Foreword: Start-up self-start function may be relatively rare in daily development, but there are still some industries that need this kind of demand. My colleagues studied it for some time before, but the results were not satisfactory. This is largely related to Android's mobile phone system, which is well known to have been changed differently by major manufacturers. We can find many such codes on the Internet, but they may fail. I also learned about this function to record my own experience.
First, we need to define a boot Broadcast Receiver:
public class BootBroadcastReceiver extends BroadcastReceiver {
static final String ACTION = "android.intent.action.BOOT_COMPLETED";
@Override
public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) {
Toast.makeText(context, "Successful startup", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
Log.i("❤Yu Lin·Chun Po☆Myth.Mayor❤", "BootBroadcastReceiver --- onReceive: " + intent.getAction());
//After booting, the screen usually stays on the lock screen page and does not unlock for a short period of time. The screen will enter a dormant state. At this time, it is necessary to wake up the screen and unlock the screen first.
//Screen wake-up call
PowerManager pm = (PowerManager) context.getSystemService(Context.POWER_SERVICE);
PowerManager.WakeLock wl = pm.newWakeLock(PowerManager.ACQUIRE_CAUSES_WAKEUP
| PowerManager.SCREEN_DIM_WAKE_LOCK, "StartupReceiver");//The final parameter is the Tag used in LogCat
wl.acquire();
//Screen Lock FX
KeyguardManager km = (KeyguardManager) context.getSystemService(Context.KEYGUARD_SERVICE);
KeyguardManager.KeyguardLock kl = km.newKeyguardLock("StartupReceiver");//The parameter is Tag used in LogCat
kl.disableKeyguard();
if (intent.getAction().equals(ACTION)) {
//Activity to start
Intent bootIntent = new Intent(context, MainActivity.class);
bootIntent.addFlags(Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK);
context.startActivity(bootIntent);
}
}
}It needs to be pointed out that if there is no operation on the phone, it will lock the screen and go to sleep. I added the screen wake-up function in the code.
List documents:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.mythmayor.powerbootdemo">
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.RECEIVE_BOOT_COMPLETED" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.WAKE_LOCK" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.DISABLE_KEYGUARD" />
<application
android:allowBackup="true"
android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:supportsRtl="true"
android:theme="@style/AppTheme">
<activity android:name=".MainActivity">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
<receiver android:name=".BootBroadcastReceiver">
<intent-filter>
<!--Register boot broadcasting address-->
<action android:name="android.intent.action.BOOT_COMPLETED"/>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.QUICKBOOT_POWERON" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.HOME"/>
</intent-filter>
</receiver>
</application>
</manifest>Explanation: We added three permissions to the list file, "RECEIVE_BOOT_COMPLETED" is the right to start, and "WAKE_LOCK" and "DISABLE_KEYGUARD" are the right to wake up the screen. At the same time, we declared the broadcaster and added "action" and "category".
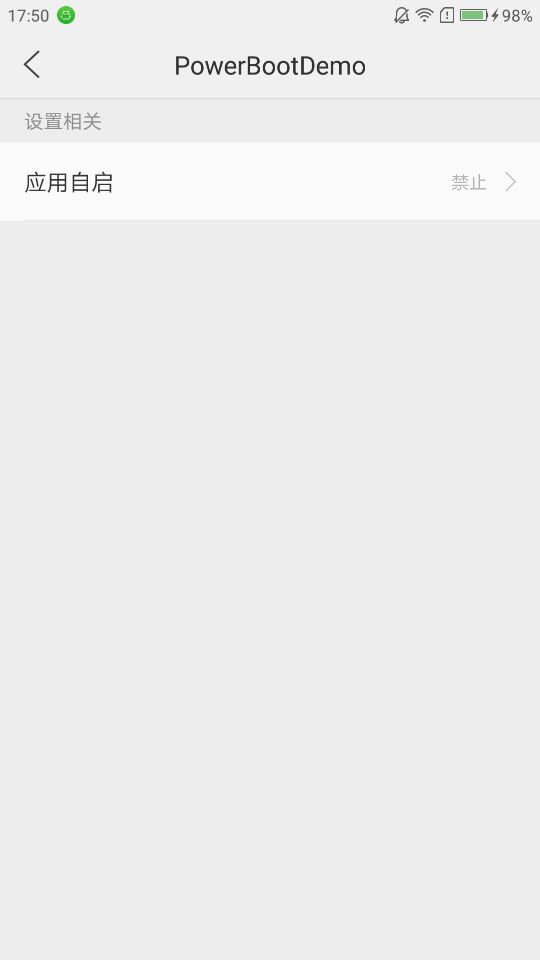
Third, the core code has been introduced. There are two main points when using this function: 1. Although we have declared permissions, we still need to go into application management to see if these permissions are actually opened. If not, start it manually. As shown in the figure below, I declared the boot privilege in the code, but it is still forbidden in application management. At this time, we need to manually change it to allow 2. There may be some delay after boot to receive boot broadcasting, because the system needs to do some initialization work, but the time will not be too long, just wait for the program to start itself.