Arrays
- Array creation
//Create Array int array[] = new int[3];
- Assigning values to elements in an array
//Assigning values to elements in an array array[0] = 1; array[1] = 2; array[2] = 3;
- Assigning values to arrays at creation time
//Create an array and assign values int array[] = new int[] {1,2,3};
- All elements in the output array
System.out.println (Arrays.toString (target array));
- Add a new element after the array
public class OpArrayTest { //Addition of Array Elements public static void main(String[] args) { //Create an array and assign values int array[] = new int[] {1,2,3}; System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array)); //Data to be added int dext = 4; //Create a new array of length + 1 of the original array int array1[] = new int[array.length+1]; //Assign elements of the original array to the new array for(int i=0;i<array.length;i++) { array1[i] = array[i]; } //Add a new element to the end of a new array array1[array.length] = dext; //New Array Replace Old Array array=array1; System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array)); }
- Delete elements from the array
package shuzu; import java.util.Arrays; public class OpArrayTest2 { //Deletion of array elements public static void main(String[] args) { //Create an array and assign values to it int array[] = new int[] {1,2,3,4,5}; System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array)); //Subscripts of array elements need to be removed int dext = 2; //Create a new array length is how long the array length is -1 int array1[] = new int[array.length-1]; //Assign elements from the original array to the new array, except those that need to be deleted for(int i=0;i<array1.length;i++) { //judge if(i<dext) { array1[i] = array[i]; }else { array1[i] = array[i+1]; } } //New Array Replace Old Array array = array1; System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array)); } }
2. Object-oriented arrays
- Create a tool class, MyArray.java, to encapsulate some methods of an array of operations.
package shuzu.util; import java.util.Arrays; public class MyArray { //Same as an array of stored data private int array[]; public MyArray() { array = new int[0]; } //Get the length of the array public int size() { return array.length; } //Print Output Array public void show() { System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array)); } //Add elements to the array public void add(int dex) { //Create a new array of length + 1 int array1[] = new int[array.length+1]; //Copy elements from the original array into the new array for(int i=0;i<array.length;i++) { array1[i] = array[i]; } //Add a new element after a new array array1[array.length] = dex; //New Array Replace Old Array array = array1; } //Delete elements from the array public void delete(int dex) { //Create a new array, length is principle, array length -1 int array1[] = new int[array.length-1]; //Copy elements from the original array into the new array except those to be deleted if(dex<0||dex>array.length-1) { throw new RuntimeException("subscript out of range"); } for(int i=0;i<array1.length;i++) { if(i<dex) { array1[i] = array[i]; }else { array1[i] = array[i+1]; } } //New Array Replace Old Array array = array1; } //Insert an element to the location specified by the array public void insert(int dex,int nex) { //dex:Specify the location nex:for the element that needs to be inserted //Create a new array of length + 1 int array1[] = new int[array.length+1]; //Copy elements from the original array into the new array if(dex<0||dex>array.length-1) { throw new RuntimeException("subscript out of range"); } for(int i=0;i<array.length;i++) { //judge if(i<dex) { array1[i] = array[i]; }else { array1[i+1] = array[i]; } } //Insert a new element array1[dex] = nex; //New Array Replaces Old Array array = array1; } //Replace elements at specified locations public void set(int dex ,int nex) { //dex: Subscript nex of the element to be replaced: Replaced element //Replace elements, array[dex] = nex; } }
- Write a test class to create a variable array and add, delete, replace, output, and so on.
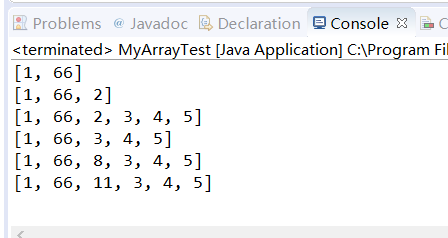
package shuzu; import shuzu.util.MyArray; public class MyArrayTest { public static void main(String[] args) { //Create a variable array MyArray ma = new MyArray(); //Array of output ma.show(); //Add an element to the array ma.add(1); ma.add(66); ma.show(); //Delete an element from the array ma.add(2); ma.show(); ma.add(3); ma.add(4); ma.add(5); ma.show(); ma.delete(2); ma.show(); //Add elements at specified locations ma.insert(2, 8); ma.show(); //Replace elements at specified locations ma.set(2, 11); ma.show(); } }
- The console effect is as follows:
3. Linear Search
- Creates a target array, compares the target element to each element in the array, and returns its subscript if it is equal
package shuzu; public class SearchTest { //Linear Find Target Elements public static void main(String[] ages) { //Create Target Array int array[] = new int[] {1,3,2,9,6,8}; //Target element of lookup int dex = 8; //Subscript of target element int nex = -1; for(int i=0;i<array.length;i++) { if(array[i] == dex) { nex = i; break; } } //Print target element subscript System.out.println("Subscript of target element:"+nex); } }
4. Binary Search
- Create an ordered array and assign values to it, recording where you start, center, and end.Each time the loop compares that intermediate element with the target element, if the intermediate element is larger than the target element, the end position becomes the position of the previous element of the intermediate element.If the middle element is smaller than the target element, the start position becomes the position of the next element after the middle element.
package shuzu; import java.util.Arrays; public class BinaryTest { public static void main(String[] ages) { //Create Target Array int array[] = new int[] {1,3,2,4,5,6,7,8,9}; Arrays.sort(array); System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array)); //Target Element int nex = 7; //Record start position int begin = 0; //Record End Position int end = array.length-1; //Record middle position int mid = (begin+end)/2; //Record Target Location int dex = -1; while(true) { //Determine if the middle element is the one to look for if(array[mid] == nex) { dex = mid; break; }else { if(array[mid]>nex) { //The intermediate element is larger than the target element end = mid-1; //Change the end position to the previous element of the intermediate element }else { //The middle element is smaller than the target element begin = mid+1; //Change the position of the start element to the next position of the intermediate element } } mid = (begin+end)/2; //New intermediate elements } System.out.println("Find the location of the target element"+dex); } //Output the location of the target element found }
9 original articles published. 0% praised. 52% visited

