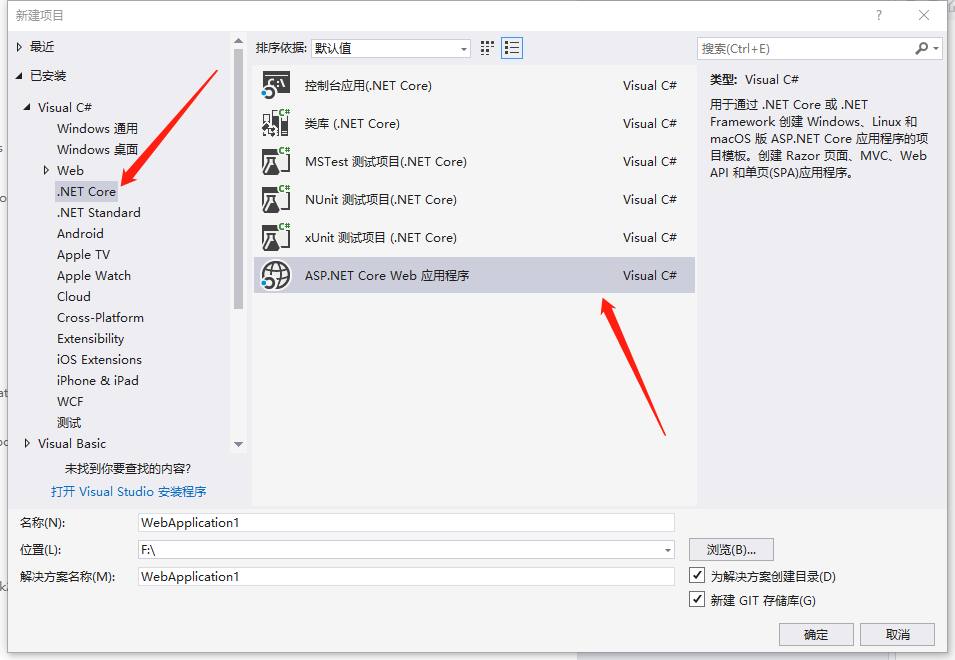
1 New ASP.NET Core MVC Application
1.1 New MVC Application
Open Visual Studio 2017, create a new ASP.NET Web Application, select MVC (Model View Controller).

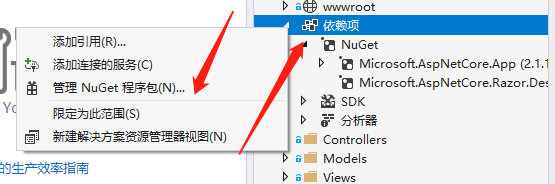
1.2 Introducing NuGet Package
Need to be introduced
- microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore
- Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Sqlite
Introducing tutorials
click
Dependencies
* Right-click
* Manage NuGet Packages
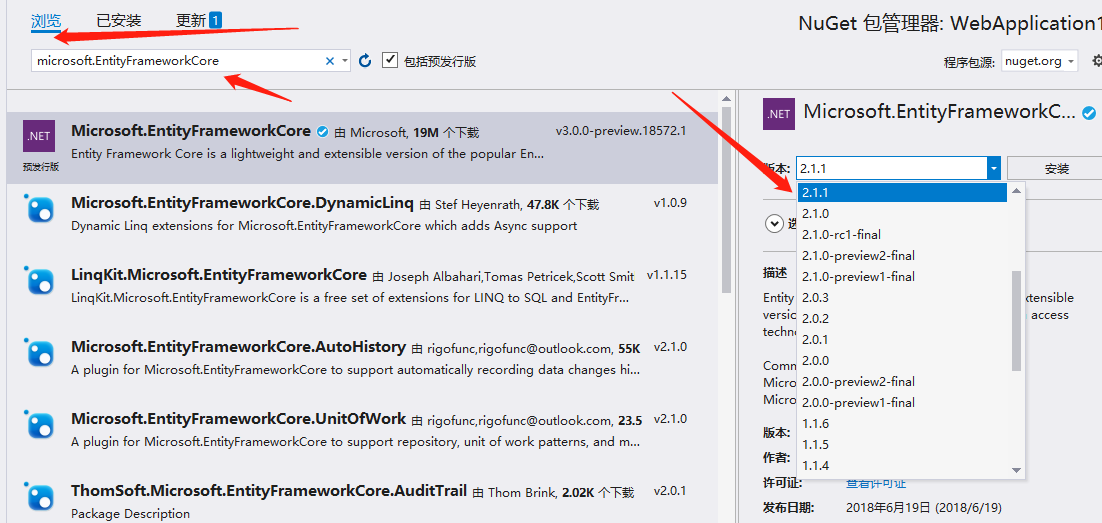
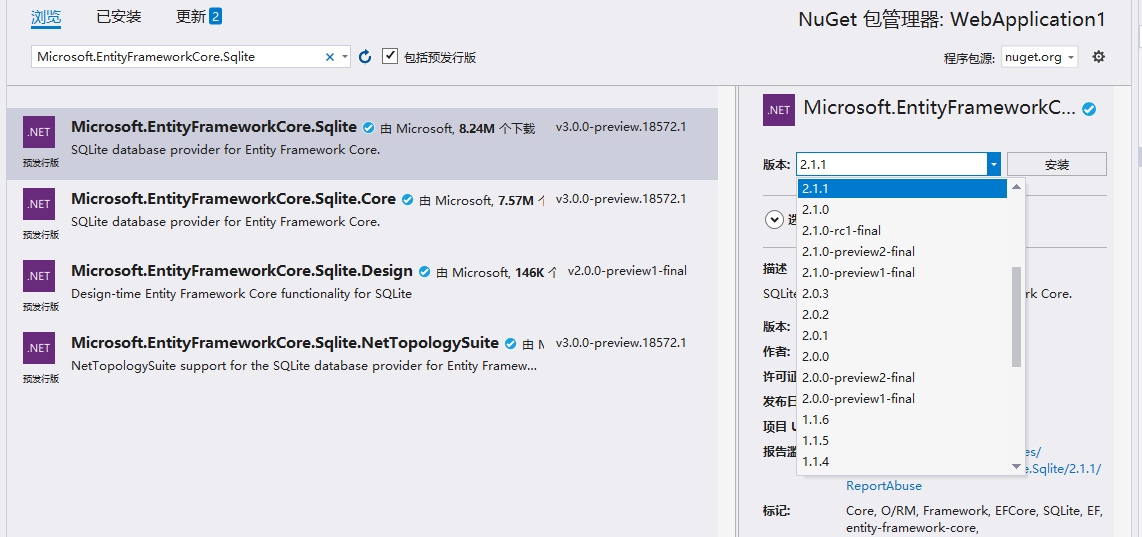
Rotate in and install microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore , Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Sqlite, attached below
Note:
Version please choose with yourself ASP.NET Core Version close.
Author Version ASP.NET Core Version is 2.1 , The NuGet package version selected is 2.11.
If your.Net Core is up-to-date, NuGet can also choose the latest.
If you choose a version and find an error, you can enter NuGet again Remove the installation.
Do not update when an update prompt appears.
2 New Model and Context
This step establishes the model and context from which the database and database tables will be generated!
A context class and a model class need to be created to include the model class in the context class, and the model class included in the context class will generate the corresponding database table.
The code below does not need to be operated on by itself, just look at it. (notice the red bold part)
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
namespace WebApplication1.Models
{
public class SqlContext:DbContext
{
public SqlContext(DbContextOptions<SqlContext> Options):base(Options)
{
}
public DbSet<A> A { get; set; } //Generating Data Table A in a Database
}
public class A
{
public int ID { get; set; }
}
public class B
{
public int ID { get; set; }
}
}
The code above has three classes,
- among The SqlContext class is a context class.
- Classes A and B are model classes.
- However, only A will generate database tables, while B will not.
- A and B are model classes because they can be used to generate database tables, so A can also be called entity classes because B does not have DbSet<B> , So B is called a model class, not an entity class.
- Class A produces a table in a real database that corresponds, so it is an Entity Class.
- Class B does not have a corresponding existence, it is just a model, there is no actual object, so it is just called "model class".
2.1 New Model Class
The code above places the model class and the context class in the same file SqlContext.cs, which makes them less readable.
Because a model class represents a data table, a context class is equivalent to a configuration class, a database has dozens of tables, and each table has several columns, this can make the file content too complex.
We can reduce the coupling, there is only one class per class file, and each class represents a table. If you want to create several tables, you can write several classes.
Actual operation
In the Models folder
- Create a new class Users.cs
- Write code directly in a class
public int ID { get; set; } //Primary key
public string Name { get; set; } //User Name
public int Age { get; set; } //User Age
public int Number { get; set; } //User mobile number
Figure

Note:
A Model Class Corresponds to a table
An attribute of the model class Corresponds to a column.
Model classes should only have attributes, not methods, and so on.
If you want more than one table, you can create a new class and add it to the context class.
2.2 New Context
The model class is already established above and will become the data table itself. However, they cannot directly map to a data table, requiring context to map model classes to a data table, otherwise they are just ordinary classes.
stay Models Catalog New Class MyContext.cs
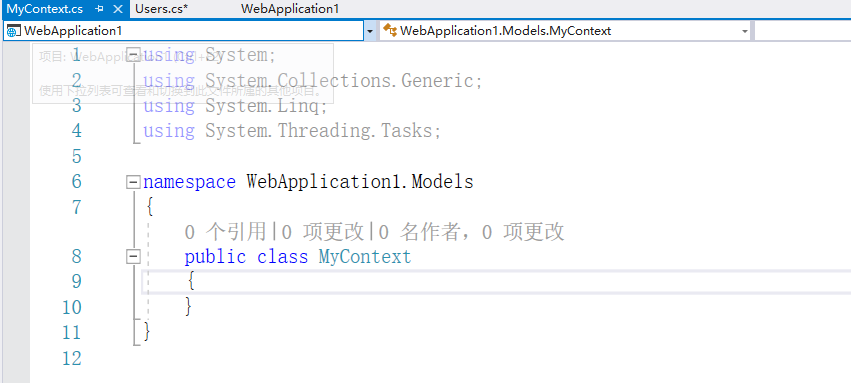
Introducing in the head EF( EntityFrameworkCore)
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
Rewrite MyContext class
Step 1
public class MyContext
Change to
public class MyContext:DbContext //Indicates that the class is a context class, the database name is My, why the class name is, why the database name is
Step 2
Write a constructor in the MyContext class
public MyContext(DbContextOptions<MyContext> options) : base(options)
{
}
This constructor involves dependent injection, which is not going to be repeated here, just knowing that it can configure settings.
The constructor content here is empty because there is nothing to configure for now.
Step 3
Add code below the constructor to map the model class.
public DbSet<Users> Uaa { get; set; }
//Dbset maps to a table
//Users in Dbset<Users>is the model class used
//Name of the Uaa Users class generated in the database
Note:
The code above indicates that a table named Uaa is generated in the database based on the model class Users.
A context corresponds to a database, the context class MyContext, the part before the Context will become the database name. For example, asdwadaaContext, the database asdwadaa will be generated.
A Model Class Corresponds to a table
The complete code is as follows
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
namespace WebApplication1.Models
{
public class MyContext:DbContext
{
public MyContext(DbContextOptions<MyContext> options) : base(options)
{
}
public DbSet<Users> Uaa { get; set; }
}
}
Generated Effect Graph Preview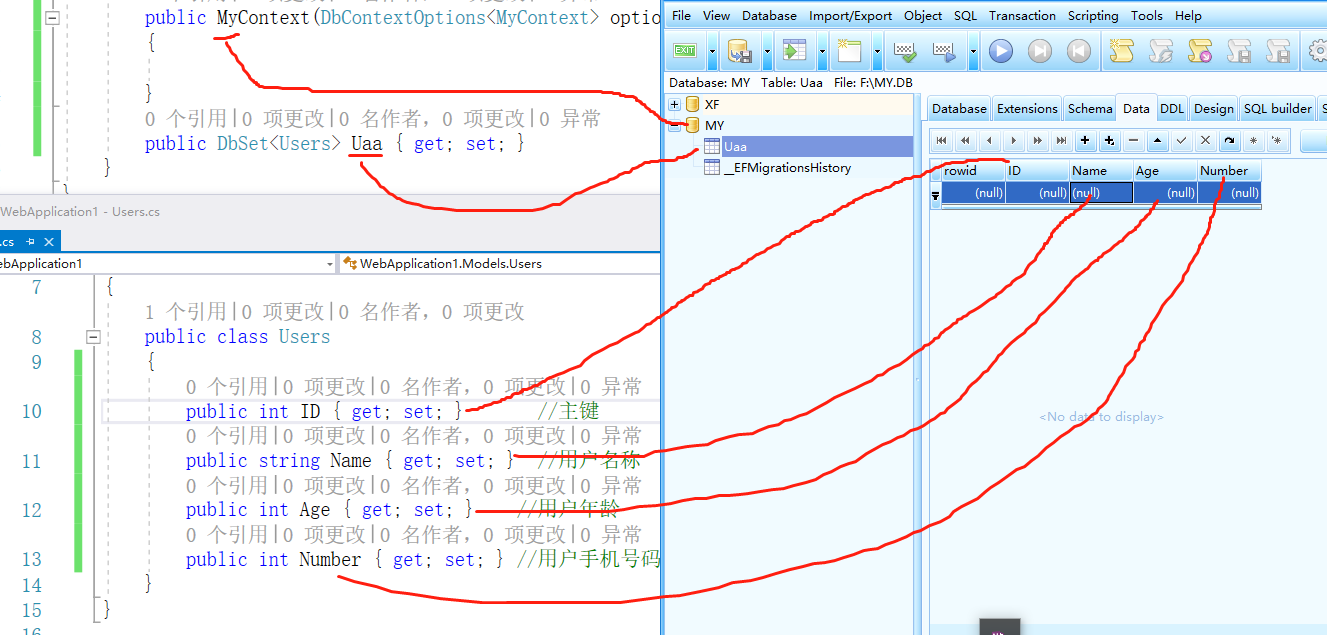
3 Configure Services
In order for the application to generate and use the database, you need to Startup.cs Add Code
Introduce three libraries in the header
using WebApplication1.Models; //Possibly named differently using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore; using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Sqlite;
Then inject the service into the application in the following ways
(Explain later, understand now, don't add)
1 Direct Writing String
stay Startup.cs Add Code
string connecttext = "Filename=F:\\MY.DB";
services.AddDbContext<MyContext>(options=>options.UseSqlite(connecttext));
2 Use JSON
stay Add content to appsettings.json file (red part)
{
"Logging": {
"LogLevel": {
"Default": "Warning"
}
},
"AllowedHosts": "*",
"ConnectionStrings": {
"MyContext": "Filename=F:\\MY.DB"
}
}
Then add code in Startup.cs
string connecttext = Configuration.GetConnectionString("MyContext");
services.AddDbContext<MyContext>(options=>options.UseSqlite(connecttext));
Note:
In both ways, the connecttext variable is used to get the database connection string, which has no special meaning but to increase readability.
SQLite's connection string, just write "Filename=[absolute path]"
Services.AddDbContext<MyContext> (options=>options.UseSqlite("connection string"));
Express
Inject DbContext (Database Context Service) into the application, and the type of context injected is MyContext>
(options=>options.UseSqlite ("connection string")
Is a lambda expression, indicating the use of sqlite databases, and the parameter is a connection string. Lambda expressions are C#basics, if not, remember first and look for data later.
To do the actual work
Please use Copy Above Mode 1 Code, and then Startup.cs Class-- ConfigureServices Add in Method
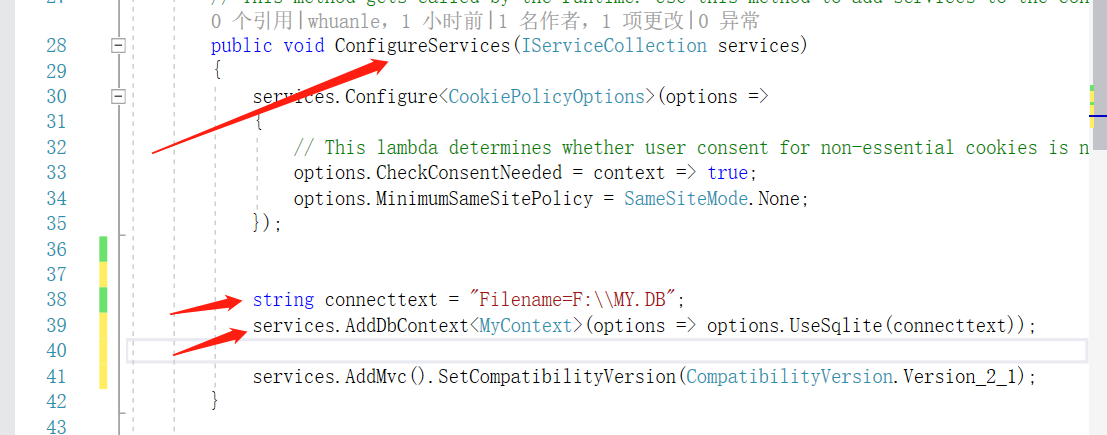
Copy the following code overrides directly ConfigureServerices
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
services.Configure<CookiePolicyOptions>(options =>
{
// This lambda determines whether user consent for non-essential cookies is needed for a given request.
options.CheckConsentNeeded = context => true;
options.MinimumSameSitePolicy = SameSiteMode.None;
});
string connecttext = "Filename=F:\\MY.DB";
services.AddDbContext<MyContext>(options => options.UseSqlite(connecttext));
services.AddMvc().SetCompatibilityVersion(CompatibilityVersion.Version_2_1);
}
Note:
SQLite database file, can be without suffix name, but suffix name will make it easy for others to recognize that this is a database file, suffix name is unlimited, can be. DB,.SQLite, SQLite3, and so on.
4 Generate database
click
- Tools
- NuGet Package Manager
Package Manager Console

input
Add-Migration InitialCreate
Note: If this occurs during installation Add-Migration: The Add-Migration item cannot be recognized as the name of a cmdlet, function, script file, or runnable program. Check the spelling of the name, and if a path is included, make sure the path is correct, and then try again.
Run the code in the Package Management Console
Install-Package Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Tools
Install the corresponding version
After waiting, enter
Update-Database
Figure

Then you will find Solution Manager, much more Migrations directory and some files, F:\directory also has one more MY.DB file
5 Use tools to manage SQLite files
After generating the database file, you will find that it cannot be opened directly, even VS2017.
You can use tools at this point SQLite Expert Professional , To manage the SQLIte database.
Download Address http://xzc.197746.com/SQLiteExpert5.zip
Software Introduction https://www.cr173.com/soft/36343.html
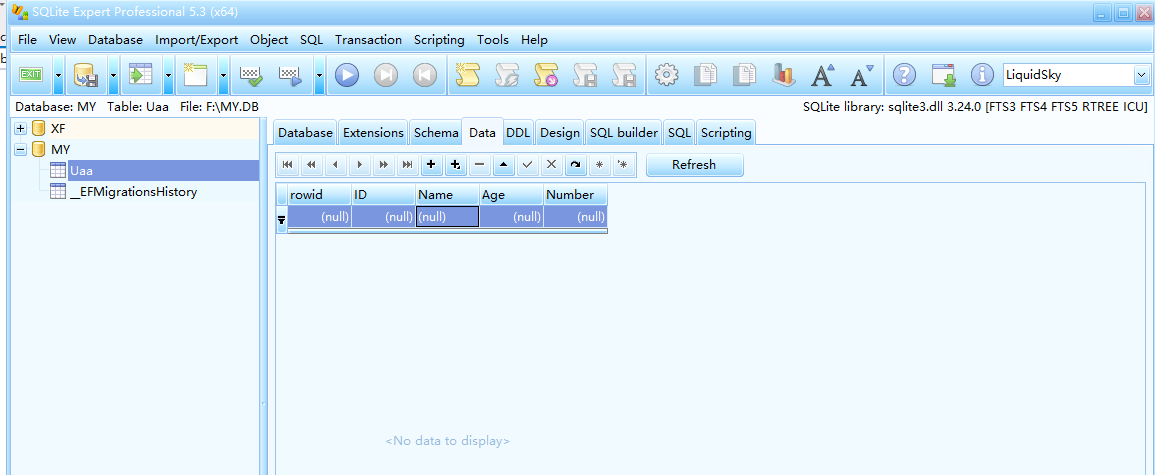
Once the software is installed, you can open the database file.
Software Open Database Files Tutorial:

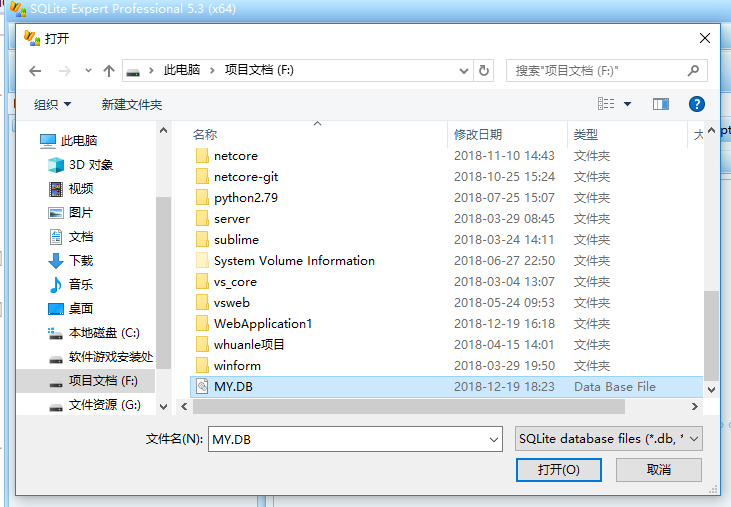
6 Generate Add-Remove Check Change Base Frame
At this point, you can operate on the database in the program. For how to use it, it is best to see Microsoft's Entity Framework documentation.
Here is a simple example.
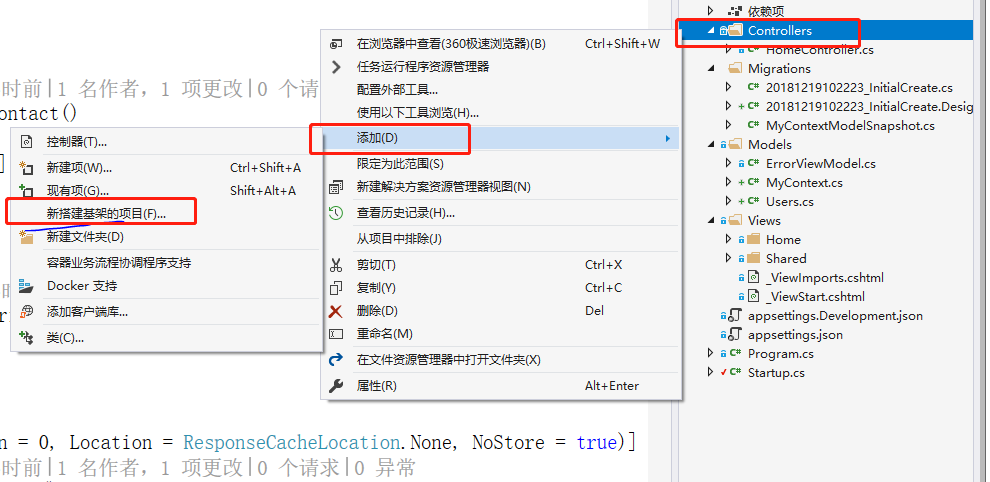
Step 1
In the Controller directory, right-click Add--New Base Item
Step 2
click View MVC Controller using Entity Framework

Model Class Selection Users([project name].Models)
Database Context Selection MyContext ([Project Name]. Models)
click Add to

Step 3
You can see it now
Controller Much more UsersController.cs file
Views Much more Users Catalog
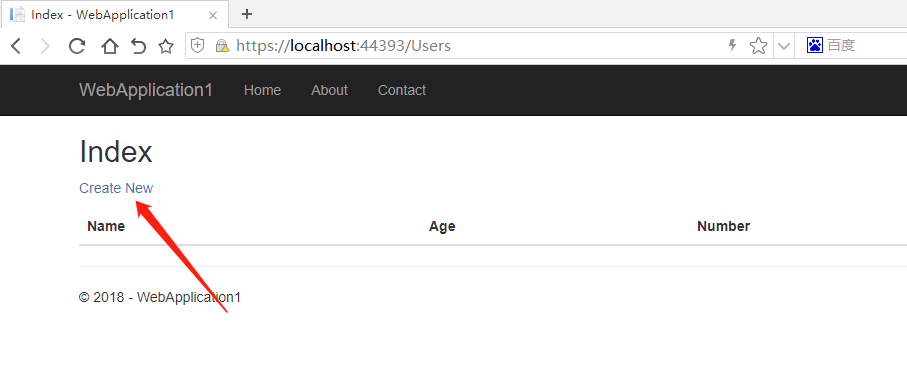
Please click Run or press F5, Start Web Site
Add to the back of the website Users
for example https://localhost: [Actual Port]/Users, you can do whatever you want with the Users table
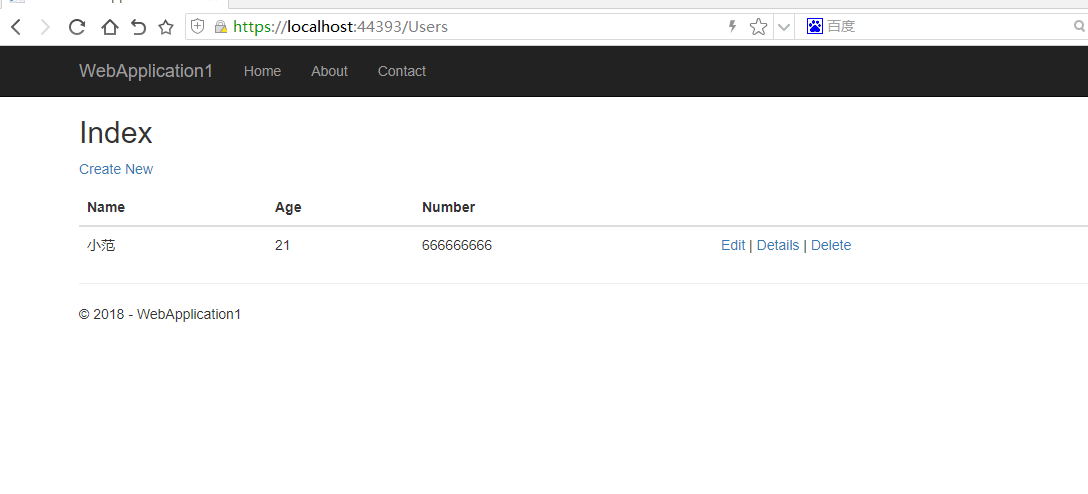
Step 4 Add data
click Create new

Result
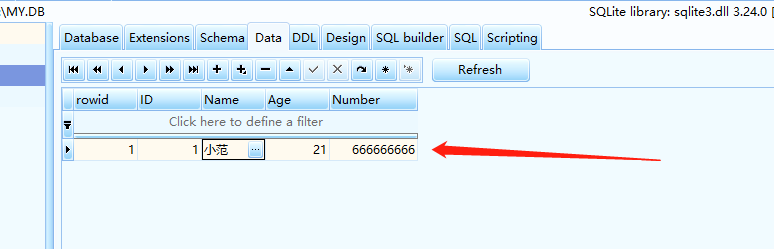
7 Fill in data cannot be empty
Note: Features and data validation are involved here. I will not dwell on them. Readers can understand them before translating other articles.
After the above operations, we can already operate on the database. In fact, although we can operate data, if I want to set an item that must be filled in, the format of an item must be a mobile phone? Don't let users fill in anything?
open Users.cs
Add Reference
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations;
The code to modify the Users class is as follows
public class Users
{
public int ID { get; set; } //Primary key
[Required]
public string Name { get; set; } /n/User Name
[Required(ErrorMessage ="Cannot be empty")]
public int Age { get; set; } //User Age
[Required]
[RegularExpression(@"^1[3458][0-9]{9}$", ErrorMessage = "Incorrect mobile number format")]
public int Number { get; set; } //User mobile number
}
Run the website, open the URL/Users, click Create New, and submit without filling in the form. You will find

Fill in the other items, and then fill in the numbers in Number, you will find

This is model validation.
It doesn't need to write any code, just add [attributes] to the attributes.
Please refer to it separately.
Note:
- [Required] indicates that the item cannot be empty
- [Required(ErrorMessage = "cannot be empty")] ErrorMessage = "" is not filled in as required and a quota prompt appears
- [RegularExpression (@'^1[3458][0-9]{9}$', ErrorMessage ='Phone Number is not in the correct format')] This is regular expression validation and an error message will appear if the content is not in the correct format.