Android Baidu Map (1): Detailed introduction of sdk-type method parameters and positioning principle for Baidu Map positioning
Android Baidu Map (3): Baidu Map Track and Layer Click Event Processing
Source address https://github.com/zhuhao Happig/BaiduMapApi
Introduction of Centennial Map and Location sdk
In the last article, the parameters and principle of positioning sdk class methods are introduced in detail, and how to use positioning sdk to locate is described in detail. The BDLocation class acquired by locating sdk contains the address information of the current location: longitude and latitude, province, city, district, street, etc. If the application only needs to get information about the city, county, district where the user is currently located, then positioning sdk can meet your needs. If you want to show exactly where the location is, besides locating sdk to get latitude and longitude, you also need to show it through Baidu Map.
Baidu MapView is a map, is a View, it will not produce location.
Location sdk can obtain longitude and latitude, which is equivalent to x and y coordinates. Maps find corresponding points according to coordinates and draw an icon on the map layer. This is the location we see on the map.
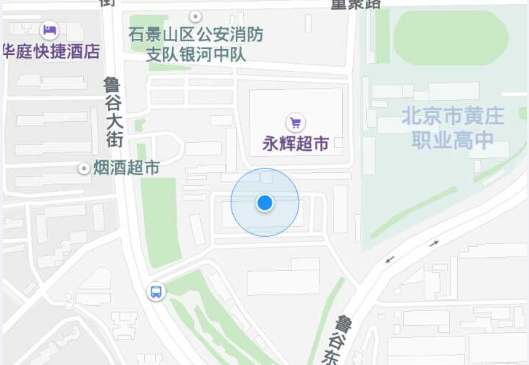
Knowing this, it's easy to show location points on a map. We need maps and locations.
The Combination of Erbai Map and Location sdk
1. Baidu Map and the jar and so files needed to locate sdk
baidumapapi_base_v4_3_1.jar, baidumapapi_map_v4_3_1.jar: Includes Baidu Map api
locSDK_6.13.jar: Contains positioning sdk api
Lib Baidu Map SDK_base_v4_3_1.so, lib Baidu Map SDK_map_v4_3_1.so: so file of Baidu Map
liblocSDK7a.so: Locate the sdkso file
Development Kit Download address It is recommended to download the basic map sample code in the libs of the BaiduMap_Android SDK_v4.3.1_Sample project; you can also download the development kit directly.
2. Initialization map
//Pseudo-code // Map Initialization MapView mMapView = (MapView) findViewById(R.id.bmapView); BaiduMap mBaiduMap = mMapView.getMap();//Getting Map Instances // Open the location layer, must not be less this sentence, otherwise the map settings, mapping location points will be invalid. mBaiduMap.setMyLocationEnabled(true);
So the map is obtained, and then the location icon is configured, very simple, a code. You can also not configure, Baidu will use the default icon
/** * To configure the location icon, you need an instance of MyLocation Configuration, which sets the display mode of the location icon. */ mBaiduMap.setMyLocationConfiguration(new MyLocationConfiguration(locationMode, true, bitmapDescriptor));
MyLocation Configuration has two constructions
new MyLocationConfiguration(LocationMode lm, boolean direction, BitmapDescriptor bd); new MyLocationConfiguration(LocationMode lm, boolean direction, BitmapDescriptor bd,int fillColor,int strokeColor);
Location Mode: Icon Type
There are three kinds:
Location Mode. NORMAL: Ordinary
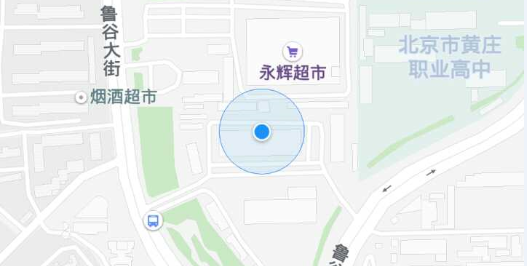
Location Mode. FOLLOWING: Follow
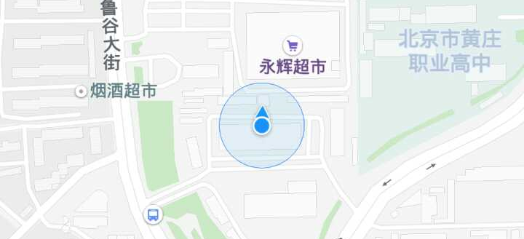
Location Mode. COMPASS: Compass
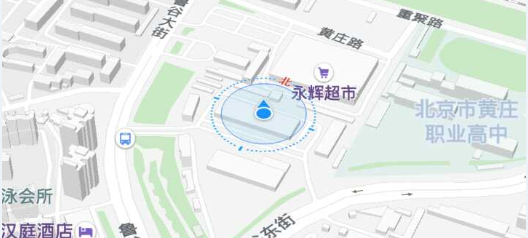
Direction: Whether direction information is allowed to be displayed, and if set to false, the icon will not have an arrow under any circumstances
BitmapDescriptor: User-defined positioning icon, you can change the style of positioning icon
fillColor: Precision circle fill color (radius equals location.getRadius())
StrkeColor: Precision Ring Border Color
If you don't want this precision circle, use location.getRadius() = 0;
3. Location sdk initialization
// Location initialization LocationClient mLocClient = new LocationClient(this); mLocClient.registerLocationListener(myListener);//Registered Location Monitoring Callback LocationClientOption option = new LocationClientOption();//Location mode parameter setting option.setOpenGps(true); // Open gps option.setCoorType("bd09ll"); // Setting coordinate type option.setScanSpan(1000);//Periodically request location, return to position once a second mLocClient.setLocOption(option);//Parameter Settings mLocClient.start();//Start positioning
Locate sdk for more api details, please read Baidu Map (1): Detailed introduction of sdk-type method parameters and positioning principle for Baidu Map positioning
4. Location monitoring callback
//Pseudo-code public class MyLocationListenner implements BDLocationListener { @Override public void onReceiveLocation(BDLocation location) { //Location position callback /** * MyLocationData Location data class, the location on the map requires several parameters, such as longitude, latitude, accuracy and direction, so here we pass these parameters to the map. * If you don't need a precision circle, builder.accuracy(0) is recommended. * mCurrentDirection The orientation is obtained through the mobile phone direction sensor; you can also set option.setNeedDeviceDirect(true) to get location.getDirection(). But this does not update the direction of the location from time to time, because periodic requests for location have time intervals. * location.getLatitude()And location.getLongitude() longitude and latitude, if you only need to show a fixed location on the map, you can write a fixed value. If latitude is 36.958454 and longitude is 114.137588, it is not necessary to locate sdk to get position. */ MyLocationData locData = new MyLocationData.Builder().accuracy(location.getRadius()) .direction(mCurrentDirection).latitude(location.getLatitude()).longitude(location.getLongitude()).build(); mBaiduMap.setMyLocationData(locData);//Set up location data for the map so that the map shows the location. /** *When locating for the first time, remember to zoom in to see the exact location. * LatLng It is the central point of zooming, so we should pay attention to the same latitude and longitude as the map set above. * MapStatus.Builder Map State Constructor */ if (isFirstLoc) { isFirstLoc = false; LatLng ll = new LatLng(location.getLatitude(), location.getLongitude()); MapStatus.Builder builder = new MapStatus.Builder(); //Setting zoom center point; zoom proportion; builder.target(ll).zoom(18.0f); //Set the status of the map mBaiduMap.animateMapStatus(MapStatusUpdateFactory.newMapStatus(builder.build())); } } }
Release resources when you exit
//Pseudo-code protected void onDestroy() { // Destruction Location at Exit mLocClient.unRegisterLocationListener(myListener); mLocClient.stop(); // Close the Location Layer mBaiduMap.setMyLocationEnabled(false); mMapView.onDestroy(); mMapView = null; }
So far, it's still very simple to get the location by locating the sdk and display it on the map.
Below is the demo code of Baidu Development Platform
/** * This Application must be available. Note the Android Manifest. XML declaration */ public class DemoApplication extends Application { @Override public void onCreate() { super.onCreate(); // Initialize context information before using SDK between groups and pass in Application Context SDKInitializer.initialize(this); //Since 4.3.0, all interfaces of Baidu Map SDK support Baidu coordinates and National Bureau of Survey coordinates. Use this method to set the type of coordinates you use. //Including BD09LL and GCJ02 coordinates, the default is BD09LL coordinates. SDKInitializer.setCoordType(CoordType.BD09LL); } } public class LocationDemo extends Activity implements SensorEventListener { // Location correlation LocationClient mLocClient; public MyLocationListenner myListener = new MyLocationListenner(); private LocationMode mCurrentMode; BitmapDescriptor mCurrentMarker; private static final int accuracyCircleFillColor = 0xAAFFFF88; private static final int accuracyCircleStrokeColor = 0xAA00FF00; private SensorManager mSensorManager; private Double lastX = 0.0; private int mCurrentDirection = 0; private double mCurrentLat = 0.0; private double mCurrentLon = 0.0; private float mCurrentAccracy; MapView mMapView; BaiduMap mBaiduMap; // UI correlation OnCheckedChangeListener radioButtonListener; Button requestLocButton; boolean isFirstLoc = true; // Whether to locate for the first time private MyLocationData locData; private float direction; @Override public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_location); requestLocButton = (Button) findViewById(R.id.button1); mSensorManager = (SensorManager) getSystemService(SENSOR_SERVICE);// Acquiring Sensor Management Services mCurrentMode = LocationMode.NORMAL; requestLocButton.setText("ordinary"); OnClickListener btnClickListener = new OnClickListener() { public void onClick(View v) { switch (mCurrentMode) { case NORMAL: requestLocButton.setText("follow"); mCurrentMode = LocationMode.FOLLOWING; mBaiduMap.setMyLocationConfiguration( new MyLocationConfiguration(mCurrentMode, true, mCurrentMarker)); MapStatus.Builder builder = new MapStatus.Builder(); builder.overlook(0); mBaiduMap.animateMapStatus(MapStatusUpdateFactory.newMapStatus(builder.build())); break; case COMPASS: requestLocButton.setText("ordinary"); mCurrentMode = LocationMode.NORMAL; mBaiduMap.setMyLocationConfiguration( new MyLocationConfiguration(mCurrentMode, true, mCurrentMarker)); MapStatus.Builder builder1 = new MapStatus.Builder(); builder1.overlook(0); mBaiduMap.animateMapStatus(MapStatusUpdateFactory.newMapStatus(builder1.build())); break; case FOLLOWING: requestLocButton.setText("compass"); mCurrentMode = LocationMode.COMPASS; mBaiduMap.setMyLocationConfiguration( new MyLocationConfiguration(mCurrentMode, true, mCurrentMarker)); break; default: break; } } }; /** * */ requestLocButton.setOnClickListener(btnClickListener); RadioGroup group = (RadioGroup) this.findViewById(R.id.radioGroup); radioButtonListener = new OnCheckedChangeListener() { @Override public void onCheckedChanged(RadioGroup group, int checkedId) { if (checkedId == R.id.defaulticon) { // When null is passed in, the default icon is restored mCurrentMarker = null; mBaiduMap.setMyLocationConfiguration(new MyLocationConfiguration(mCurrentMode, true, null)); } if (checkedId == R.id.customicon) { // Modified to custom marker mCurrentMarker = BitmapDescriptorFactory.fromResource(R.drawable.ic_launcher); mBaiduMap.setMyLocationConfiguration(new MyLocationConfiguration(mCurrentMode, true, mCurrentMarker, accuracyCircleFillColor, accuracyCircleStrokeColor)); } } }; group.setOnCheckedChangeListener(radioButtonListener); // Map Initialization mMapView = (MapView) findViewById(R.id.bmapView); mBaiduMap = mMapView.getMap(); // Open Location Layer mBaiduMap.setMyLocationEnabled(true); // Location initialization mLocClient = new LocationClient(this); mLocClient.registerLocationListener(myListener); LocationClientOption option = new LocationClientOption(); option.setOpenGps(true); // Open gps option.setCoorType("bd09ll"); // Setting coordinate type option.setScanSpan(1000); //option.setNeedDeviceDirect(true); mLocClient.setLocOption(option); mLocClient.start(); } @Override public void onSensorChanged(SensorEvent sensorEvent) { //Each time the direction is changed, the map is re-positioned, and the latitude, longitude and accuracy obtained by the last onReceive Location are used. double x = sensorEvent.values[SensorManager.DATA_X]; if (Math.abs(x - lastX) > 1.0) {// Change direction more than 1 degree before setting, lest arrows on the map rotate too frequently mCurrentDirection = (int) x; locData = new MyLocationData.Builder().accuracy(mCurrentAccracy) // Set the direction information the developer gets here, clockwise 0-360 .direction(mCurrentDirection).latitude(mCurrentLat).longitude(mCurrentLon).build(); mBaiduMap.setMyLocationData(locData); } lastX = x; } @Override public void onAccuracyChanged(Sensor sensor, int i) { } /** * Locating SDK listener function */ public class MyLocationListenner implements BDLocationListener { @Override public void onReceiveLocation(BDLocation location) { // No new receiving location is processed after the map view is destroyed if (location == null || mMapView == null) { return; } // 06-22 16:00:31.872: I/System.out(16196): 39.998954,116.338588 mCurrentLat = location.getLatitude(); mCurrentLon = location.getLongitude(); mCurrentAccracy = location.getRadius(); // System.out.println(mCurrentLat+","+mCurrentLon); locData = new MyLocationData.Builder().accuracy(location.getRadius()) // Set the direction information the developer gets here, clockwise 0-360 .direction(mCurrentDirection).latitude(location.getLatitude()).longitude(location.getLongitude()).build(); mBaiduMap.setMyLocationData(locData); if (isFirstLoc) { isFirstLoc = false; LatLng ll = new LatLng(location.getLatitude(), location.getLongitude()); MapStatus.Builder builder = new MapStatus.Builder(); builder.target(ll).zoom(18.0f); mBaiduMap.animateMapStatus(MapStatusUpdateFactory.newMapStatus(builder.build())); } } } @Override protected void onPause() { mMapView.onPause(); super.onPause(); } @Override protected void onResume() { mMapView.onResume(); super.onResume(); // Register the listener for the direction sensor of the system mSensorManager.registerListener(this, mSensorManager.getDefaultSensor(Sensor.TYPE_ORIENTATION), SensorManager.SENSOR_DELAY_UI); } @Override protected void onStop() { // Cancel Registered Sensor Monitoring mSensorManager.unregisterListener(this); super.onStop(); } @Override protected void onDestroy() { // Destruction Location at Exit mLocClient.unRegisterLocationListener(myListener); mLocClient.stop(); // Close the Location Layer mBaiduMap.setMyLocationEnabled(false); mMapView.onDestroy(); mMapView = null; super.onDestroy(); } }
Other files are retrieved in demo
download Basic Map - Example Code In the BaiduMap_Android SDK_v4.3.1_Sample project, map location corresponds to the LocationDemo class
Don't forget to apply for apikey
There are other needs to download more demo s, you can read more development documents and class reference to develop good habits.
The above article is a summary of my work for your reference. Please correct any mistakes.