For decimal system, for example, 1234.5 = 1 * 10 ^ 3 + 2 * 10 ^ 2 + 3 * 10 ^ 1 + 4 * 10 ^ 0 + 5 * 10 ^ - 1 (sum by weight expansion).
○ 1 other hexadecimal to decimal systems are summed according to weight expansion, such as hexadecimal 0x123=1*16^2 + 2*16^1 + 3*16^0
○ 2 decimal to other base systems: integer part: Radix division and remainder in reverse order. Decimal part: Radix multiplication, rounding in order
○ 3 decimal to binary: in addition to the above method, it can also be rounded up. As shown below

○ 4 binary to octal: binary is divided into three groups from right to left, and then summed according to weight expansion, as shown in figure 0136457 below
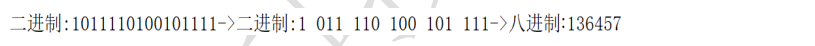
○ 5 binary to hexadecimal: binary is divided into four groups from right to left, and then summed according to weight expansion, as shown in figure 0xBD2F below
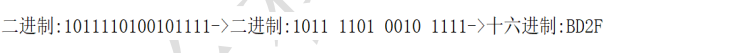
○ 6 decimal to eight, hexadecimal: first to binary, then to eight or hexadecimal.
2. Original code, inverse code and complement code:
○ 1 unsigned integer: all digits represent values;
The value range of N-bit unsigned integer data is 0~2^N-1 (2^N represents the nth power of 2)
○ 2 signed integer number: the highest bit 0 is a positive number and 1 is a negative number
Positive number: the original code, inverse code and complement code are the same;
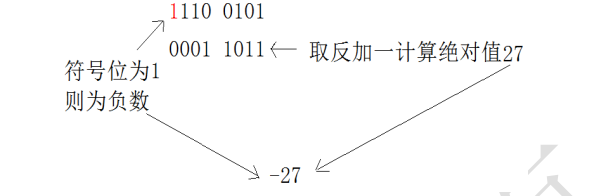
Negative number: the binary of its absolute value, take the inverse and add one, as shown in the figure below

○ 3 based on the binary calculated value, assume that the number is 1 byte:
Unsigned numbers are all numeric bits and are summed according to the weight expansion. 1010 1000->1*2^7 + 1*2^5 + 1*2^3=168
For signed numbers, first look at the sign bit to determine the sign. 0 is a positive number and 1 is a negative number.
If it is a positive number, sum according to the weight expansion. 0101 1000->1*2^6 + 1*2^4 + 1*2^3=88
If it is a negative number, first determine the symbol, and then take the inverse plus one to calculate its absolute value. 1110 0101
3. Shaping data type:
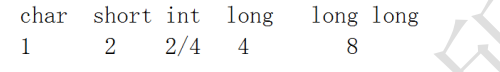
char: - 128 ~ 127, 256 different numbers in total.
unsigned char:0~255.
int: 4 bytes without description.
Note the value range of the data.
4. Floating point type:
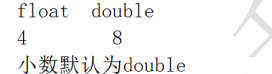
float: from left to right, the first digit is the sign digit, followed by the next 8 digits, and the last 23 digits are the trailing digits

Sign bit p: 0 is positive and 1 is negative
Index e: read index = actual index - 127
Mantissa m: excluding 1 to the left of the decimal point
For example, 12.5f - > 1100.1 - > 1.1001 * 2 ^ 3, the stored data is as follows:

Operator:
Bool: true, false C99
Logical predicate:! (non), & & (and), | (or)
True: not 0
False: 0
Expression 1 & & expression 2: only when expression 1 is true and expression 2 is true can it be true (only when both are true can it be true)
Expression 1 | expression 2: if expression 1 is true or expression 2 is true, it is true (as long as one is true)
&& And |: short circuit phenomenon (in & &, if expression 1 is false, expression 2 will not be calculated; in |, if expression 1 is true, expression 2 will not be calculated)
Bit operator: for binary (assuming that the following number is 1 byte), 1 byte = 8 bits
Decimal to binary: a method of rounding up one hundred and twenty-eight sixty-four 32 16 8 4 2 1
80 to binary: 0101 0000
100 to binary: 0110 0100
12:0000 1100
13:0000 1101
~ 12: 1111 0011 bit inversion
13 & 12:0000 1100 by bit and the same bit is 1
13 | 12:0000 1101 by bit or, if one of the same bits is 1, it is 1
13 ^ 12:0000 0001 by bit XOR, the same bit is different, which is 1. Pay attention to the exponential distinction between mathematics and mathematics
13 < < 1:000 11010 26 = 13 * 2 move left according to the position, and supplement 0 uniformly on the right
13<<2:00 110100 52=13*4
13> > 1:00000 110 6 = 13 / 2 shift right by bit and fill the sign bit on the left
/: Division, integer division: divide an integer by an integer, and the result is also an integer (discard decimals). Use more and test more
%: remainder: get the remainder after division. It can be used to judge whether to divide
=: assign the value on the right to the value on the left
==: equal sign
!=: Unequal sign
3*4:
>: error prone and cannot be compared continuously
Expression 1? Expression 2: expression 3 If expression 1 is true, expression 2 is executed, and if expression 1 is false, expression 3 is executed
#include <stdio.h>
//Find the maximum of two numbers
int main()
{
int a;
int b;
scanf_s("%d%d",&a,&b);
int c = a > b ? a : b;
/* int c;
if (a > b)
{
c = a;
}
else
{
c = b;
}*/
printf("Maximum=%d\n",c);
return 0;
}
/*
int main()
{
int a = 10;
// if (0 < a < 5)//error
if(0<a && a<5)
{
printf("True \ n "");
}
else
{
printf("False \ n "");
}
return 0;
}
*/
/*
int main()
{
int n;
scanf_s("%d", &n);//Get an integer value from the keyboard
// printf("%d\n",n);
//Judge whether this n is a leap year
if (n % 4 == 0 && n % 100 != 0 || n % 400 == 0)
{
printf("%d Is a leap year \ n",n);
}
else
{
printf("%d Not a leap year \ n",n);
}
return 0;
}
*/
/*
int main()
{
// printf("%d\n",5/2);//%d:Output decimal integer
//printf("%d\n",-9/0);//error
//printf("%d\n", -9 / 2);
printf("%d\n",5%2);//1 5/2 = 2 ... 1
printf("%d\n", -5 % 2);//-1 -5/2 = -2 -1
printf("%d\n", 5 % -2);//1
printf("%d\n", -5 % -2);//-1
return 0;
}
*/
/*
int main()
{
int a = 0;
int b = 0;
int c = 0;
if (++a && b++ && ++c)//Short circuit phenomenon
{
printf("True \ n "");
}
else
{
printf("False \ n "");
}
printf("%d,%d,%d\n",a,b,c);
return 0;
}
*/
/*
int main()
{
int i = 10;
//int j = ++i;//Front++
//int j = --i;//Front--
// int j = i++;//Post++
int j = i--;
printf("%d,%d\n",i,j);
return 0;
}
*/
/*
int main()
{
// if (!10)
//if(5>3 && 5<4)
if(5>3 || 5<4)
{
printf("True \ n "");
}
else
{
printf("False \ n "");
}
return 0;
}
*/
/*
//True and false value
int main()
{
//if (1)//If
//if(2)//really
//if(0.5)//really
// if("Hello ") / / really
if(0)//false
{
printf("True \ n "");
}
else//otherwise
{
printf("False \ n "");
}
//printf("Welcome to study graph theory \ n "");
return 0;
}
*/