The cloud disk data volume is usually used for data storage when deploying stateful services in the Alibaba cloud ACK cluster. The cloud disk itself provides a backup (snapshot) recovery mechanism for data. However, how to integrate the underlying capabilities and K8S services and flexibly provide them to applications is a problem that the cloud original survival storage service needs to solve. K8S uses the following two features to achieve backup recovery capability:
The backup of cloud disk (snapshot function) is realized by VolumeSnapshot object;
Data recovery (snapshot recovery) is realized by the DataSource function in PVC;
Because VolumeSnapshot is in Alpha state in K8S 1.16, there is no default deployment snapshot function in the ACK cluster at present, so you need to install the plug-in manually to use it;
K8S snapshot Description:
In order to realize snapshot related functions in Kubernetes, the following three related resource types are defined through CRD:
Volume snapshot content: describes the snapshot instance of the storage back end, which is created and maintained by the system administrator without NameSpace; similar to PV concept;
VolumeSnapshot: declare a snapshot instance, created and maintained by the user, belonging to a specific NameSpace; similar to the PVC concept;
VolumeSnapshotClass: defines a snapshot class that describes the parameters and Controller used to create the snapshot; similar to the StorageClass concept;
Snapshot resource binding rules:
When using Snapshot objects, like pv and pvc, VolumeSnapshot and VolumeSnapshotContent need to be bound first;
Volumesnapshotif no static VolumeSnapshotContent can be bound, a dynamic VolumeSnapshotContent will be created;
The binding between VolumeSnapshotContent and VolumeSnapshot is one-to-one;
Deleting the VolumeSnapshotContent will delete the back-end snapshot at the same time;
1. Volume snapshot template
Here is a VolumeSnapshotClass definition template:
apiVersion: snapshot.storage.k8s.io/v1alpha1 kind: VolumeSnapshotClass metadata: name: default-snapclass snapshotter: disk-snapshot parameters: forceDelete: "false"
Among them:
Snapshot: defines the controller used by the VolumeSnapshot using this snapshot class;
forceDelete: indicates whether the snapshot can be deleted when the cloud disk references the snapshot (it is not allowed to delete by default, because when the cloud disk is created with the snapshot as the data source, there will be a delay in the creation process, and forced deletion may cause data loss);
Here is a VolumeSnapshot definition template:
apiVersion: snapshot.storage.k8s.io/v1alpha1 kind: VolumeSnapshot metadata: name: snapshot-test spec: snapshotClassName: default-snapclass source: name: pvc-disk kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
Among them:
Definition in VolumeSnapshot: data source (PVC name) and class name of snapshot creation;
Snapshot data source (PVC): it is defined to take a snapshot of the cloud disk volume, and find the disk id through PVC PV handler;
Snapshot classname: defines the snapshot class used for snapshot;
Create a snapshot instance of a cloud disk (associated with PVC) by creating a volume snapshot resource;
2. Recover data through snapshot
Creating a cloud disk from a cloud disk snapshot is the basic function provided by alicloud cloud disk. In the container service, you can specify which snapshot to use by defining DataSource in pvc. When you create a cloud disk dynamically, you can use the snapshot to create a cloud disk;
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim apiVersion: v1 metadata: name: disk-snapshot spec: accessModes: - ReadWriteOnce storageClassName: alicloud-disk-ssd dataSource: name: snapshot-test kind: VolumeSnapshot apiGroup: snapshot.storage.k8s.io resources: requests: storage: 20Gi
Among them:
storageClassName: to create a storage class of pv. The disk controller pointed to needs to support the DataSource feature;
dataSource: Specifies the snapshot resource, indicating that the snapshot data will be used when creating a cloud disk;
Plug in deployment:
Before deploying CSI snapshot, you need to create an ACK 1.16 cluster, and choose to use CSI plug-in when creating cluster; Cluster creation
Download the CSI snapshot template: https://github.com/kubernetes-sigs/alibaba-cloud-csi-driver/blob/master/deploy/disk/snapshot/csi-snapshotter.yaml
Deployment plug-ins:
$ kubectl apply -f csi-snapshotter.yaml
After deployment, the csi plug-ins in the cluster are as follows:
# kubectl get pod -nkube-system |grep csi csi-plugin-25xhh 9/9 Running 0 28h csi-plugin-5xjqh 9/9 Running 0 28h csi-plugin-9p4kd 9/9 Running 0 28h csi-plugin-tmlmg 9/9 Running 0 28h csi-plugin-tw57q 9/9 Running 0 28h csi-provisioner-577d66cbb7-zks24 8/8 Running 0 161m csi-provisioner-577d66cbb7-kja32 8/8 Running 0 161m csi-snapshotter-859bdf8888-mq4dk 2/2 Running 0 161m
use:
The following figure is an example flow chart, which is divided into three steps: 1, 2 and 3:
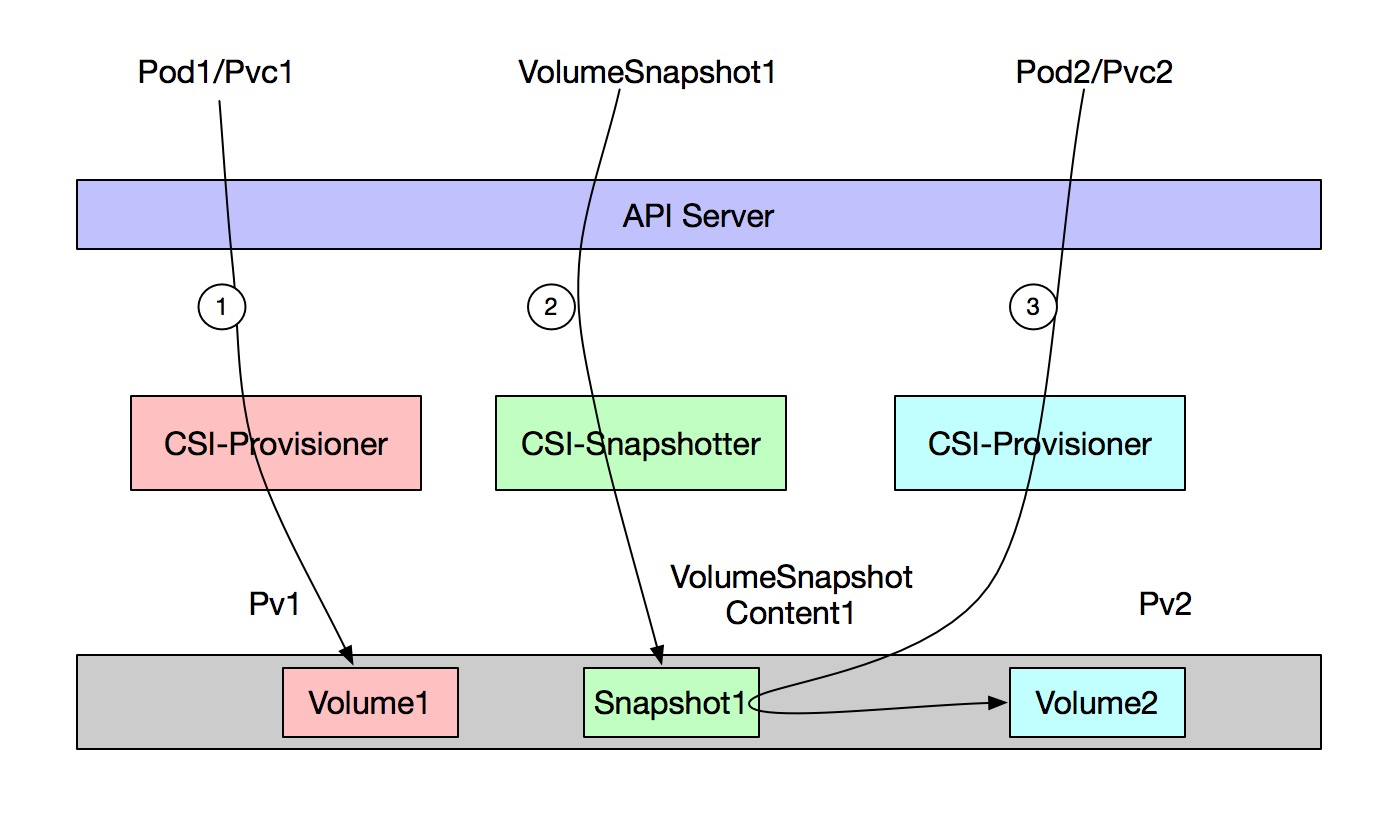
Step 1: create the original application, create a cloud disk volume and save the data;
Step 2: create a VolumeSnapshot, which will automatically create the VolumeSnapshotContent and the snapshot instance of the storage side;
Step 3: create a new application and configure PVC to reference the snapshot object created in step 2;
Through the above three steps:
Backup: data in Volume1 is backed up to Snapshot1;
Recovery: the data of snapshot 1 (data of Volume1) is recovered to Volume2;
To create a VolumeSnapshotClass snapshot class:
$ kubectl apply -f volumesnapshotcalss.yaml
apiVersion: snapshot.storage.k8s.io/v1alpha1 kind: VolumeSnapshotClass metadata: name: default-snapclass snapshotter: diskplugin.csi.alibabacloud.com parameters: forceDelete: "true"
# kubectl get VolumeSnapshotClass NAME AGE default-snapclass 4h40m
Step 1: create the original application and write the data:
$ kubectl apply -f sts.yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: StatefulSet metadata: name: web spec: selector: matchLabels: app: nginx serviceName: "nginx" replicas: 1 template: metadata: labels: app: nginx spec: containers: - name: nginx image: nginx volumeMounts: - name: disk-ssd mountPath: /data volumeClaimTemplates: - metadata: name: disk-ssd spec: accessModes: [ "ReadWriteOnce" ] storageClassName: "alicloud-disk-snap" resources: requests: storage: 20Gi
Write data to pod:
# kubectl exec -ti web-0 touch /data/test # kubectl exec -ti web-0 ls /data lost+found test
Step 2: create a VolumeSnapshot:
$ kubectl apply -f snapshot.yaml
apiVersion: snapshot.storage.k8s.io/v1alpha1 kind: VolumeSnapshot metadata: name: new-snapshot-test spec: snapshotClassName: default-snapclass source: name: disk-ssd-web-0 kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
Check the cluster status. The creation of VolumeSnapshot and VolumeSnapshotContent is completed. At the same time, check the ECS console to see that the creation of snapshot instances is completed
# kubectl get VolumeSnapshot NAME AGE new-snapshot-test 173m # kubectl get VolumeSnapshotContent NAME AGE snapcontent-b9bcccde-9ea4-41f0-967d-3647b8a5cc29 173m
Step 3: Data Recovery
$ kubectl apply -f sts-snapshot.yaml
apiVersion: v1 kind: PersistentVolumeClaim metadata: name: disk-snapshot-restore spec: accessModes: - ReadWriteOnce storageClassName: alicloud-disk-snap resources: requests: storage: 20Gi dataSource: name: new-snapshot-test kind: VolumeSnapshot apiGroup: snapshot.storage.k8s.io --- apiVersion: apps/v1beta2 kind: StatefulSet metadata: name: web-restore spec: selector: matchLabels: app: nginx serviceName: "nginx" template: metadata: labels: app: nginx spec: containers: - name: nginx image: nginx ports: - containerPort: 80 name: web volumeMounts: - name: pvc-disk mountPath: /data volumes: - name: pvc-disk persistentVolumeClaim: claimName: disk-snapshot-restore
In the PVC definition, specify dataSource as VolumeSnapshot type, and select VolumeSnapshot with the name of new snapshot test created in step 2.
View the container data and verify that the recovery was successful:
# kubectl exec -ti web-restore-0 ls /data lost+found test
It can be seen that data recovery is realized.
This scheme only gives a scenario of creating a snapshot and recovering. Later, we will provide a scheme of creating a timed snapshot.