1. General
I talked about the installation of Elasticsearch before. Today, let's talk about the basic use of Elasticsearch.
two Use of Elasticsearch index
The index is equivalent to a table in mysql.
2.1 index creation
1) Head plug-in mode
Select the index tab, click [new index], enter the index name, number of slices and number of copies, and click [OK]
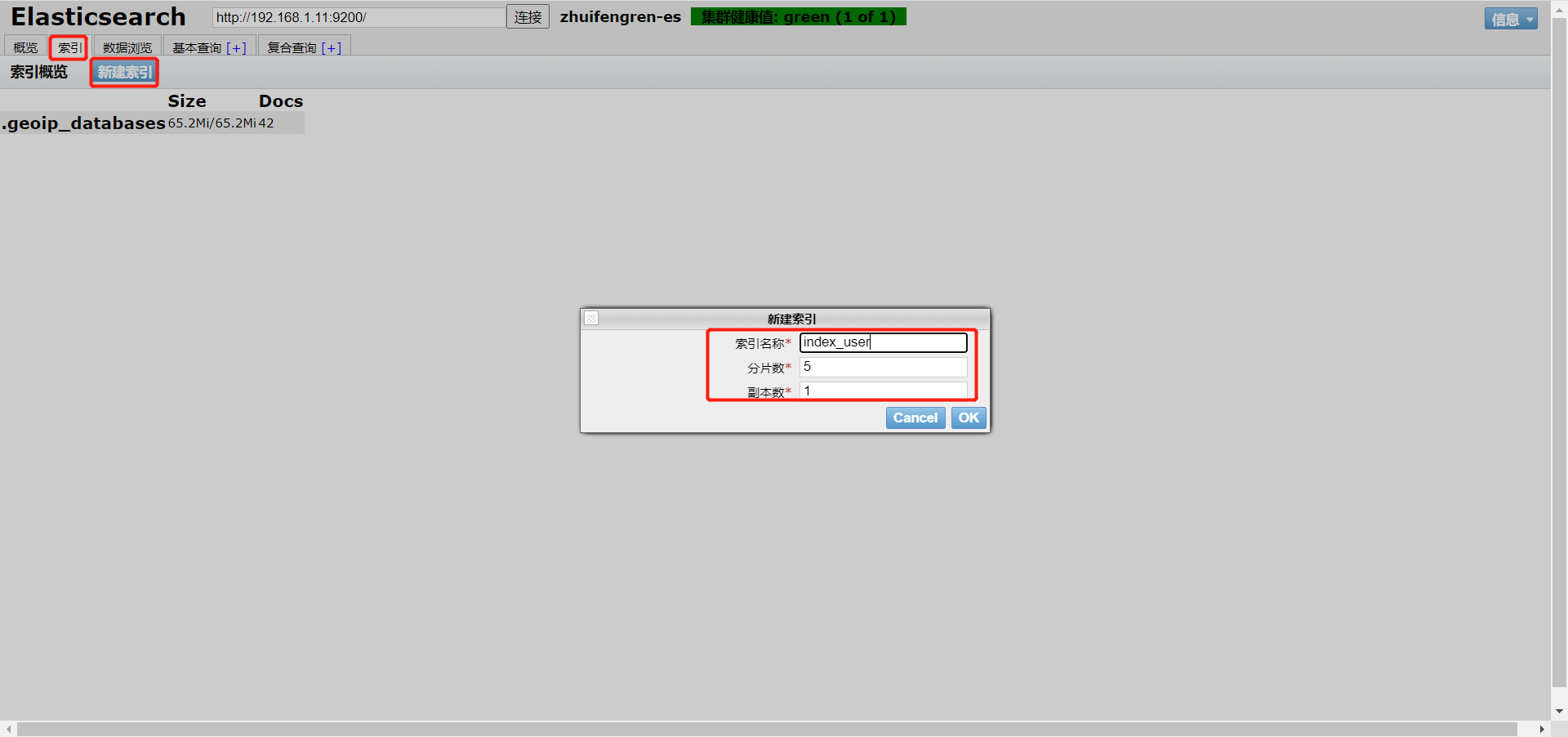
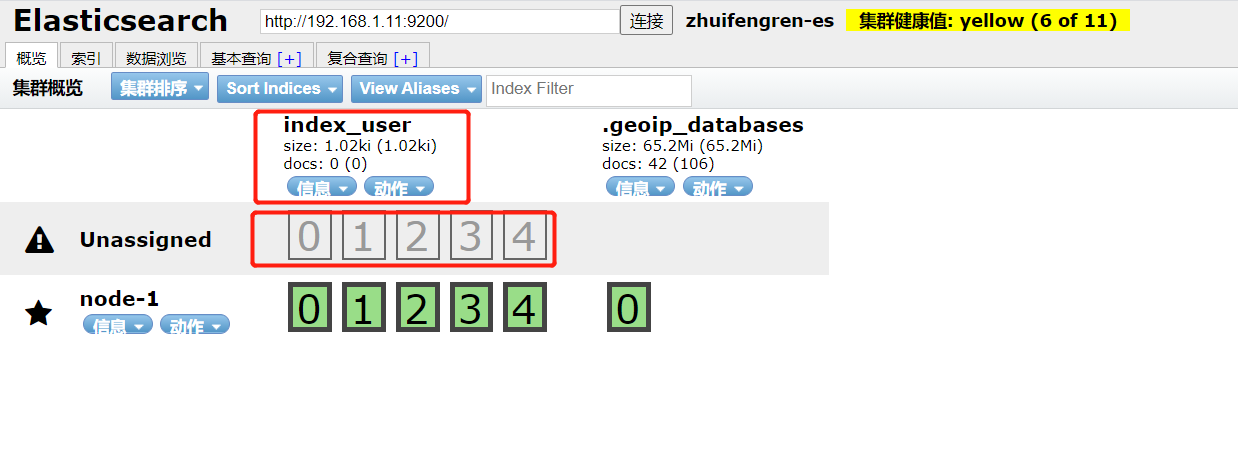
The reason why the cluster health value is yellow is that at present, Elasticsearch is run with a single server, and the replicas are stored on different servers. I'll talk about the construction of Elasticsearch cluster later.
2) RESTFUL interface mode
PUT http://192.168.1.11:9200/index_user
Parameters:
{
"settings":{
"index":{
"number_of_shards":5, // Number of slices
"number_of_replicas":0 // Number of copies
}
}
}2.2 viewing cluster health
RESTFUL interface mode
GET http://192.168.1.11:9200/_cluster/health
Response:
{
"cluster_name": "zhuifengren-es",
"status": "yellow",
"timed_out": false,
"number_of_nodes": 1,
"number_of_data_nodes": 1,
"active_primary_shards": 6,
"active_shards": 6,
"relocating_shards": 0,
"initializing_shards": 0,
"unassigned_shards": 5,
"delayed_unassigned_shards": 0,
"number_of_pending_tasks": 0,
"number_of_in_flight_fetch": 0,
"task_max_waiting_in_queue_millis": 0,
"active_shards_percent_as_number": 54.54545454545454
}2.3 delete index
1) Head plug-in mode
On the overview tab, find the index to delete and select action - > delete
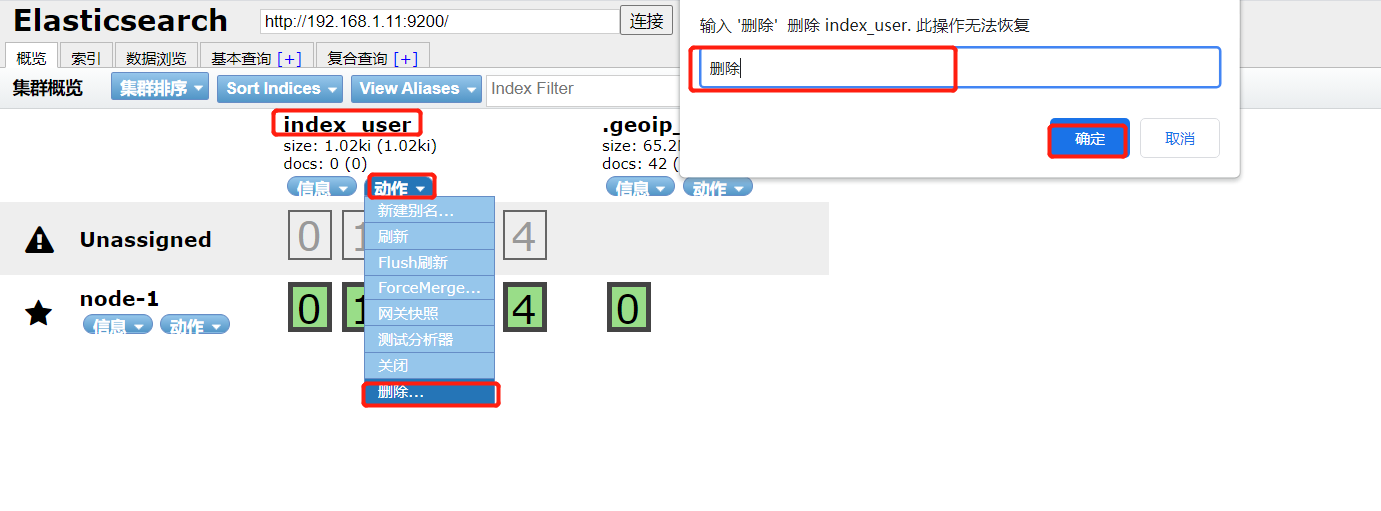
2) RESTFUL interface mode
DELETE http://192.168.1.11:9200/index_user
2.4 viewing the overall cluster information
RESTFUL interface mode
GET http://192.168.1.11:9200/_cat/indices?v
Response:
health status index uuid pri rep docs.count docs.deleted store.size pri.store.size green open .geoip_databases pE4IpIAeSA2AiJzdDdviYA 1 0 42 64 65.1mb 65.1mb green open index_user 2z4cELBeQeijTagp86ShbQ 5 0 0 0 1kb 1kb
three Use of Elasticsearch mapping
mapping is equivalent to the table structure definition in mysql.
3.1 main data types in elasticsearch
Text type: text, keyword
Integer: long, integer, short, byte
Floating point type: double, float
boolean: boolean
date type: date
Object type: object
3.2 create indexes and create mappings
RESTFUL interface mode
PUT http://192.168.1.11:9200/index_user
Parameters:
{
"settings":{
"index":{
"number_of_shards":5,
"number_of_replicas":0
}
},
"mappings" : {
"properties":{
"name":{
"type":"text", // data type
"index":true // Index
},
"loginName":{
"type":"keyword",
"index":false
},
"age":{
"type":"integer",
"index":false
}
}
}
}three point three Maintaining mapping on existing indexes
RESTFUL interface mode
POST http://192.168.1.11:9200/index_user/_mapping
Parameters:
{
"properties":{
"nickname":{
"type":"keyword",
"index":false
}
}
}Note: attributes in mapping can only be added and cannot be modified. If the property setting needs to be changed, the index needs to be deleted and rebuilt.
3.4 view the word segmentation effect of the index
RESTFUL interface mode
GET http://192.168.1.11:9200/index_user/_analyze
Parameters:
{
"field": "name",
"text": "lisa brown"
}four Use of Elasticsearch documents
A document is equivalent to a row of data in mysql.
4.1 new documents
RESTFUL interface mode
POST http://192.168.1.11:9200/index_user/_doc/1
Note: the last 1 in the url is the ID of the document in Elasticsearch, which has nothing to do with the business ID. if it is not written, a random string will be automatically generated as the ID of the document
Parameters:
{
"name":"zhang san",
"loginName":"zs",
"age":30
}If you do not create mapping manually, Elasticsearch will automatically create mapping according to the field type of the document after adding a document.
4.2 deleting documents
RESTFUL interface mode
DELETE http://192.168.1.11:9200/index_user/_doc/1
4.3 modifying documents
RESTFUL interface mode
1) Modify only some fields
POST http://192.168.1.11:9200/index_user/_doc/1/_update
Parameters:
{
"doc":{
"name":"zhangsan2",
"age":33
}
}2) Replace all
PUT http://192.168.1.11:9200/index_user/_doc/1
Parameters:
{
"name":"zhangsan",
"loginName":"zs",
"age":31
}
4.4 query documents
RESTFUL interface mode
1) Query by document ID
GET http://192.168.1.11:9200/index_user/_doc/1
Response data:
{
"_index": "index_user",
"_type": "_doc",
"_id": "1",
"_version": 5,
"_seq_no": 7,
"_primary_term": 1,
"found": true,
"_source": {
"name": "zhangsan",
"loginName": "zs",
"age": 31
}
}2) Query all
GET http://192.168.1.11:9200/index_user/_doc/_search
Response data:
{
"took": 2,
"timed_out": false,
"_shards": {
"total": 5,
"successful": 5,
"skipped": 0,
"failed": 0
},
"hits": {
"total": {
"value": 2,
"relation": "eq"
},
"max_score": 1.0,
"hits": [
{
"_index": "index_user",
"_type": "_doc",
"_id": "_TVW-XsBNDgg-BBCeUvY",
"_score": 1.0,
"_source": {
"name": "lisi",
"loginName": "ls",
"age": 31
}
},
{
"_index": "index_user",
"_type": "_doc",
"_id": "1",
"_score": 1.0,
"_source": {
"name": "zhangsan",
"loginName": "zs",
"age": 31
}
}
]
}
}3) Custom result set when querying
GET http://192.168.1.11:9200/index_user/_doc/1?_source=name,age
GET http://192.168.1.11:9200/index_user/_doc/_search?_source=name,age
5. Overview
Today, I briefly talked about the basic use of Elasticsearch. I hope it can be helpful to everyone's work.
You are welcome to help us with praise, comments and attention:)
Pay attention to those who follow the wind to talk about Java and update Java dry goods every day.