Reference
AST and Front End Engineering
AST abstract grammar tree - the most basic key knowledge of javascript, 99% of people don't understand it at all
13 examples Quick Start JS abstract syntax tree
AST Explorer
concept
JavaScript parsing:
- Lexical Analysis : convert the JavaScript code (char string) character stream (char stream) to token stream (token stream) according to the ECMAScript standard.
- Syntactic Analysis Converting the lexical unit flow into a grammatical structure tree consisting of elements nested step by step, AST
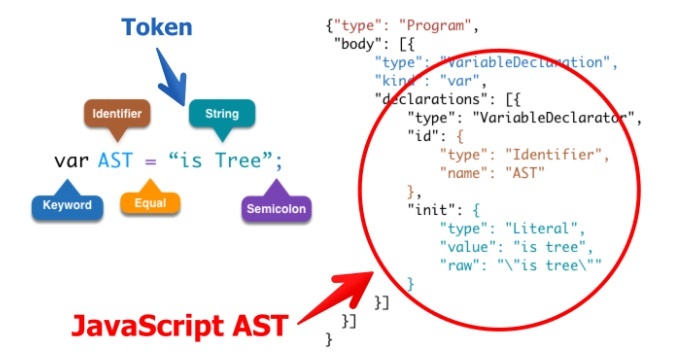
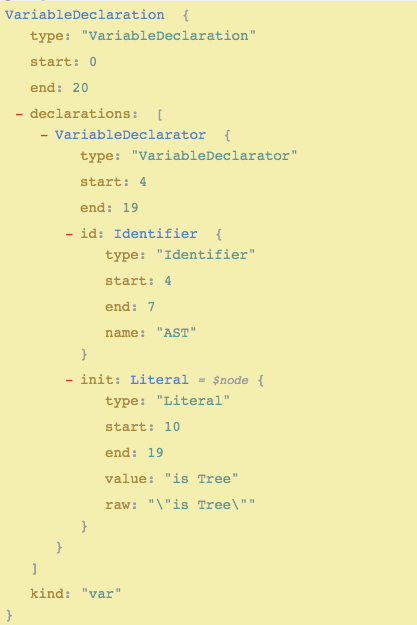
Demo
Code:
var AST = "is Tree";
Lexical analysis = symbol flow
Keyword: var
Identifier: AST
Punctuator: =
String: "is Tree"
Punctuator: ;
Grammar Analysis=> AST
AST Tool: Recast
Parser (recast.parse): code => AST
Code Case 1
const recast = require("recast"); const code = ` function add(a, b) { return a + // What strange things have mixed in? b } ` const ast = recast.parse(code); const add = ast.program.body[0] console.log(add)
Output Of Case 1
{ "type": "FunctionDeclaration", "id": { "type": "Identifier", "name": "add" }, "params": [ { "type": "Identifier", "name": "a" }, { "type": "Identifier", "name": "b" } ], "body": { "type": "BlockStatement", "body": [ { "type": "ReturnStatement", "argument": { "type": "BinaryExpression", "operator": "+", "left": { "type": "Identifier", "name": "a" }, "right": { "type": "Identifier", "name": "b", "comments": [ { "type": "Line", "value": " What strange things have mixed in?", "loc": {}, "leading": true, "trailing": false } ] } } } ] }, "generator": false, "expression": false, "async": false }
recast.types.builders: AST => code
Code Case 2
After Code Case 1, add the following code to reassemble the ast:
- Change the add method to the arrow function
- Increasing Square Sum Method for Calculating Squares
// Three kinds of "mould" are introduced: variable declaration, variable symbol and function declaration. const { variableDeclaration, variableDeclarator, identifier: id, arrowFunctionExpression, binaryExpression, blockStatement, returnStatement } = recast.types.builders // Place the prepared components into the die and assemble them back into the original ast object. // Change the add method to the arrow function ast.program.body[0] = variableDeclaration("const", [ variableDeclarator(add.id, arrowFunctionExpression( add.params, binaryExpression('+', ...add.params) )) ]); // New Square Sum Method for Calculating Squares ast.program.body.push(variableDeclaration('var', [ variableDeclarator(id('squareSum'), arrowFunctionExpression( [id('a'), id('b')], blockStatement([ variableDeclaration('let', [ variableDeclarator(id('c'), binaryExpression('*', id('a'), id('a'))), variableDeclarator(id('d'), binaryExpression('*', id('b'), id('b')))]), returnStatement(binaryExpression('+', id('c'), id('d'))) ]) )) ])) //Return AST objects back to readable code const output = recast.print(ast).code; console.log(output)
Output Of Case 2
const add = (a, b) => a + b; var squareSum = (a, b) => { let c = a * a, d = b * b; return c + d; };
Tree node traversal (recast.types.visit)
recast.visit(ast, { visitExpressionStatement: function(path) { const { node} = path; }, visitBlockStatement(path) { // do something here } });
Application scenario
- Interpreter and compiler
- Static code analysis (extracting duplicate code and judging code similarity)
- Code conversion

- Code formatting