1. What is an exception
When an error is detected, the interpreter cannot continue to execute. Instead, some error prompts appear, which is the so-called "exception".
2. Exception presentation
# operator
# print(10/0)
# File exception
f = open('python.txt', 'r')
content = f.readlines()
print(content)
3. Exception capture
Basic grammar
try:
Possible error codes
except(capture):
Code to execute if an exception occurs
try... Exception is mainly used to catch code runtime except ions
case
try:
f = open('python.txt', 'r')
content = f.readline()
print(content, end='')
except:
f = open('python.txt', 'w', encoding='utf-8')
f.write('Exception occurred, execute except Code in statement')
f.close()
4. Catch specified exception
In the above case code, exception is equivalent to capturing all exceptions. No matter what error is encountered, the code encapsulated in exception will be automatically executed. However, in some cases, we capture exceptions to the targeted and execute the corresponding code.
Basic grammar
try:
Code that may encounter exceptions
except Exception type:
Code executed after the corresponding error is captured
① If the exception type of the code you are trying to execute is inconsistent with the exception type you are trying to catch, you cannot catch an exception.
② Generally, there is only one line of code to try to execute below try.
case
Caught FileNotFoundError exception
try:
f = open('python.txt', 'r')
except FileNotFoundError as e:
print(e)
5. Catch multiple exceptions at the same time
try:
print(name)
# print(10/0)
except (NameError, ZeroDivisionError) as e:
print(e)
6. Catch all unknown exceptions
No matter how many Exception types we define after Exception, unknown exceptions that cannot be captured may occur in practical applications. At this time, we consider using the Exception exception type to catch all unknown exceptions that may be encountered:
try:
Possible error codes
except Exception as e:
print(e)
Case: print an undefined variable and use the Exception class to catch it
try:
print(name)
except Exception as e:
print(e)
7. else statement in exception capture
else statement: it represents the code to be executed if there is no exception.
try:
print(1)
except Exception as e:
print(e)
else:
print('Ha ha, it's really Kaisen. I haven't encountered any exceptions')
case
try:
f = open('python.txt', 'r')
except Exception as e:
print(e)
else:
content = f.readlines()
print(content, end='')
f.close()
8. finally statement in exception capture
finally indicates the code to be executed regardless of whether there is an exception, such as closing the file and closing the database connection.
try:
f = open('python.txt', 'r')
except:
f = open('python.txt', 'w')
else:
print('Ha ha, it's really Kaisen. I haven't encountered any exceptions')
finally:
print('Close file')
f.close()
9. Abnormal comprehensive cases
☆ abnormal transmission
demand
- Try to open the python.txt file in read-only mode. If the file exists, read the file content. If the file does not exist, prompt the user.
- Read content requirements: try to read the content circularly. During the reading process, if it is detected that the user accidentally terminates the program, except ion will be captured
import time
try:
f = open('python.txt', 'r')
try:
while True:
content = f.readline()
if len(content) == 0:
break
time.sleep(3)
print(content, end='')
except:
# Ctrl + C (in the terminal, it represents the continuation of the terminated program)
print('python.txt Not all reads completed, interrupted...')
finally:
f.close()
except:
print('python.txt file cannot be found...')
☆ raise throws a custom exception
In Python, the syntax for throwing custom exceptions is raise exception class object.
demand
If the password length is insufficient, an exception will be reported (if the user enters the password, if the length is less than 6 digits, an error will be reported, that is, a user-defined exception will be thrown and caught).
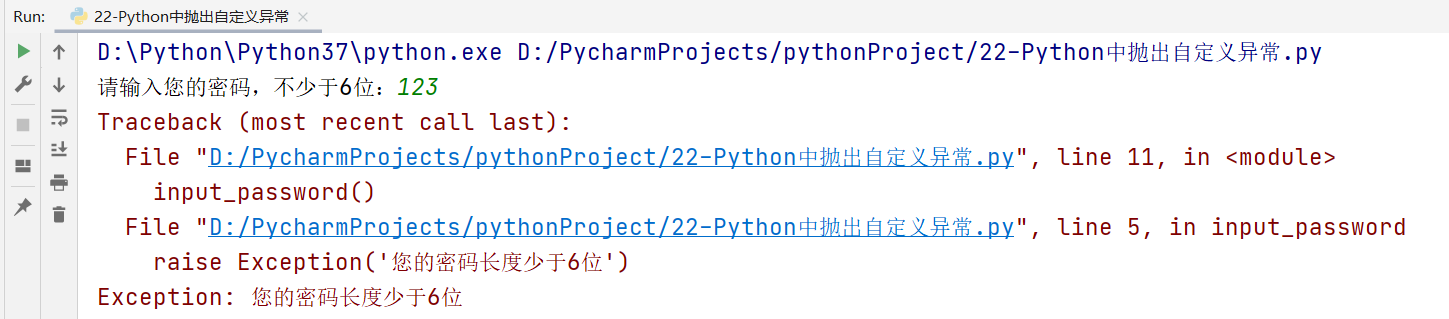
def input_password():
password = input('Please enter your password, no less than 6 digits:')
if len(password) < 6:
# Throw exception
raise Exception('Your password is less than 6 digits long')
return
# If the password length is normal, the password will be displayed directly
print(password)
input_password()
Object oriented throw custom exception:
class ShortInputError(Exception):
# Length represents the length of the input password, min_length represents the minimum length of ShortInputError
def __init__(self, length, min_length):
self.length = length
self.min_length = min_length
# Define a__ str__ Method to output string information
def __str__(self):
return f'The length of the password you entered is{self.length},Not less than{self.min_length}Characters'
try:
password = input('Please enter your password, no less than 6 digits:')
if len(password) < 6:
raise ShortInputError(len(password), 6)
except Exception as e:
print(e)
else:
print(f'The password is entered. Your password is:{password}')
10. Common exception types
| Exception name | describe |
|---|---|
| BaseException | Base class for all exceptions |
| SystemExit | Interpreter requests exit |
| KeyboardInterrupt | User interrupts execution (usually enter ^ C) |
| Exception | Base class for general errors |
| StopIteration | The iterator has no more values |
| GeneratorExit | An exception occurred in the generator to notify it to exit |
| SystemExit | Python interpreter requests exit |
| StandardError | Base class for all built-in standard exceptions |
| ArithmeticError | Base class for all numeric errors |
| FloatingPointError | Floating point calculation error |
| OverflowError | The numeric operation exceeds the maximum limit |
| ZeroDivisionError | Divide (or modulo) zero (all data types) |
| AssertionError | Assertion statement failed |
| AttributeError | Object does not have this property |
| EOFError | No built-in input, EOF flag reached |
| EnvironmentError | Base class for operating system error |
| IOError | Input / output operation failed |
| OSError | Operating system error |
| WindowsError | system call filed |
| ImportError | Failed to import module / object |
| KeyboardInterrupt | User interrupts execution (usually enter ^ C) |
| LookupError | Base class for invalid data query |
| IndexError | This index does not exist in the sequence |
| KeyError | This key is not in the map |
| MemoryError | Memory overflow error (not fatal for Python interpreter) |
| NameError | Object not declared / initialized (no properties) |
| UnboundLocalError | Accessing uninitialized local variables |
| ReferenceError | A weak reference attempts to access an object that has been garbage collected |
| RuntimeError | General runtime error |
| NotImplementedError | Methods not yet implemented |
| SyntaxError | Python syntax error |
| IndentationError | Indent error |
| TabError | Mixing tabs and spaces |
| SystemError | General interpreter system error |
| ValueError | Invalid parameter passed in |
| UnicodeError | Unicode related errors |
| UnicodeDecodeError | Error in Unicode decoding |
| UnicodeEncodeError | Error encoding Unicode |
| Warning | Warning base class |
| DeprecationWarning | Warning about deprecated features |
| FutureWarning | Warning about future semantic changes in constructs |
| OverflowWarning | Old warning about automatically promoting to long |
| PendingDeprecationWarning | Warning that features will be discarded |
| RuntimeWarning | Warning of suspicious runtime behavior |
| SyntaxWarning | Warning of suspicious syntax |
| UserWarning | Warnings generated by user code |
| FileNotFoundError | File not found error |