Catalog
I. Introduction
Why encapsulate logs?
First, compare the effect:
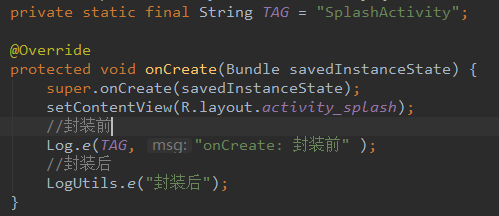
Print results:

Before encapsulation: enter Log.e(TAG, "onCreate:",); you need to enter TAG and msg. And we can view the log information on the Logcat page.
Disadvantages:
(1) The input parameters are many and repeated
(2) When too much log information is printed, it is not convenient to find the information we need
(3) Unable to quickly specify which line of printed information
(4) When the application is published to the market, you need to manually delete the printed logs one by one
After encapsulation: just input the msg you want to print, easy to use. You can click the class name on the Logcat page to jump to the corresponding location.
2, Log specific package
import android.util.Log;
/**
*
* Log encapsulation
*/
public class LogUtils {
static String className;//Class name
static String methodName;//Method name
static int lineNumber;//Row number
/**
* Judge whether it can be debugged
* @return
*/
public static boolean isDebuggable() {
return BuildConfig.DEBUG;
}
private static String createLog(String log ) {
StringBuffer buffer = new StringBuffer();
buffer.append("================"+methodName);
buffer.append("(").append(className).append(":").append(lineNumber).append(")================:");
buffer.append(log);
return buffer.toString();
}
/**
* Get file name, method name and number of lines
* @param sElements
*/
private static void getMethodNames(StackTraceElement[] sElements){
className = sElements[1].getFileName();
methodName = sElements[1].getMethodName();
lineNumber = sElements[1].getLineNumber();
}
public static void e(String message){
if (!isDebuggable())
return;
getMethodNames(new Throwable().getStackTrace());
Log.e(className, createLog(message));
}
public static void i(String message){
if (!isDebuggable())
return;
getMethodNames(new Throwable().getStackTrace());
Log.i(className, createLog(message));
}
public static void d(String message){
if (!isDebuggable())
return;
getMethodNames(new Throwable().getStackTrace());
Log.d(className, createLog(message));
}
public static void v(String message){
if (!isDebuggable())
return;
getMethodNames(new Throwable().getStackTrace());
Log.v(className, createLog(message));
}
public static void w(String message){
if (!isDebuggable())
return;
getMethodNames(new Throwable().getStackTrace());
Log.w(className, createLog(message));
}
}3, Turn off debugging
When we want to publish the application to the market, we need to clear the log (turn off debugging).
(1) The first way: open project structure
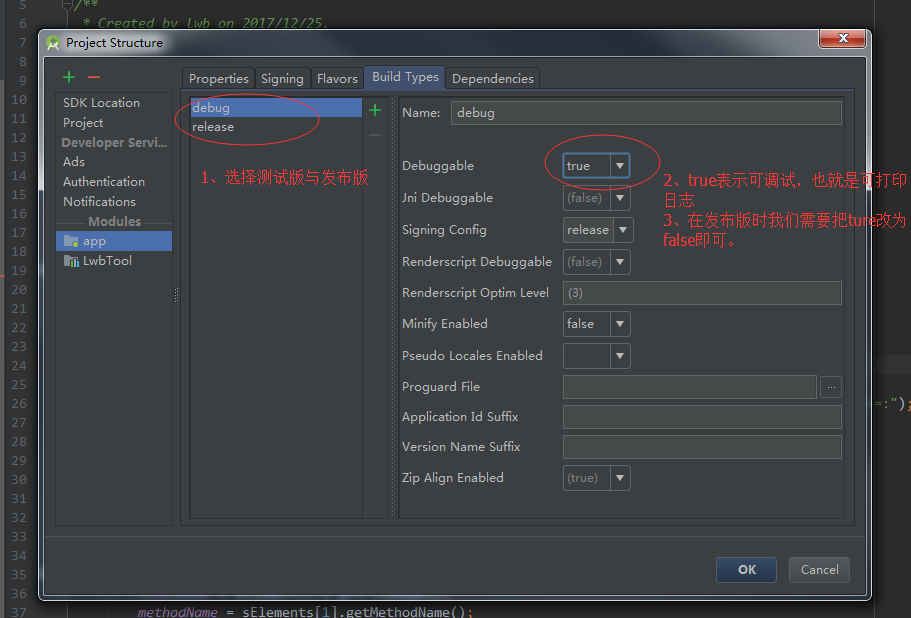
(2) The second way: open build.gradle
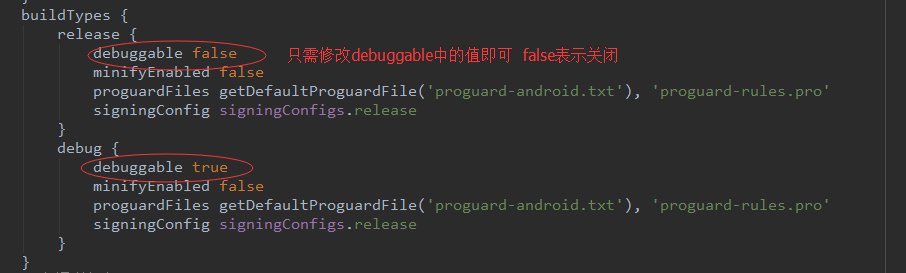
You don't need to delete lines as before. Open it again when you want to use it
4, Source address
https://github.com/DayorNight/BLCS
5, Content recommendation
Address: https://www.jianshu.com/p/f947d6e77fd1
Last article Android alliance multi channel packaging
Reference documents: https://blog.csdn.net/lmj623565791/article/details/52506545