First, Series
pandas.Series(): used to create a one-dimensional array of ndarray s with "axis labels"
Call method:
pandas.Series(data=None, index=None, dtype=None, name=None, copy=False)
data: it can be a one-dimensional array created by list, dictionary, scalar value and numpy
Index: the "label" of data is allocated from 0 by default. The length of index and data are the same. If data is a dictionary and index is given, index will replace the key of the dictionary and become the label of value. The default label and the given label coexist.
import pandas as pd import numpy as np
#List creation a1 = pd.Series([1,2,3], index=['a','b','c']) print(a1) #Scalar value creation a2 = pd.Series(10, index=list('12345')) print(a2) #Dictionary creation a3 = pd.Series({'a':1, 'b':2, 'c':3}) print(a3) a4 = pd.Series({'a':1, 'b':2, 'c':3}, index=['e','b','a']) #index automatically matches the key of dict print(a4) #numpy Establish a5 = pd.Series(np.arange(1,5), index=np.arange(1,5)) print(a5)
Common properties:
index: returns the label of the array
values: returns the value of the array
Name: returns the name of the Series. It can also be used to modify the name of the Series
size: returns the number of elements in the array
value_counts(self, normalize=False, sort=True, ascending=True, bins=None, dropna=True): returns the number of elements. When normalize is True, the proportion of each element is counted; when bins is an integer, the array is discretized into integer segments according to the integer value; when dropna is False, the number of NaN in the array is counted
Common methods:
Series.add(self, other, fill_value=None)
If the tags are the same, the tags will return NaN if they are different; if the fill value is given, the missing value will be filled with fill value
import pandas as pd import numpy as np a = pd.Series(np.arange(1,5), index=list('abcd')) b = pd.Series(np.arange(5,9), index=list('abce')) print(a.add(b)) #6.0, 8.0, 10.0, NaN, NaN print(a.add(b, fill_value=0)) #6.0, 8.0, 10.0, 4.0, 8.0
Series.copy(self, deep=True)
Copy of array. The default is deep copy. data and index are shared between the shallow copy array and the original array. If one of them is modified, the other will also be modified. The deep copy will not be affected
import pandas as pd import numpy as np a = pd.Series(np.arange(1,5), index=list('abcd')) b = a.copy() c = a.copy(deep=False) a['a'] = 10 print(a) #10, 2, 3, 4 print(b) #1, 2, 3, 4 print(c) #10, 2, 3, 4
Series.get(self, key, default=None)
Get the value corresponding to the key in the array (for example, the column of DataFrame). If not found, return the default value
Indexes:
When an index is given, you can use either the given index or the default index. You can slice through a custom index list
import pandas as pd a = pd.Series([1,2,3], index=list('abd')) #Cannot index like this on DataFrame print(a[0]) #1 print(a['a']) #1 #Both of the following methods can be used for slicing print(a['a':'d']) print(a[['a','b','d']])
Two. DataFrame
pandas.DataFrame(): used to create a tabular data type with row label and column label
Call method:
pandas.DataFrame(data=None, index=None, columns=None, dtype=None, copy=False)
Data: 2D ndarray array, including Series, array, tuple, list and other data type Dictionaries
index: row label. If it is not defined or data is not provided, it starts from 0 by default
columns: column label. If it is not defined, it starts from 0 by default
import pandas as pd import numpy as np df = pd.DataFrame(np.arange(1,10).reshape(3,3), columns=list('abc')) print(df) # Create from dictionary d1 = {'one':[1,2,3], 'two':[4,5,6]} df1 = pd.DataFrame(d1, index=list('abc')) print(df1)
# Change column index
df2 = pd.DataFrame(d1, columns=['two', 'one'])
print(df2)
A way to change a DataFrame into a list:
import numpy as np import pandas as pd frame = pd.DataFrame(np.arange(12).reshape(3,4), columns=list('abcd')) frame_to_list1 = frame.values.tolist() frame_to_list2 = frame['a'].tolist() print(frame_to_list1) #[[0, 1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6, 7], [8, 9, 10, 11]] print(frame_to_list2) #[0, 4, 8]
Common properties:
index: return row label
columns: return column labels
values: returns the value of an element in an array
Shape: returns the shape of the DataFrame
size: returns the number of elements in the ndarray array
at: accessing individual elements through Tags
iat: accessing individual elements through integers
iloc: accessing DataFrame data through integers
loc: access DataFrame data through tags or Boolean arrays
import numpy as np import pandas as pd frame = pd.DataFrame(np.arange(12).reshape(3,4),
index=list('abc'), columns=['num','name','sex','age']) #Single label print(frame.loc['a']) #Label list, return a DataFrame print(frame.loc[['a','b'],['num','name']]) #Single label of row and column, output corresponding single element print(frame.loc['a','num']) #When slicing, the start and end of the slice are included in it print(frame.loc['a':'c']) #Boolean list print(frame.loc[[False,True,True]])
#Filter by criteria
print(frame[frame.age>4].iloc[:, :3])
print(frame[frame['age']>4].iloc[:, :3])
#To get the data of a row in DataFrame, use iloc or loc instead of row label
Add a new column:
import pandas as pd dict = {'one':[1,2,3], 'two':[4,5,6]} df1 = pd.DataFrame(dict, index=['a','b','c']) col = pd.Series([7,8,9], index=df1.index) df1['three'] = col print(df1)
Common methods:
drop: delete the specified row or column label
import pandas as pd import numpy as np frame = pd.DataFrame(np.arange(12).reshape(3,4),
index=list('123'),columns=list('abcd')) #Delete a,b The two column print(frame.drop(['a','b'],axis=1)) #Delete 1,2 Two elements print(frame.drop(index=['1','2']))
#Permanently delete a column
del frame['d']
print(frame.columns)
reindex: reorder or add a newly defined index
Call method:
DataFrame.reindex(self,labels = None,index = None,column = None,axis = None,method = None,copy = True,fill_value = nan)
index\columns: Custom index for new columns
Fill value: the fill value of the new row and column
import pandas as pd import numpy as np frame = pd.DataFrame(np.arange(12).reshape(3,4),index=list('123'),columns=list('abcd')) #Reorder row indexes print(frame.reindex(index=list('321'))) #Add new index column newc = frame.columns.insert(3,'e') print(frame.reindex(columns=newc,fill_value='20')) #Create a new index new_index = ['0','2','3'] print(frame.reindex(new_index))
head: returns the first n rows of data. The default is 5 rows
Arithmetic operation (index corresponding operation):
add(self, other, axis='columns', level=None, fill_value=None): add operation
sub(self, other, axis='columns', level=None, fill_value=None): subtraction
div(self, other, axis='columns', level=None, fill_value=None): division operation
mul(self, other, axis='columns', level=None, fill_value=None): multiplication
import pandas as pd import numpy as np frame1 = pd.DataFrame(np.arange(12).reshape(3,4)) print(frame1) frame2 = pd.DataFrame(np.arange(9).reshape(3,3)) print(frame2) #frame1 And frame2 Add corresponding, add the non corresponding place with the filled value, no data loss of the filled value print(frame1.add(frame2, fill_value=100)) series = pd.Series(np.arange(3)) print(series) #default frame1 Add each line of series print(frame1.add(series)) #frame1 Subtract from each column of series print(frame1.sub(series,axis=0))
append: add a DataFrame to the end of another DataFrame to return a new object
Call method: append(self, other, ignore_index=False)
import pandas as pd import numpy as np frame1 = pd.DataFrame(np.arange(6).reshape(3,2)) frame2 = pd.DataFrame(np.arange(4).reshape(2,2)) print(frame1.append(frame2)) #Discard original index, row index starts from 0
print(frame1.append(frame2, ignore_index=True))
info: print brief information of DataFrame
Where: keep the original value when the given condition is true; when the given condition is not true, replace the value where the condition is not true with the given value

corr(self, method='pearson ', min_periods=1): calculates the pairwise correlation of columns, excluding NA and null values
sort_values(by, axis=0, ascending=True): sorts the values. By is a list of labels in one column or several columns
sort_index(axis=0, ascending=True): sort labels
Function application and mapping apply(func, axis=0):
import numpy as np import pandas as pd frame = pd.DataFrame(np.random.randn(3,4), index=list('abc'), columns=['name','sex','age','score']) print(frame) frame1 = frame.apply(lambda x: x.max()-x.min())#Line by line, top down print(frame1) frame2 = frame.apply((lambda x: x.max()-x.min()), axis=1) print(frame2)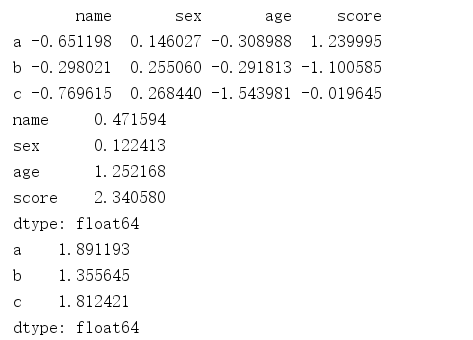
#Series.map(arg)
import numpy as np import pandas as pd frame = pd.DataFrame(np.random.randn(3,4), index=list('abc'), columns=['name','sex','age','score']) print(frame) frame1 = frame['score'].map(lambda x: '%.2f'%x) print(frame1)
Group by (by = none, axis = 0): group data as required, and then perform numerical operations
Missing value handling:
dropna(axis=0, how=any): delete the missing value. Axis can be {0, 'index', 1, 'columns'}; how can be {' any ',' all '}. All means delete if all values are missing
fillna(value=None, method=None, axis=None): fill in the missing value in some way. Value cannot be list if scalar, dict, Series, DataFame
replace(to_replace=None,value=None) : fill the value of to replace with the value of value. To replace can be scalar, list, dict