Here are the use of some methods in String type, including:
- Extraction of elements in string;
- Appending of elements in string;
- String ignore case for comparison;
- Conversion of Chinese and English letters in string;
- Get string length;
- Replace the element or substring in the string;
- String truncation;
- Eliminate the first and last space characters in the string;
- Insert a new character or string into the string;
- Reverse the order of characters in the string;
The following ten methods are demonstrated in the same procedure:
/**
* Learning supplement · String
* @author Turn off the lock
*/
public class Yushu {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
* charAt Method can extract the elements in the string concat method can append the string
*/
String str = "This is the first";
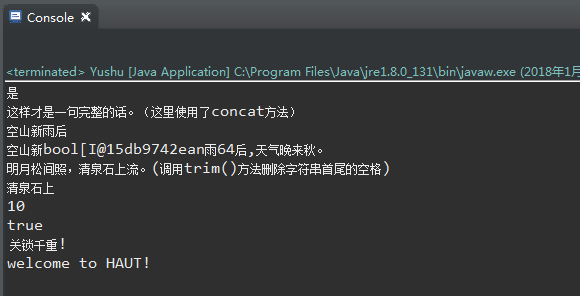
System.out.println(str.charAt(3));
String ing = "A complete sentence.";
String string = str.concat(ing + "(It's used here concat Method)");
System.out.println(string);
String str1 = " The moon shines among the pines, and the clear spring stone flows upward.(call trim()Method to remove spaces at the beginning and end of a string) ";
StringBuffer part1 = new StringBuffer("Houyuxinshankong");
part1.reverse();// The reverse() method reverses the order of all characters in a string without defining a new variable to receive them
System.out.println(part1);
part1.append("Come autumn.");// The StringBuffer append() method can be used to connect strings
part1.insert(5, ",It's late");// StringBuffer insert() method can be used to insert elements
/*
* insert Method must have two parameters: 1. Insert location; 2. Insert element
* When the element "boolean" needs to be inserted, the insertion part must write "boolean.class" to be valid
* If you are inserting other data types, you need to insert them according to the writing format of their data types
* For example: char type must use single quotation marks, and can also insert variables, arrays, etc
* Note, however, that there is an order of insertion
*/
int array[] = new int[] { 8, 37 };
part1.insert(4, 64);
part1.insert(3, boolean.class);
part1.insert(7, array);
System.out.println(part1);
String y = str1.trim();// The trim() method is used to delete spaces at the beginning and end of a string
System.out.println(y);
/*
* substring()Method to intercept a string from beginIndex to endIndex in a string
* Where, endIndex can be left blank, which means to intercept the string after beginIndex
* In addition, select the part that needs multiline annotation, and use control+shift + / to make quick multiline annotation
*/
String z = y.substring(6, 10);
System.out.println(z);
String s00 = "wElcOme To";
String s01 = "WeLCoMe tO";
// Use the length() method to get the length of the string
System.out.println(s00.length());
/*
* toLowerCase()And str02=s02.toUpperCase() method can perform case conversion
* But it should be noted that the case conversion here converts the case of Chinese and English letters in the whole string
*/
String str01 = s01.toLowerCase();
// Using the equalsIgnoreCase() method, you can compare strings regardless of the case of English letters. The result is a boolean type
System.out.println(s00.equalsIgnoreCase(s01));
String s02 = " heut!";
/*
* Use the replace() method to replace the elements in a string (including a single character of char type and a string of multiple characters connected)
* Note: when replacing consecutive substrings in a string, the substring to be replaced must be the connected part of the original string.
* But when replacing a substring, you can replace it with a different length
*/
String s03 = s02.replace('e', 'a');
String s04 = s02.replace("heut", "Turn off the lock");
System.out.println(s04);
String str02 = s03.toUpperCase();
System.out.println(str01 + str02);
}
}Attached with output rendering: