I always feel that express's middleware system is a very image of streamlined processing, just like the processing pipeline, each link completes its own work for different parts of the same product, and finally gets a finished product. Today we will implement a simple middleware queue.
I. API level
-
Initialization method
let middleware = new MiddleWare();
-
Method of Adding Middleware Functions
// Fn is added middleware.use(Fn);
-
Start middleware queues
middleware.start(req, res);
2. Definition of Core Classes
class MiddleWare{ constructor(){ this.queue = [];//Used to store middleware queues
} //Add Middleware
use(fn){ this.queue.push(fn);//Add custom middleware to the queue
} //Executing Middleware in sequence
start(req, res){ let i = 0;//Execution pointer
//Actuator
const next = (err)=>{ //If there is an error, hang the error message on response and exit directly.
if(err){
res.hasError = true;
res.data = err.toString(); return;
} //If there are no errors, check to see if it reaches the end of the queue, and if not, continue executing the next Middleware
if(i < this.queue.length){ this.queue[i++](req, res, next); /*Pass next directly into the currently executed function as a callback
At any stage of execution of the current execution function, the relevant information can be passed to the next middleware by calling the next method on its own initiative.*/
}else{ //If it's at the end of the team, it's over.
console.log('finish');
}
} //Start the first
next();
}
}3. Use the use method to add Middleware
//Add the first middleware/*
Here is a demonstration of a basic error capture approach when an error occurs in the middleware,Errors are caught and passed in next
*/middleware.use(function(req, res, next){ try{
req.addon1 = 'I add something';
}catch(err){
next(err);
}
next();
});//Add the second middleware.use(function(req, res, next){
res.addon2 = 'I add something more';
next();
});//Add the third middleware. use (function (req, res, next) {if (req. addon2) {delete req. addon2);
}
res.addon3 = 'I add something a lot';
next();
});IV. Classes of Definition of Consumption
"Consumption" is a recently learned word. It feels like X, so I'll install it here.~
let req = {};let res = {};let result = middleware.start(req,res);console.log(req, res);
V. View the results of the operation
Different results can be seen when errors occur and normal responses occur:
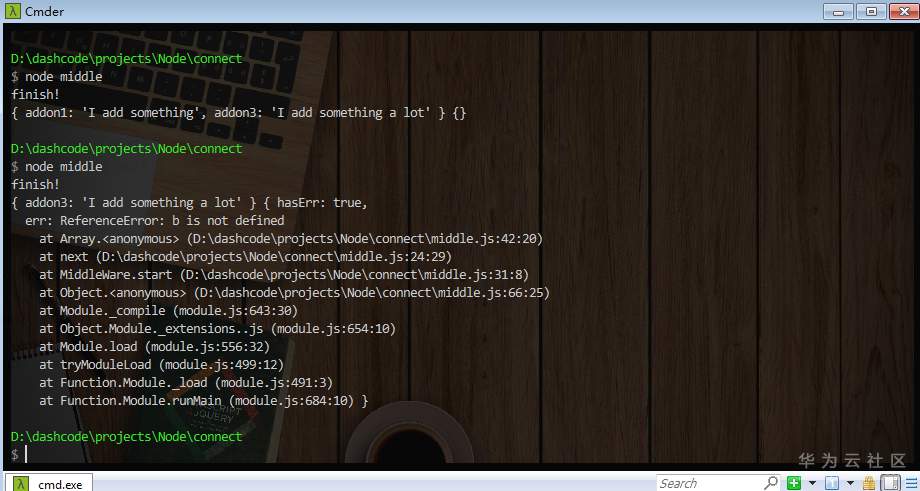
6. Running on the server side
It's too casual to start a web server with node~
const http = require('http');//The above stack of code http. createServer (function (req, res) {let result = {};
middleware.start(req, result);
res.end(JSON.stringify(result));
}).listen(9527);Take a look at the effect (custom messages can be sent to the front desk when accessing the server):
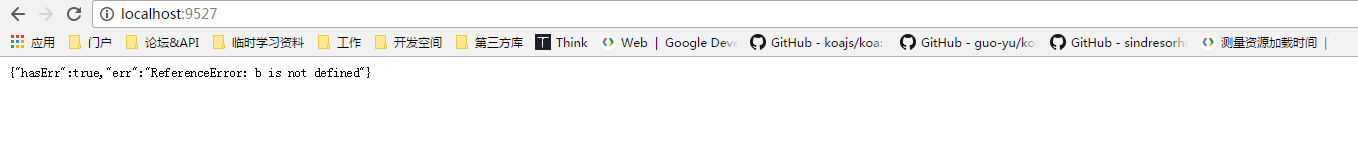
Author: Dashi is silent.