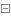
class BenHang extends Card{ /*Constructors and Inheritance of Constructions*/ function __construct($cardno,$pwd, $name,$money){ parent::__construct($cardno,$pwd, $name,$money); } function take($money){ echo "Bank withdrawal{$money}No handling fee·····<br>"; } function zhuan($money){ echo "Bank Transfer{$money}·····<br>"; } } $benhang=new BenHang(123,344,444,444); $benhang->check(); $benhang->take(234); $benhang->zhuan(4555); /*Classes of other bank cards*/ class Qita extends Card{ function __construct($cardno,$pwd, $name,$money){ parent::__construct($cardno,$pwd, $name,$money); } function take($money){ echo "Non-bank withdrawals{$money}There is a handling fee of 2 yuan.·····<br>"; } } $qita=new Qita(123,344,444,444); $qita->check(); $qita->take(99);
Analysis of Three Object-Oriented Characteristics of PHP
PHP's three object-oriented features: inheritance, encapsulation and polymorphism
Inheritance
1. How to realize inheritance?
Use extends keywords for subclasses, and let subclasses inherit parent classes.
class Student extends Person{}
2. Notices for Achieving Inheritance?
(1) Subclasses can only inherit non-private attributes of the parent class.
(2) After the subclass inherits the parent class, it is equivalent to copy ing the attributes and methods of the parent class to the subclass, which can be invoked directly with $this.
(3) PHP can only inherit single class, and does not support one class inheriting multiple classes. But a class has multiple inheritances.
class Person{}
class Chengnian extends Person{}
class Student extends Chengnian{}
// Student class has the properties and methods of Chengnian class and Person class at the same time.
3. Method Coverage (Method Rewriting)
Conditions 1. Subclasses inherit the parent class.
Conditions 2. Subclasses override existing methods of parent classes.
The two conditions mentioned above are called method coverage. After overwriting, the subclass calls the method, which calls the subclass's own method.
Similarly, in addition to method coverage, subclasses can also have attributes with the same name as the parent class for attribute coverage.
4. If the subclass overrides the parent method, how do you call the parent method with the same name in the subclass?
Parent:: Method name ();
Therefore, when a subclass inherits a parent class, the first step in the construction of a subclass is to call the parent class construction to replicate.
function __construct($name,$sex,$school){
parent::__construct($name,$sex);
$this->school = $school;
}
Example 1:
class Person{ protected $name; public $sex; function __construct($name,$sex){ //Declare constructor $this->name = $name; $this->sex = $sex; } function say(){ echo "My name is{$this->name},I am{$this->sex}Life!<br>"; } } class Student extends Person{ //Subclasses inherit parent classes public $school; function __construct($name,$sex,$school){ //Constructors of subclasses parent::__construct($name,$sex); //Call the parent class construct for replication $this->school = $school; } function program(){ echo "PHP What fun! I love PHP!PHP The best programming language in the world!<br>"; } function say(){ parent::say(); //Override the Homonymous Method of the Parent Class echo "I am{$this->school}Of"; } } $zhangsan = new Student("Zhang San","male","Set sail"); $zhangsan->say(); $zhangsan->program();
II. Packaging
class Person{ public $name; public $age; public $sex; function __construct($name, $age,$sex){ $this->name=$name; $this->setAge($age); $this->setSex($sex); } function setAge($age){ if($age>=0&&$age<=120){ return $this->age=$age; }else{ die("Error in age input!!!"); } } function setSex($sex){ if($sex=="female"||$sex=="male"){ return $this->sex=$sex; }else{ die("Error in gender input!!!"); } } function say(){ echo "My name is{$this->name},My age{$this->age},My gender is{$this->sex}<br>"; } } class Work extends Person{private $position; function __construct($name, $age,$sex,$position){ parent::__construct($name, $age,$sex); $this->job=$job; $this->setPosition($position); } function setPosition($position){ $arr=['Chief inspector','Chairman','Programmer','Cleaner']; if(in_array($position, $arr)){ return $this->position=$position; }else{ die("There is no such position."); } } function __set($key,$value){ if($key=="age"){ return parent::setAge($value); } elseif($key=="sex"){ return parent::setSex($value); } elseif($key=="position"){ return $this->setPosition($value); } return $this->$key=$value; } function say(){ parent::say(); echo "My position is{$this->position}"; } } $zhangsan=new Work("Zhang San",22,"male","Chief inspector"); $zhangsan->setSex("female"); $zhangsan->setAge(30); // $zhangsan->setPosition("Chairman"); $zhangsan->position="Chairman"; $zhangsan->name="lisi"; $zhangsan->say();
/*Cartridge Interface * Paper interface*/ interface InkBox{ function color(); } interface Paper{ function sizes(); } class Computer{ function fangfa(InkBox $a,Paper $b){ //Parent Class Reference echo "Printing is about to begin····<br>"; $a->color(); $b->sizes(); echo "Print End···<br>"; } } class Color implements InkBox{ function color(){ echo "Loading color cartridges<br>"; echo "Realization of color cartridge<br>"; } } class White implements InkBox{ function color(){ echo "Loading black and white cartridges<br>"; echo "Implementing black and white ink cartridges<br>"; } } class A4 implements Paper{ function sizes(){ echo "Loading A4 paper<br>"; echo "Realization A4 paper<br>"; } } class A5 implements Paper{ function sizes(){ echo "Realization A5 paper<br>"; } } $com=new Computer();//create object $com->fangfa(new Color(),new A4());//Subclass object