Introduction to AWT
AWT Definition
AWT: A GUI class library, the Abstract Window Toolkit
GUI applications created with AWT share the same interface style as the platform on which they run
Inheritance System of AWT
Componet:
Represents an object that can be displayed pictorially and interact with the user, such as Button for a button, TextField for a text box, etc.
MenuComponent:
Menu components that represent the graphical interface, including subclasses such as MenuBar (menu bar), MenuItem (menu item)
Container:
Is a special kind of Componet that represents a container that can hold ordinary COMponents
Container's Inheritance System
AWT usage
Use of Window,Panel,ScrollPane
- Window is a stand-alone top-level window that manages its internal component layout by default using BorderLayout
- Panel can accommodate other components but cannot exist independently. It must be used inside other containers, and FlowLayout is used by default to manage its internal component layout
- ScrollPane is a container with scrollbars and cannot exist independently. BorderLayout is used by default to manage its internal component layout
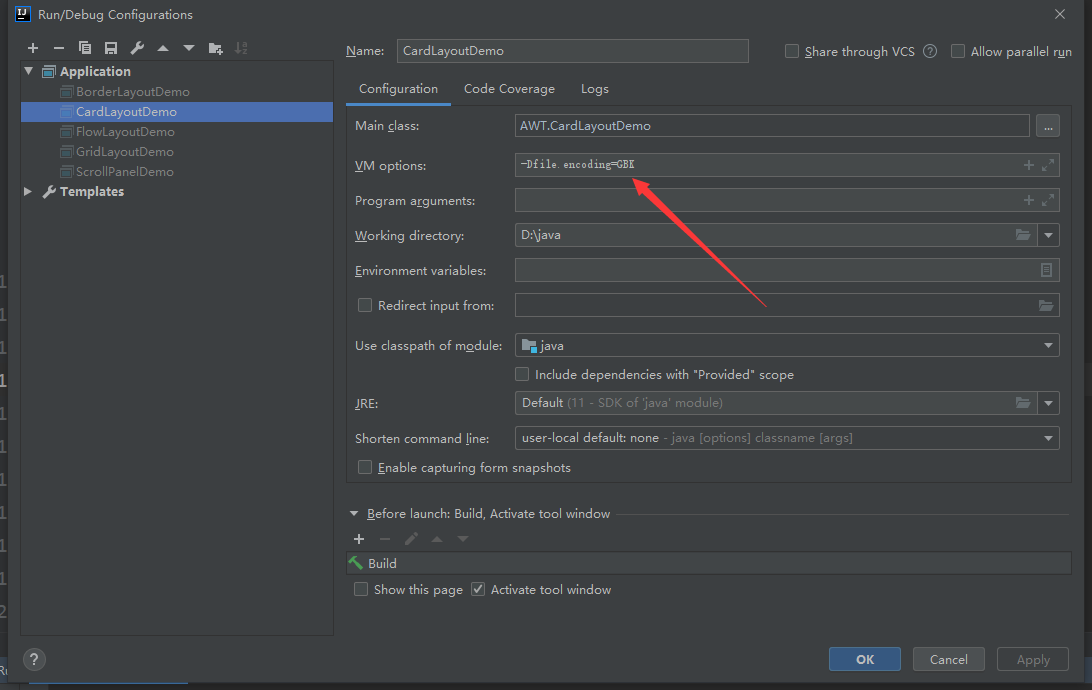
Possible Chinese encoding problems:
- -Dfile.encoding=GBK
Window:
public class WindowDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Frame frame = new Frame("window");
frame.setLocation(100, 100); //Set Location
frame.setSize(500, 300); //Set window size
frame.setVisible(true); // Set Visibility
}
}

Panel:
public class PanelDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Panel object must be dependent on Window
//Create a window object
Frame frame = new Frame("panel");
//Create Panel Object
Panel panel = new Panel();
panel.add(new TextField("textField")); // Add Text Box
panel.add(new Button("button")); // add button
//panel added to window
frame.add(panel);
//Set window position and size
frame.setBounds(100, 100, 500, 300);
//Set window s visibility
frame.setVisible(true);
}
}

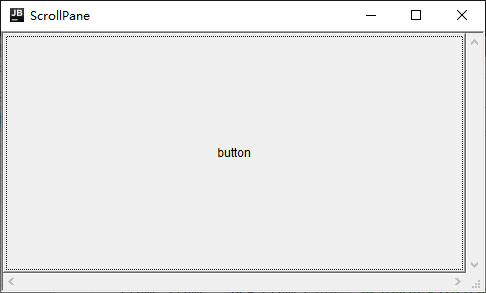
ScrollPane:
public class ScrollPanelDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Create a window object
Frame frame = new Frame("ScrollPane");
//Create Panel Object
ScrollPane scrollPane = new ScrollPane(ScrollPane.SCROLLBARS_ALWAYS); //Setting the scrollbar to always display
scrollPane.add(new TextField("textField"));
scrollPane.add(new Button("button"));
//panel added to window
frame.add(scrollPane);
//Set window position and size
frame.setBounds(100, 100, 500, 300);
//Set window s visibility
frame.setVisible(true);
}
}
Layout Manager
- LayoutMananger Layout Manager can automatically resize components based on the running platform
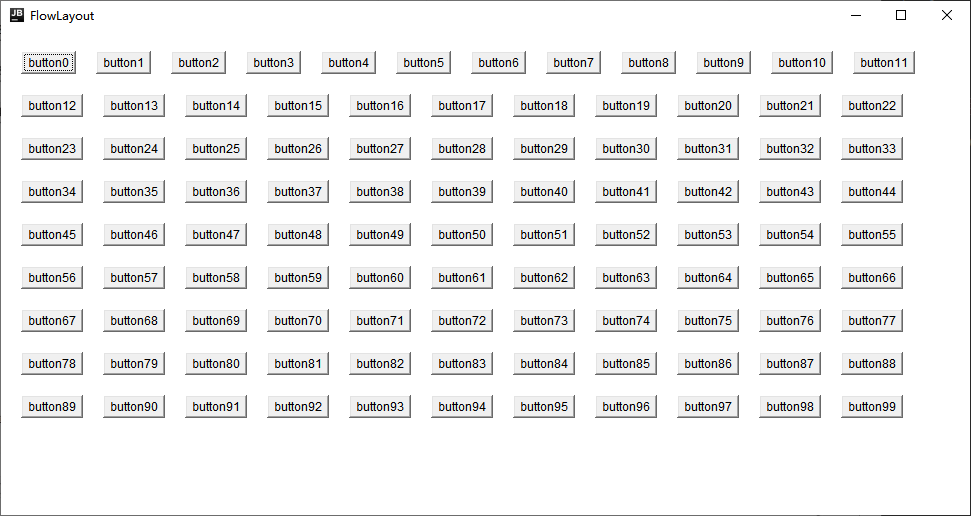
FlowLayout
- Arrange all components from left to right, and when boundaries are encountered, fold back to the next line to start over
public class FlowLayoutDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Frame frame = new Frame("FlowLayout");
// Set up Layout Manager with left alignment, horizontal and vertical spacing of 20
frame.setLayout(new FlowLayout(FlowLayout.LEFT, 20, 20));
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
frame.add(new Button("button" + i));
}
//Set optimal size
frame.pack();
frame.setVisible(true);
}
}
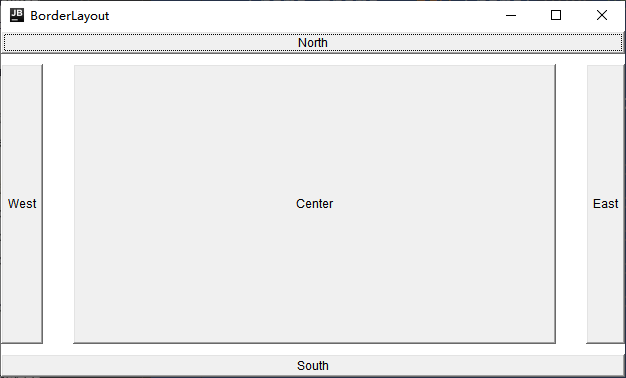
BorderLayout
- Containers are divided into five zones: EAST,SOUTH,WEST,NORTH,CENTER. Common components can be placed in any of these five zones
- When changing the container size using BorderLayout, the NORTH,SOUTH, and CENTER regions are adjusted horizontally, while the EAST,WEST, and CENTER regions are adjusted vertically
- When adding components, you need to specify which zone to add, and if you don't specify which zone to add, add them by default to the middle zone
- If more than one component is added to the same zone, the component that is put later overwrites the component that was put first
public class BorderLayoutDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Frame frame = new Frame("BorderLayout");
// Horizontal spacing 30, Vertical spacing 10
frame.setLayout(new BorderLayout(30, 10));
frame.add(new Button("North"), BorderLayout.NORTH);
frame.add(new Button("South"), BorderLayout.SOUTH);
frame.add(new Button("East"), BorderLayout.EAST);
frame.add(new Button("West"), BorderLayout.WEST);
frame.add(new Button("Center"), BorderLayout.CENTER);
frame.pack();
frame.setVisible(true);
}
}
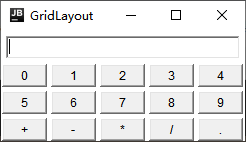
GridLayout
- Split containers into grids with vertical and horizontal lines, each of which occupies the same size of area
- When adding components, add them to each grid by default from left to right, top to bottom
public class GridLayoutDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Frame frame = new Frame("GridLayout");
// Add Input Text Box
Panel p_text = new Panel();
p_text.add(new TextField(30));
frame.add(p_text, BorderLayout.NORTH);
//Add Array
Panel p_num = new Panel();
// 3 rows 5 columns
p_num.setLayout(new GridLayout(3, 5, 4, 4));
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
p_num.add(new Button(String.valueOf(i)));
}
p_num.add(new Button("+"));
p_num.add(new Button("-"));
p_num.add(new Button("*"));
p_num.add(new Button("/"));
p_num.add(new Button("."));
frame.add(p_num);
frame.pack();
frame.setVisible(true);
}
}
GridBagLayout
- Similar to GridLayout, but the layout can occupy multiple grids
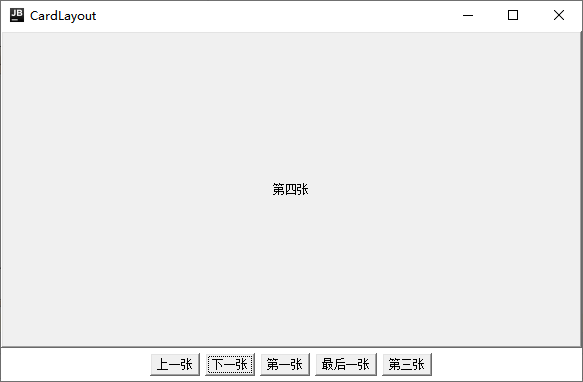
CardLayout
- Consider all components added to the container as a stack of cards, with only the top component visible at a time.
public class CardLayoutDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Frame frame = new Frame("CardLayout");
CardLayout cardLayout = new CardLayout();
//Middle area panel
Panel p1 = new Panel();
p1.setLayout(cardLayout);
String[] names = {"First","Second","Third","Fourth","Fifth"};
for (int i = 0; i < names.length; i++) {
p1.add(names[i], new Button(names[i]));
}
frame.add(p1);
//Five button areas
Panel p2 = new Panel();
Button b1 = new Button("Previous");
Button b2 = new Button("Next");
Button b3 = new Button("First");
Button b4 = new Button("Last");
Button b5 = new Button("Third");
//Create an event listener to listen for button clicks
ActionListener listener = new ActionListener() {
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent actionEvent) {
// Get the text on the button
String actionCommend = actionEvent.getActionCommand();
switch (actionCommend) {
case "Previous":
cardLayout.previous(p1);
break;
case "Next":
cardLayout.next(p1);
break;
case "First":
cardLayout.first(p1);
break;
case "Last":
cardLayout.last(p1);
break;
case "Third":
cardLayout.show(p1, "Third");
break;
}
}
};
//Bind event listeners and buttons together
b1.addActionListener(listener);
b2.addActionListener(listener);
b3.addActionListener(listener);
b4.addActionListener(listener);
b5.addActionListener(listener);
p2.add(b1);
p2.add(b2);
p2.add(b3);
p2.add(b4);
p2.add(b5);
frame.add(p2, BorderLayout.SOUTH);
frame.pack();
frame.setVisible(true);
}
}
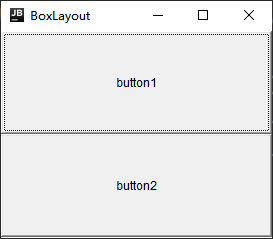
BoxLayout
- GUI components can be accessed vertically and horizontally
public class BoxLayoutDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Frame frame = new Frame("BoxLayout");
//Create a BoxLayout object that holds components vertically
BoxLayout boxLayout = new BoxLayout(frame, BoxLayout.Y_AXIS);
frame.setLayout(boxLayout);
frame.add(new Button("button1"));
frame.add(new Button("button2"));
frame.pack();
frame.setVisible(true);
}
}
Box Container
- The container's default layout manager is BoxLayout. In most cases, use the Box container to hold multiple GUI components, then add the Box container as a component to other containers to form the overall window layout.
public class BoxDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Frame frame = new Frame("Box");
//Create Box Containers for Horizontally Arranged Components
Box hBox = Box.createHorizontalBox();
hBox.add(new Button("h_button1"));
hBox.add(Box.createHorizontalGlue()); // Stretch in both directions
hBox.add(new Button("h_button2"));
hBox.add(Box.createHorizontalStrut(30)); //Fixed split length
hBox.add(new Button("h_button3"));
//Create Box Containers for Vertically Arranged Components
Box vBox = Box.createVerticalBox();
vBox.add(new Button("v_button1"));
vBox.add(Box.createVerticalGlue());
vBox.add(new Button("v_button2"));
vBox.add(Box.createVerticalStrut(30));
vBox.add(new Button("v_button3"));
//Add to frame
frame.add(hBox, BorderLayout.NORTH);
frame.add(vBox);
frame.pack();
frame.setVisible(true);
}
}

Basic components in AWT
| Component Name | function |
|---|---|
| Button | Button |
| Canvas | Canvas for Drawing |
| Checkbox | Checkbox components (also used when cell box components) |
| CheckboxGroup | Used to group multiple Checkbox components into a group, where only one Checkbox component is selected, that is, all become radio box components |
| Choice | Select |
| Frame | Window, through which windows are created in GUI programs |
| Label | Label class for placing prompt text |
| List | List box component that adds multiple entries |
| Panel | Basic container classes cannot exist separately and must be placed in other containers |
| Scrollbar | Slider bar component. If you need the user to enter a value that is within a range, you can use the slider component, such as the slider used to set the three values of RGB in the color palette. When you create a slider bar, you must specify its direction, initial value, size of the slider, minimum value, and maximum value. |
| ScrollPane | Container assembly with horizontal and vertical sliders |
| TextArea | Multiline Text Fields |
| TextField | JTextField |
public class BasicComponentDemo {
Frame frame = new Frame("Basic Components");
//Multiline Text Area
TextArea ta = new TextArea(5, 20);
//Select
Choice colorChooser = new Choice();
//Selection box
CheckboxGroup cbg = new CheckboxGroup();
Checkbox male = new Checkbox("male", cbg, true);
Checkbox female = new Checkbox("female", cbg, false);
//Selection box
Checkbox isMarried = new Checkbox("Were you married?");
//Single Line Text Area
TextField tf = new TextField(50);
Button ok = new Button("confirm");
//list box
List colorList = new List(6, true);
public void init(){
//Assembly Bottom
Box bBox = Box.createHorizontalBox();
bBox.add(tf);
bBox.add(ok);
frame.add(bBox, BorderLayout.SOUTH);
//Assembly selection section
colorChooser.add("gules");
colorChooser.add("blue");
colorChooser.add("green");
Box cBox = Box.createHorizontalBox();
cBox.add(colorChooser);
cBox.add(male);
cBox.add(female);
cBox.add(isMarried);
frame.add(cBox);
//Assembling text fields and selection sections
Box topLeft = Box.createVerticalBox();
topLeft.add(ta);
topLeft.add(cBox);
frame.add(topLeft);
//Assemble top left and list box
Box top = Box.createHorizontalBox();
colorList.add("gules");
colorList.add("green");
colorList.add("blue");
top.add(topLeft);
top.add(colorList);
frame.add(top);
frame.pack();
frame.setVisible(true);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
BasicComponentDemo bc = new BasicComponentDemo();
bc.init();
}
}
