Implementation of SDS
SDS is a simple dynamic string. It is one of the basic data structures of Redis and has a wide range of uses
Overview of basic functions
| function | function | Complexity |
|---|---|---|
| sdsnewlen | Create SDS from given string | O(N) |
| sdslen | Return string length | O(1) |
| sdsdup | Copy an SDS | O(N) |
| sdsfree | Free string space | O(1) |
| sdsavail | Get free space size | O(1) |
| sdsMakeRoomFor | Expand SDS buf space | O(N) |
| sdsgrowzero | Extend the string to the specified length, and fill in more with 0 | O(N) |
| sdscatlen | Concatenate string to end of existing string | O(N) |
| sdscpylen | Copy string to existing SDS | O(N) |
| ... | ... | ... |
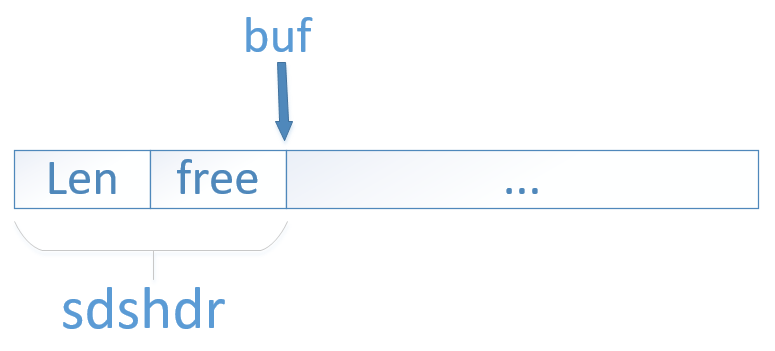
sdshdr structure
/*
* Type alias, used to point to the buf attribute of sdshdr
*/
typedef char *sds;
/*
* Save the structure of string object, obviously sizeof (sdshdr) in 32 bits = 8
*/
struct sdshdr {
// Length of occupied space in buf
int len;
// Length of free space remaining in buf
int free;
// Data space
char buf[];
};The structure of sds is shown in the figure
sdsnewlen
/*
* Create a string of initlen length that init points to
*/
sds sdsnewlen(const void *init, size_t initlen) {
struct sdshdr *sh;
// Select the appropriate memory allocation method according to whether there is initialization content or not
// T = O(N)
if (init) {
// zmalloc does not initialize allocated memory
sh = zmalloc(sizeof(struct sdshdr)+initlen+1);
} else {
// zcalloc initializes all allocated memory to 0
sh = zcalloc(sizeof(struct sdshdr)+initlen+1);
}
// Memory allocation failed, return
if (sh == NULL) return NULL;
// Set initialization length
sh->len = initlen;
// New sds does not reserve any space
sh->free = 0;
// If you specify initialization contents, copy them to buf of sdshdr
// T = O(N)
if (initlen && init)
memcpy(sh->buf, init, initlen);
// Ends with \ 0
sh->buf[initlen] = '\0';
// Return buf part instead of the whole sdshdr
return (char*)sh->buf;
}
sdslen
static inline size_t sdslen(const sds s) {
struct sdshdr *sh = (void*)(s-(sizeof(struct sdshdr)));
return sh->len;
}sdsdup
sds sdsdup(const sds s) {
return sdsnewlen(s, sdslen(s));
}
sdsfree
void sdsfree(sds s) {
if (s == NULL) return;
zfree(s-sizeof(struct sdshdr));
}
zfree was introduced in the previous memory allocation
sdsavail
static inline size_t sdsavail(const sds s) {
struct sdshdr *sh = (void*)(s-(sizeof(struct sdshdr)));
return sh->free;
}sdsMakeRoomFor
/*
* Extend the length of buf in sds to ensure that after function execution
* buf There will be at least addlen + 1 length of free space
* Return value sds: if the extension succeeds, the sds after the extension will be returned; if the extension fails, NULL will be returned
*/
sds sdsMakeRoomFor(sds s, size_t addlen) {
struct sdshdr *sh, *newsh;
// Obtain the current free space length of s
size_t free = sdsavail(s);
size_t len, newlen;
// s the current free space is enough, so there is no need to expand it and return directly
if (free >= addlen) return s;
// Get the length of the space occupied by s
len = sdslen(s);
sh = (void*) (s-(sizeof(struct sdshdr)));
// s minimum required length
newlen = (len+addlen);
// The size required to allocate new space for s based on the new length
if (newlen < SDS_MAX_PREALLOC)
// If the new length is less than SDS? Max? Prealloc
// Then allocate twice as much space for it as you need
newlen *= 2;
else
// Otherwise, the allocation length is the current length plus SDS Max prealloc (1024 * 1024)
newlen += SDS_MAX_PREALLOC;
// T = O(N)
newsh = zrealloc(sh, sizeof(struct sdshdr)+newlen+1);
// Out of memory, allocation failed, return
if (newsh == NULL) return NULL;
// Update the free length of sds
newsh->free = newlen - len;
// Return to sds
return newsh->buf;
}sdsgrowzero
/*
* Expand the sds to the specified length, and fill the unused space with 0. If the given length is smaller than the existing length, directly return
* Return value sds: the new sds is returned after expansion, and NULL is returned after failure
*/
sds sdsgrowzero(sds s, size_t len) {
struct sdshdr *sh = (void*)(s-(sizeof(struct sdshdr)));
size_t totlen, curlen = sh->len;
// If len is smaller than the existing length of the string,
// Then go straight back and do nothing
if (len <= curlen) return s;
s = sdsMakeRoomFor(s,len-curlen);
// If there is not enough memory, return directly
if (s == NULL) return NULL;
/* Make sure added region doesn't contain garbage */
// Fill the newly allocated space with 0 to prevent garbage content
// T = O(N)
sh = (void*)(s-(sizeof(struct sdshdr)));
memset(s+curlen,0,(len-curlen+1)); /* also set trailing \0 byte */
// Update attribute
totlen = sh->len+sh->free;
sh->len = len;
sh->free = totlen-sh->len;
// Return to new sds
return s;
}sdscatlen
/*
* Concatenate a new string to the end of an existing string
*/
sds sdscatlen(sds s, const void *t, size_t len) {
struct sdshdr *sh;
// Original string length
size_t curlen = sdslen(s);
// Expand sds space
// T = O(N)
s = sdsMakeRoomFor(s,len);
// Out of memory? Direct return
if (s == NULL) return NULL;
// Copy the contents of t to the back of the string
sh = (void*) (s-(sizeof(struct sdshdr)));
memcpy(s+curlen, t, len);
// Update attribute
sh->len = curlen+len;
sh->free = sh->free-len;
// Add a new ending symbol
s[curlen+len] = '\0';
// Return to new sds
return s;
}sdscpylen
sds sdscpylen(sds s, const char *t, size_t len) {
struct sdshdr *sh = (void*) (s-(sizeof(struct sdshdr)));
// Length of existing buf of sds
size_t totlen = sh->free+sh->len;
// If the buf length of s does not meet len, then extend it
if (totlen < len) {
// T = O(N)
s = sdsMakeRoomFor(s,len-sh->len);
if (s == NULL) return NULL;
sh = (void*) (s-(sizeof(struct sdshdr)));
totlen = sh->free+sh->len;
}
// Copy content
// T = O(N)
memcpy(s, t, len);
// Add end symbol
s[len] = '\0';
// Update attribute
sh->len = len;
sh->free = totlen-len;
// Return to new sds
return s;
}
Summary
In a continuous memory, the sdshdr header is stored in the front, including string length and free space size, and the specific string is stored in the back. In this way, the string length is O (1), which is easy to implement and has reference significance