1. Use execSQL API to operate the database.
Step 1: create the Class MyOpenHelper implementation interface SQLiteOpenHelper, copy the constructor, onCreate and onUpgrade methods;
Step 2, after creating the myOpenHelper object myOpenHelper, use the relevant API of myOpenHelper to operate the database.
package com.xiaohui.createdb;
import android.content.Context;
import android.database.sqlite.SQLiteDatabase;
import android.database.sqlite.SQLiteOpenHelper;
public class MyOpenHelper extends SQLiteOpenHelper {
public MyOpenHelper(Context context) {
super(context,"xiaohui2.db", null, 1);
}
/**
* Execute when the library is first created
* Called when the database is created for the first time
*/
@Override
public void onCreate(SQLiteDatabase db) {
String sql = "create table user(_id integer primary key autoincrement,name varchar(20),phone varchar(12))";
db.execSQL(sql);
}
/**
* Called when the database version is upgraded
*/
@Override
public void onUpgrade(SQLiteDatabase db, int oldVersion, int newVersion) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
// System.out.println("onUpgrade. . . ");
// String sql = "alter table user add phone varchar(20)";
// db.execSQL(sql );
}
}
package com.xiaohui.createdb;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.database.Cursor;
import android.database.sqlite.SQLiteDatabase;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.EditText;
import android.widget.TextView;
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
private MyOpenHelper myOpenHelper;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
myOpenHelper = new MyOpenHelper(getApplicationContext());
}
public void insert(View v){
SQLiteDatabase wdb = myOpenHelper.getWritableDatabase();
EditText etName = (EditText)findViewById(R.id.et_name);
EditText etPhone = (EditText)findViewById(R.id.et_phone);
wdb.execSQL("insert into user(name,phone) values(?,?)", new Object[]{etName.getText().toString(),etPhone.getText().toString()});
wdb.close();
}
public void delete(View v){
SQLiteDatabase wdb = myOpenHelper.getWritableDatabase();
EditText etName = (EditText)findViewById(R.id.et_name);
wdb.execSQL("delete from user where name=?", new Object[]{etName.getText().toString()});
wdb.close();
}
public void update(View v){
SQLiteDatabase wdb = myOpenHelper.getWritableDatabase();
EditText etName = (EditText)findViewById(R.id.et_name);
EditText etPhone = (EditText)findViewById(R.id.et_phone);
wdb.execSQL("update user set phone=? where name=?", new Object[]{etPhone.getText().toString(),etName.getText().toString()});
wdb.close();
}
public void select(View v){
SQLiteDatabase wdb = myOpenHelper.getWritableDatabase();
Cursor cursor = wdb.rawQuery("select * from user", null);
String list = "";
if(cursor != null && cursor.getCount() > 0){
while (cursor.moveToNext()) {
String id = cursor.getString(cursor.getColumnIndex("_id"));
int i = cursor.getColumnIndex("name");
String name = cursor.getString(i);
String phone = cursor.getString(cursor.getColumnIndex("phone"));
list += "{id="+id+",name="+name+",phone="+phone+"},";
}
}
TextView tVlist = (TextView)findViewById(R.id.tv_list);
tVlist.setText(list);
}
}
2. Use the Android API to operate the database.
The steps are the same as the above, and Android's own API is used
package com.xiaohui.createdb;
import com.xiaohui.createdb4API.R;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.ContentValues;
import android.database.Cursor;
import android.database.sqlite.SQLiteDatabase;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.EditText;
import android.widget.TextView;
import android.widget.Toast;
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
private MyOpenHelper myOpenHelper;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
myOpenHelper = new MyOpenHelper(getApplicationContext());
}
public void insert(View v){
SQLiteDatabase wdb = myOpenHelper.getWritableDatabase();
EditText etName = (EditText)findViewById(R.id.et_name);
EditText etPhone = (EditText)findViewById(R.id.et_phone);
// wdb.execSQL("insert into user(name,phone) values(?,?)", new Object[]{etName.getText().toString(),etPhone.getText().toString()});
ContentValues values = new ContentValues();
values.put("name", etName.getText().toString());
values.put("phone", etPhone.getText().toString());
long insert = wdb.insert("user", null, values );
wdb.close();
if(insert>0){
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), "New success", 1).show();
}else{
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), "New failure", 1).show();
}
}
public void delete(View v){
SQLiteDatabase wdb = myOpenHelper.getWritableDatabase();
EditText etName = (EditText)findViewById(R.id.et_name);
// wdb.execSQL("delete from user where name=?", new Object[]{etName.getText().toString()});
int delete = wdb.delete("user", "name=?", new String[]{etName.getText().toString()});
wdb.close();
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), "Deleted"+delete+"strip", 1).show();
}
public void update(View v){
SQLiteDatabase wdb = myOpenHelper.getWritableDatabase();
EditText etName = (EditText)findViewById(R.id.et_name);
EditText etPhone = (EditText)findViewById(R.id.et_phone);
// wdb.execSQL("update user set phone=? where name=?", new Object[]{etPhone.getText().toString(),etName.getText().toString()});
ContentValues values = new ContentValues();
values.put("phone", etPhone.getText().toString());
int update = wdb.update("user", values , "name=?", new String[]{etName.getText().toString()});
wdb.close();
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), "Revised"+update+"strip", 1).show();
}
public void select(View v){
SQLiteDatabase wdb = myOpenHelper.getWritableDatabase();
// Cursor cursor = wdb.rawQuery("select * from user", null);
EditText etName = (EditText)findViewById(R.id.et_name);
Cursor cursor = wdb.query("user", null,"name != ?", new String[]{etName.getText().toString()}, null, null, null);
String list = "";
if(cursor != null && cursor.getCount() > 0){
while (cursor.moveToNext()) {
String id = cursor.getString(cursor.getColumnIndex("_id"));
int i = cursor.getColumnIndex("name");
String name = cursor.getString(i);
String phone = cursor.getString(cursor.getColumnIndex("phone"));
list += "{id="+id+",name="+name+",phone="+phone+"},";
}
}
TextView tVlist = (TextView)findViewById(R.id.tv_list);
tVlist.setText(list);
}
}
3. SQLite database transaction control
The standard formats in the document are described as follows
Here is the standard idiom for transactions:
db.beginTransaction();
try {
...
db.setTransactionSuccessful();
} finally {
db.endTransaction();
}
package com.xiaohui.transation;
import android.content.Context;
import android.database.sqlite.SQLiteDatabase;
import android.database.sqlite.SQLiteOpenHelper;
public class MyDBHelper extends SQLiteOpenHelper {
public MyDBHelper(Context context) {
super(context, "Account.db", null, 1);
}
@Override
public void onCreate(SQLiteDatabase db) {
db.execSQL("create table account(idCard carchar(20),name varchar(20),money varchar(15))");
db.execSQL("insert into account(idCard,name,money) values(?,?,?)",new String[]{"111","Zhang San","2000"});
db.execSQL("insert into account(idCard,name,money) values(?,?,?)",new String[]{"222","Li Si","3000"});
}
@Override
public void onUpgrade(SQLiteDatabase db, int oldVersion, int newVersion) {
}
}
package com.xiaohui.transation;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.database.sqlite.SQLiteDatabase;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Toast;
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
SQLiteDatabase db;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
MyDBHelper dbHelper = new MyDBHelper(getApplicationContext());
db = dbHelper.getReadableDatabase();
}
public void trans(View v) {
db.beginTransaction();
try {
db.execSQL("update account set money=money-100 where idCard=?",new String[]{"1111"});
if(Math.random()*10 > 5){
throw new Exception();
}
db.execSQL("update account set money=money+100 where idCard=?",new String[]{"2222"});
db.setTransactionSuccessful();
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), "Successful transfer", 1).show();
}catch(Exception e){
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), "Transfer failure", 1).show();
} finally {
db.endTransaction();
}
}
}
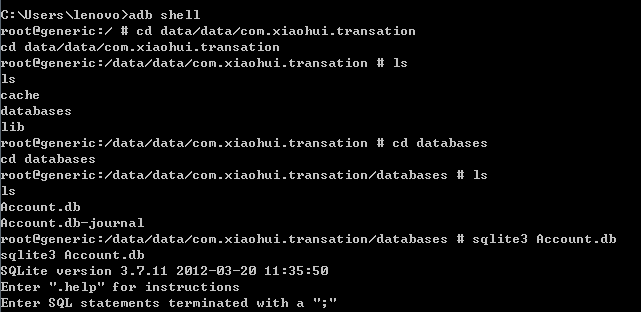
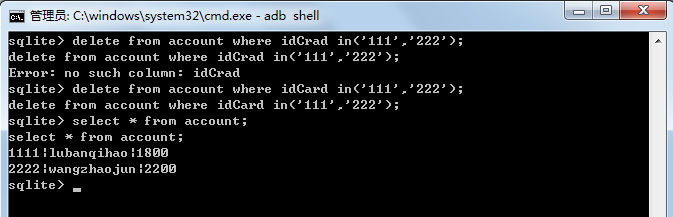
4. Use the command line to view data
After class has configured the Android SDK environment, use the relevant commands: adb shell;sqlite3; and standard SQL for database operations.