1. The user needs to obtain the usb device name to determine whether it is our printer
2. code
public String getProductName(){
byte[] rawDescs = mUsbDeviceConnection.getRawDescriptors();
String manufacturer = "", product = "";
try
{
byte[] buffer = new byte[255];
int idxMan = rawDescs[14];
int idxPrd = rawDescs[15];
Logger.i("index",idxMan);
int rdo = mUsbDeviceConnection.controlTransfer(UsbConstants.USB_DIR_IN
| UsbConstants.USB_TYPE_STANDARD, STD_USB_REQUEST_GET_DESCRIPTOR,
(LIBUSB_DT_STRING << 8) | idxMan, 0, buffer, 0xFF, 0);
manufacturer = new String(buffer, 2, rdo - 2, "UTF-16LE");
rdo = mUsbDeviceConnection.controlTransfer(UsbConstants.USB_DIR_IN
| UsbConstants.USB_TYPE_STANDARD, STD_USB_REQUEST_GET_DESCRIPTOR,
(LIBUSB_DT_STRING << 8) | idxPrd, 0, buffer, 0xFF, 0);
product = new String(buffer, 2, rdo - 2, "UTF-16LE");
} catch (Exception e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
Logger.e(e.getMessage());
}
Logger.i("","Manufacturer:" + manufacturer + "\n");
Logger.i("","Product:" + product + "\n");
Logger.i("","Serial#:" + mUsbDeviceConnection.getSerial() + "\n");
return product.trim()+manufacturer.trim();
}3. The description of controltransfer method is shown in the two figures. The first parameter refers to whether you are reading or writing. 2. What content you want to read or write. 3. The index of the field in the content structure. 4. What offset to start reading and writing. 5. The read container or the write data. 6. Length https://blog.csdn.net/obanaganastar/article/details/72866260
4. When tracking this method, it will break when it comes to here, so I guess the above 3 parameters
int usb_device_control_transfer(struct usb_device *device,
575 int requestType,
576 int request,
577 int value,
578 int index,
579 void* buffer,
580 int length,
581 unsigned int timeout)
582{
583 struct usbdevfs_ctrltransfer ctrl;
584
585 // this usually requires read/write permission
586 if (!usb_device_reopen_writeable(device))
587 return -1;
588
589 memset(&ctrl, 0, sizeof(ctrl));
590 ctrl.bRequestType = requestType;
591 ctrl.bRequest = request;
592 ctrl.wValue = value;
593 ctrl.wIndex = index;
594 ctrl.wLength = length;
595 ctrl.data = buffer;
596 ctrl.timeout = timeout;
597 return ioctl(device->fd, USBDEVFS_CONTROL, &ctrl);
598}
//Then call the kernel method.
#define USBDEVFS_CONTROL _IOWR('U', 0, struct usbdevfs_ctrltransfer)5. results
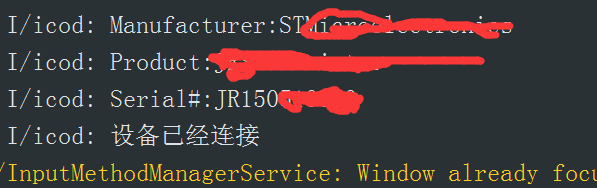
ps: because most of the underlying software of the printer is written by Epson, the product s used can be the same, and three splices are needed for comparison