westward Journey]Boss is: %s\n", master);
}
int main(void) {
char master[16] = "Buddha";
printf("[main]Boss is: %s\n", master);
char c;
printf("Enter the country of daughters? ( Y or N)\n");
fflush(stdin);
scanf("%c", &c);
if (c=='Y' || c=='y') {
char master[16] = "Queen";
printf("[main-Daughter country]Boss is: %s\n", master);
}
printf("[main]Boss is: %s\n", master);
east_travel();
return 0;
}test2.c
#include <stdio.h>
extern char master[16]; //Cannot initialize! Indicates that this global variable is defined in other files!
void east_travel(void) {
printf("[East tour]Boss is: %s\n", master);
}gcc test1.c test2.c
Project practice
Exercise 1
Independent implementation project 10
Exercise 2
1. Define a structure to describe the basic information of a game character.
The role information includes: name, gender, force value
And let the user enter 1 role.
The operation effect is as follows: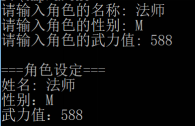
Reference code:
#include <stdio.h>
struct role {
char name[32];
char sex; //'M': Male 'W': Female
int power;
};
int main(void) {
struct role r1, r2;
printf("Please enter the name of the role: ");
scanf("%s", r1.name);
fflush(stdin);
printf("Please enter the gender of the role: ");
scanf("%c", &r1.sex);
printf("Please enter the force value of the role: ");
scanf("%d", &r1.power);
printf("\n===Role setting===\n");
printf("Full name: %s\n", r1.name);
printf("Gender:%c\n", r1.sex);
printf("Force value:%d\n", r1.power);
return 0;
}