The author bought the worry free java simulation problem in a treasure. After reading it, the evaluation said that after brushing, the little partner who hopes to pass the exam can pass it once. This is the basic operation problem brushed by the author. A total of 49 questions were repeated by the author It's super simple to get rid of the partners who want to take the second level. They buy brush questions and do better by themselves. Knocking on the code is their own
1
import javax.swing.JOptionPane;
public class Java_1 {
public static void main( String args[] )
{
____________________________________(
null, "welcome \n you \n participate in \n Java \n examination!" );
System.exit( 0 ); // End program
}
}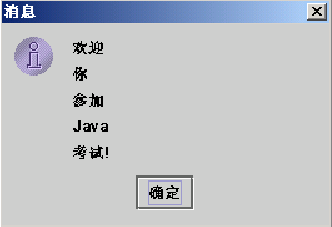
Because the jooptionpane class is imported into the question, it is a message box Showinputdialog (enter text in the pop-up box)
Showconfirmdialog (click OK to cancel in the pop-up box)
Showmessagedialog
Showoptiondialog
stay java: jooptionpane class message box summary_ liqiancao's column - CSDN blog_ Jooptionpane class This understanding can be opened separately two
import java.__________________.*;
import java.awt.Graphics;
public class Java_1 extends __________________ {
public void paint( Graphics g )
{
g.__________________( "You are welcome to attend Java Language test!", 25, 25 );
}
}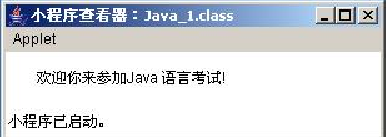
paint method in class needs to inherit applet Import the package import java.applet. *;
drawString means drawing
drawString (String str, int x, int y)x and y are variables 3 that hold the X and Y positions on the graphics window
import javax.________.JOptionPane;//No, look at the first question
public class Java_1{
public static void main( String args[] ){
String s1, s2, s3, s4, output;
s1 = new String( "hello" );
s2 = new String( "good bye" );
s3 = new String( "Happy Birthday" );
s4 = new String( "happy birthday" );
output = "s1 = " + s1 + "\ns2 = " + s2 +
"\ns3 = " + s3 + "\ns4 = " + s4 + "\n\n";
//Test string equality
if ( s1.equals( "hello" ) )
output = output + "______________________";
else
output = output + "s1 does not equals \"hello\"\n";
//Test equality with = =
if ( s1 == "hello" )
output += "s1 equals \"hello\"\n";
else
output += "s1 does not equal \"hello\"\n";
//Ignore character format test equality
if ( s3.equalsIgnoreCase( s4 ) )
output += "s3 equals s4\n";
else
output += "s3 does not equal s4\n";
//Content comparison
output +=
"\ns1.compareTo( s2 ) is " + s1.compareTo( s2 ) +
"\ns2.compareTo( s1 ) is " + s2.compareTo( s1 ) +
"\ns1.compareTo( s1 ) is " + s1.compareTo( s1 ) +
"\ns3.compareTo( s4 ) is " + s3.compareTo( s4 ) +
"\ns4.compareTo( s3 ) is " + s4.compareTo( s3 ) +
"\n\n";
//Test field matching with character format
if ( s3.regionMatches( 0, s4, 0, 5 ) )
output += "First 5 characters of s3 and s4 match\n";
else
output +=
"First 5 characters of s3 and s4 do not match\n";
//Ignore field matching in character format
if ( s3.regionMatches( true, 0, s4, 0, 5 ) )
output += "First 5 characters of s3 and s4 match";
else
output +=
"First 5 characters of s3 and s4 do not match";
JOptionPane._________________( null, output,
"Example of string construction method",
JOptionPane.INFORMATION_MESSAGE );//No, look at the link shared in question 1
System.exit( 0 );
}
}
The second question is to look at the picture and you will know the fifth line in the picture
The fourth question relates to the binary decimal system
Binary of 10 one thousand and ten Decimal 10
10 divided by 2 = 5 Yu 0 10 divided by 10 = 1, the remainder is 0
5 divided by 2 = 2 leaves 1 1 divided by 10 = 0 Yu 1
Divide 2 by 2 = 1 and leave 0
1 divided by 2 = 0, remaining 1 four
import java.____________.*;
public class Java_1{
public static void main(String[] args) ____________ Exception{
InputStreamReader ir;
BufferedReader in;
ir=new InputStreamReader(System.in);
in=new BufferedReader(ir);
System.out.println("The year entered is:");
String s=____________.readLine();//Read one line at a time until empty
int year=Integer.parseInt(_____________); //Integer.parseInt() string resolves to int type
if(year%4==0&&year%100!=0||year%400==0){
System.out.println(""+year+"Year is a leap year.");
}
else{
System.out.println(""+year+"Year is not a leap year.");
}
}
}The stream in the class is divided into byte stream and character stream (with buffer) import java.io. * provides classes that support stream based read and write operations
Byte stream InputStream OutStream Character stream Reader writer
The second empty Exception is an Exception class to use throws throw Third empty in Fourth empty s
Rectangular multiplication
Line A3 = a b c
d e f
g h i
Column B2 = A D
B E
C F
AB three rows and two columns = aA+bB+cC aD+bE+cF
dA+eB+fC dD+eE+fF
gA+hB+iC gD+hE+iF
Question 5 Find the sum of the inverse diagonals 21 17 13 9 5
public class Java_1 {
public static void ____(String args[]) {
int _____= {{1, 2, 3, 4, 5},
{6, 7, 8, 9, 10},
{11, 12, 13, 14, 15},
{16, 17, 18, 19, 20},
{21, 22, 23, 24, 25}};
int i, j,_____;
for (i = 0; i < 5; i++)
for (j = 0; j < 5; j++)
if (_______==4)
sum += arr[i][j];
System.out.println(sum);
}
}
The first one is empty The second null declares an array based on the penultimate row sum += arr[i][j]; the array name arr [] []
The third blank is to declare that the variable must be assigned. There is also a sum variable according to the penultimate line int i,j,sum=0;
Fourth empty Look at the declared array. Sum i for rows and j for columns
21 is index line 4 Index column 0
17 is index line 3 Index column 1 So i+j==4
Question 6
public class Java_1 {
//Find the maximum even number of the array and swap this number with the first element
public static void main(String[] args) {
int []a = {5,9,2,8,7};
int max = 0;
int k = 0,t ;
for(int i=0;i<5;i++){
if (a[i]______&& max < a[i]){
max = a[i];
______;
}
}
t = a[0];
a[0] = a[k];
a[k] = t;
for(int i=0;i<______;i++)
System.out.print(a[i] + " ");
}
}The first null cause is even, so a[i]%2==0
Because the penultimate number 6 means that the maximum even number is assigned to K in the first number a[k], and the value is assigned in the second space k=i
The third null means re output, so I < a.length
Question 7
public class Java_1{
public static void main( String args[] ){
double amount, principal = 1000.0, rate = .05;
DecimalFormat precisionTwo = new DecimalFormat( "0.00" );
JTextArea outputTextArea = new ____________________( 11, 20 );
outputTextArea.append( "year\t Total deposits\n" );
for ( int year = 1; year <= 10; year++ ) {
amount = principal * Math.pow( 1.0 + rate, year );
outputTextArea.append( year + "\t" +
precisionTwo.___________________( amount ) + "\n" );
}
JOptionPane._____________________(null, outputTextArea, "compound interest",JOptionPane.INFORMATION_MESSAGE );
System.exit( 0 );
}
}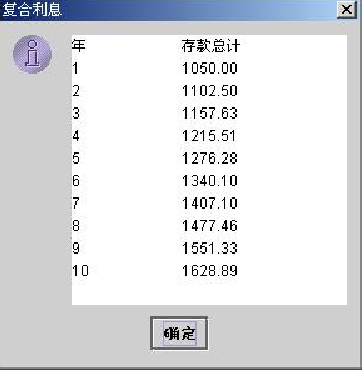 The first empty jtextarea (single line text box) outputtextarea = new JTextArea(11, 20);
The first empty jtextarea (single line text box) outputtextarea = new JTextArea(11, 20);
According to the figure, precisionTwo.format with two decimal places is obtained Is formatting The third space won't look at the first question
The format method is used to format the object into the string PS of the specified pattern. I don't understand this second question. Please tell me
Question 8
import java.lang.*;
import java.util.*;
//According to the prompt, enter the integer n > 0 to calculate the first n values of 6 + 66 + 666 +
public class Java_1 {
public static void main(String [] args){
System.out.print("Please enter n: ");
Scanner scan = new Scanner (_______);
String nstr = scan.next();
int n = Integer.______(nstr);
int b = 6;
long sum=0,item=b;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
sum += item;
item = item * 10 + ___;
}
System.out.print(n + "The sum of items is " + sum);
}
}First empty System.in fixed The second null converts nstr to int type, using parseInt() or valueOf()
The third blank, such as i=1 sum(6)=0+6 item66=item(6)*10+___b__
i=2 sum=sum(6)+item(66) item(666)=item(66)*10+___b_
i=3 sum=sum(66)+item(666) item(6666)=item(666)*10+__b__
Question 9
public class Java_1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i, j, k, t;
int[] m = {10, 21, 123, 5, 94};
//Select sorting method, sort by single digit from small to large, and then output
for (i = 0; i < m.length - 1; i++) {
k = ___;
for (j =____; j < m.length; j++) {
if ( ______ > _____ ) {
k = j;
}
}
if (k != i) {
t = m[i];
__________;
m[k] = t;
}
}
for (i = 0; i <______; i++) {
System.out.print(" " + m[i]);
}
System.out.println();
}
}The first null assigns i to k Second, j should be moved back one bit than i to select the sorting method
Third, m [k]% 10 > m [J]% 10 Because it is a single digit comparison, use% 10 to see the remainder The following value of k = J is assigned to K
fourth m[i]=m[k] element exchange The fifth cycle outputs m.length
Question 10
public class Java_1{
public static void main(String[] args){
_________ grades = {62,53,84,77,65,85,91,94,61,78,86,88};
int sum=0, avg = 0;
int stus=0;
int a=0,b=0,c=0,d=0,e=0;
for (int i=0; i<_______________; i++){
if (grades[i] <60 )
e++;
else if (grades[i] >=60 && grades[i]<=69)
d++;
else if (grades[i] >=70 && grades[i]<=79)
c++;
else if (grades[i] >=80 && grades[i]<=89)
b++;
else
a++;
_______+= grades[i];
}
stus = ________________;
_______ = sum/stus;
System.out.println(">=90: "+a+"; 80-89: " +b+"; 70-79: "
+ c +"; 60-69: " + d+"; <60: "+e);
System.out.println(stus+" students, and the average is : "+avg);
}
}
First int [] Second grades.length Third sum
The fourth stus is the number of students, that is, the length of the grades array Fifth avg means average score
Question 11
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class Java_1 {
Select sorting is used to sort the four integers entered by the keyboard from small to large
static int number=4;
static ________ t1 = new int[number];
public static void main(String[] args) {
Java_1 work=new Java_1();
work.__________();
}
void sort(){
System.out.println("Please enter 4 numbers:");
Scanner in_t1 = ___________ Scanner(System.in);
for(int i=0;i<number;i++){
t1[i]=in_t1.nextInt();
}
for (int i = 0; i < t1.length; i++) {
int pos = i;
for (int j = i + 1; j < t1.length; j++) {
if (t1[pos] ________ t1[j])
pos = j;
}
if (pos != i) {
t1[i] = t1[i] + t1[pos];
t1[pos] = t1[i] - t1[pos];
t1[i] = t1[i] - t1[pos];
}
}
for (int i = 0; i <= t1.length - 1; i++)
System.out.print(t1[i] + "\t");
}
}First int [] The second sort() method is used to sort the elements of the array Third new
Fourth > because it is sorted from small to large If the current is greater than the following Assign the following value to the current value
Question 12
public class Java_1{
public static void main(String[] args){
_________arrayOfInts = { 33, 88, 5, 458, 18, 107, 200, 8, 622, 127 };
int searchfor = 18;
Find the specified number in this shaping array. If found, stop and put the modified number in the position in the array for output
int i = 0;
_________ foundIt = false;
for ( ; i<arrayOfInts.length; i++){
if (arrayOfInts[i] == _________ ){
foundIt = true;
_________;
}
}
if (foundIt) {
System.out.println("Found " + searchfor + " at index " + i);
} else {
System.out.println(searchfor + "not in the array");
}
}
}First int [] The second false is that boolean is used to define boolean types
The third specified number is searchfor Fourth, after finding the number, the output prevents i from increasing and exiting the for loop break
The questions will be supplemented later
That's all for the time being. If you don't know how to do it, you can do it or ask me to do it as much as possible. Don't just look at it
These are some of the authors who don't know how to write them to enhance their memory The basic operation is relatively simple
Test two partners must buy a number, do it yourself