New Year's opening, welcome to some praise; this article shares with you the use of Web API to do interface service verification framework, the source of demand is that I intend to make the picture authentication code mentioned above into a service for you, although I have packaged the code open source in the last, but if there is a fast docking service, I think many people would like to use it, at present. This service has been online and published on nuget with the sdk client package (nuget package address: Install-Package ShenNiuApi.SDK). Fortunately, there are 46 downloads in one day (very happy). Perhaps interested friends can visit the nuget official address: Nuget Pack of Shenniu Walking 3 Next, I want to share the architecture of the verification caller involved in publishing the service. I hope you like it. I also hope that you will have more "scanner support" and "recommendation" thanks (I have recently made a clothing store address: Shenniu Wardrobe 3 I hope that friends who need to buy clothes and shoes will be more popular.
Requirements analysis and table structure design of verification architecture
Unified verification of accounts using ActionFilterAttribute of webapi
Sharing of ShenNiuApi.SDK Client Code
NuGet Package Explorer tool is used to generate the nuget package of ShenNiuApi.SDK and publish it on the nuget website.
The next step is to share one footprint:
Requirements analysis and table structure design of verification architecture
Requirements analysis of verification architecture
First of all, for an interface service, there are usually some account restrictions. It is necessary for the caller to pass the correct account to the interface in order to call the successful interface. Here we use the general interface validation of the Internet industry to formulate our requirements:
1. Interface verification needs: account number, password, ip group, Token; password need to be encrypted generally, and there are many encryption methods on the market, such as Md5,3des and so on; ip group, as its name implies, is used to verify whether the ip requested by the caller meets the specified ip bound by the new account opening of the interface party. Distributed invocation is not a new thing for today's Internet industry, so it is needed here. Token is generally a tamper-proof parameter protection measures formulated by the interface side. For both requesters and recipients, the same Token value is needed to respond to the interface, usually a secret key is needed to facilitate encryption.
2. In addition to account validation, some interfaces need to be charged according to the number of calls. So we have the requirement to limit the number of calls. But as a different business interface, the cost may be high. Although the interface provided by the same provider is likely to be fine enough to limit the number of calls per interface, so we design it in this way. True. Business depends on demand.
3. Usually when the other side opens the interface, it will provide the sdk client directly. It is convenient for the caller to directly invoke the method after directly referring to it. It does not need to care about what the request protocol is or the interface method is not right. This way of providing sdk can be used directly only with account number, password, secret key and so on. It is convenient, fast and avoids to some extent. Exposure of interface addresses has many advantages; bad third is like mobile client, as long as the server updates some necessary parameter attributes, it needs the caller to update the sdk package every time, but this is not a matter of fact.
Design of table structure
With the above brief analysis, let's look at the table structure of the database. Here, the database is mainly used to store the corresponding open interface account, password and other information and the corresponding number of calls to the interface:
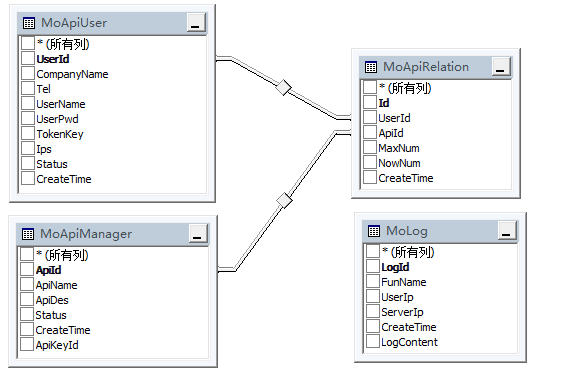
Table: MoApiUser (Account Table), MoApiManager (Interface Method Table), MoApiRelation (Account and Method Table Relation Table, which contains the number of calls) MoLog (Log Table)
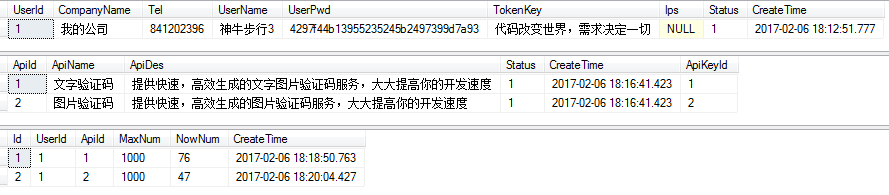
Table data:
Use ActionFilterAttribute to Unify Account Verification
With the above requirements and table design, let's take a look at how to use Action filters to unify verification. Before that, we need to understand: Why not get a parent ApiController and do verification in it to inherit, and use Action filters to do both, but the latter can be used for interfaces that do not require interface accounts? Open, easy to control; Okay, let's look at what's validated in the Action filter, first create the class UserValidateAttribute and inherit the ActionFilterAttribute, and then give her an attribute ApiKeyId, which is used to pass the interface number (that is, the corresponding interface Id, which corresponds to the ApiKeyId in the database table MopiManager) The purpose of doing this is to use numbers to facilitate the statistics of calling an interface in the database, and to limit the number of times that we need to analyze to an interface, not to an account (of course, the former and must be associated with the account), so we define an enumeration that facilitates the number in the corresponding interface:
1 /// <summary>
2///Interface and Database Association Number
3 /// </summary>
4 public enum ApiKeyId
5 {
6
7 Text Verification Code = 1,
8 Picture Verification Code = 2
9
10 }
Then in the filter, the public override void OnAction Executing (System. Web. Http. Controllers. HttpActionContext actionContext) is re-constructed to do non-null verification in OnAction Executing, whether the account password matches, Token's verification, ip group matches, the number of comparisons, so there is the following overall custom filter code:
1 public class UserValidateAttribute : ActionFilterAttribute 2 { 3 4 /// <summary> 5 /// Database and Program Association Label 6 /// </summary> 7 public MoEnumHelper.ApiKeyId ApiKeyId { get; set; } 8 9 public UserValidateAttribute(MoEnumHelper.ApiKeyId apiKeyId) 10 { 11 this.ApiKeyId = apiKeyId; 12 } 13 14 public override void OnActionExecuting(System.Web.Http.Controllers.HttpActionContext actionContext) 15 { 16 17 var response = new MoShenNiuBaseResponse(); 18 var sbLog = new StringBuilder(string.Empty); 19 try 20 { 21 22 if (this.ApiKeyId <= 0) { response.Msg = "The interface is not open yet. Please contact the administrator."; return; } 23 sbLog.AppendFormat("Current services:{0};", this.ApiKeyId); 24 25 var request = actionContext.Request; 26 27 #region Verification 28 29 #region Non empty verification 30 if (actionContext.ActionArguments.Count <= 0) { response.Msg = "The request format is incorrect. Please check it."; return; } 31 var moRequest = actionContext.ActionArguments["request"] as MoShenNiuBaseRequest; 32 33 dynamic httpContext = actionContext.Request.Properties["MS_HttpContext"]; 34 var userIp = httpContext.Request.UserHostAddress; 35 sbLog.AppendFormat("UserName: {0};Ip: {1};Token: {2};UserPwd: {3};", moRequest.UserName, userIp, moRequest.Token, moRequest.UserPwd.ToUpper()); 36 if (string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(moRequest.UserName) || string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(moRequest.UserPwd)) 37 { 38 response.Msg = "Interface account or password cannot be empty"; 39 return; 40 } 41 else if (string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(moRequest.Token)) 42 { 43 response.Msg = "Token Can not be empty"; 44 return; 45 } 46 #endregion 47 48 using (StageEntities db = new StageEntities()) 49 { 50 51 #region Verify that the account exists 52 53 var userInfo = db.MoApiUsers.Where(b => b.UserName.ToUpper() == moRequest.UserName.ToUpper() && b.UserPwd.ToUpper() == moRequest.UserPwd.ToUpper()).SingleOrDefault(); 54 if (userInfo == null) 55 { 56 response.Msg = "Interface account or password error"; 57 return; 58 } 59 #endregion 60 61 #region Get the corresponding account secret key and verify it token 62 63 var newToken = Md5Extend.GetMd5Hash(string.Format("{0}_{1}_{2}", 64 moRequest.UserName.ToUpper(), 65 userInfo.TokenKey.ToUpper(), 66 moRequest.UserPwd.ToUpper())); 67 68 sbLog.AppendFormat("The server TokenKey: {0};Token: {1};", userInfo.TokenKey.ToUpper(), newToken); 69 70 if (!moRequest.Token.Equals(newToken, StringComparison.OrdinalIgnoreCase)) 71 { 72 response.Msg = "Token Validation failed"; 73 return; 74 } 75 #endregion 76 77 #region Account availability 78 if (userInfo.Status != (int)MoEnumHelper.EmStatus.Enable) 79 { 80 response.Msg = "Interface account suspended"; 81 return; 82 } 83 else if (!string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(userInfo.Ips)) 84 { 85 if (!userInfo.Ips.Contains(userIp)) 86 { 87 response.Msg = "Interface ip invalid"; 88 return; 89 } 90 } 91 92 var realationInfo = userInfo.MoApiRelations.Where(b => b.MoApiManager.ApiKeyId == (int)ApiKeyId && b.MoApiManager.Status == (int)MoEnumHelper.EmStatus.Enable).SingleOrDefault(); 93 if (realationInfo == null) 94 { 95 response.Msg = "Interface is not enabled yet. Please try again later."; 96 return; 97 } 98 else if (realationInfo.MaxNum <= realationInfo.NowNum) 99 { 100 response.Msg = "The number of interface calls is full. Please contact the administrator."; 101 return; 102 } 103 #endregion 104 105 //Through validation 106 response.Status = (int)MoEnumHelper.EmStatus.Enable; 107 108 #region Users increase the number of times they authenticate 109 110 realationInfo.NowNum++; 111 var result = db.SaveChanges(); 112 sbLog.AppendFormat("Maximum number of times:{0};Current times:{1};Increase the number of times:{2};", realationInfo.MaxNum, realationInfo.NowNum, result); 113 #endregion 114 } 115 116 #endregion 117 118 119 } 120 catch (Exception ex) 121 { 122 response.Msg = "500 Interface handles request exceptions, please try again later"; 123 sbLog.AppendFormat("Exception information:{0};", ex.Message); 124 } 125 finally 126 { 127 128 sbLog.AppendFormat("Return Status: {0};Msg: {1};", response.Status, response.Msg); 129 //Log 130 StageClass._WrigLog(sbLog.ToString()); 131 132 //Validation Failure Return 133 if (response.Status != (int)MoEnumHelper.EmStatus.Enable || !string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(response.Msg)) 134 { 135 actionContext.Response = new HttpResponseMessage() 136 { 137 138 StatusCode = System.Net.HttpStatusCode.OK, 139 Content = new StringContent(JsonConvert.SerializeObject(response)) 140 }; 141 } 142 } 143 } 144 }
You can read the instructions of the validation step module in the code. It is important to note that the way to get the object parameters passed to the interface by post in the Action filter is: var moRequest = actionContext.ActionArguments["request"] as MoShenNiuBaseRequest; this allows you to get the object data passed by the client directly; and then we can replace it with Controller. The filter defined in the code mainly adds the tag [User Validate (MoEnumHelper.ApiKeyId. Text Verification Code)] above the Action method, and passes the interface called by the caller through MoEnumHelper.ApiKeyId. Text Verification Code. Here I encapsulate the interface of Text Verification Code and Picture Verification Code. As for the code that generates the Verification Code, I have written the previous article. MVC Pseudo-12306 Picture Verification Code The Controller code for the entire web API interface is directly available.
1 /// <summary> 2 /// ShenNiuApi - Interface 3 /// </summary> 4 [RoutePrefix("shenniuapi")] 5 public class ShenNiuController : ApiController 6 { 7 8 /// <summary> 9 /// Text Verification Code 10 /// </summary> 11 /// <param name="request">Verification Code Request request</param> 12 /// <returns>Text Authentication Code Picture Stream</returns> 13 [Route("WenZiValidateCode")] 14 [HttpPost] 15 [UserValidate(MoEnumHelper.ApiKeyId.Text Verification Code)] 16 public MoValidateCodeResponse GetWenZiValidateCode(MoValidateCodeRequest request) 17 { 18 19 var response = new MoValidateCodeResponse(); 20 21 try 22 { 23 //The returned validation code text 24 var code = string.Empty; 25 //Picture flow 26 response.CodeStream = ValidateCode.GetValidateCodeStream(ref code); 27 if (string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(code) || response.CodeStream.Length <= 0) { response.Msg = "Failed to get the authentication code. Please try again later."; return response; } 28 29 response.Code = code; 30 response.Status = (int)MoEnumHelper.EmApiStatus.Success; 31 } 32 catch (Exception ex) 33 { 34 response.Msg = "Failed to get the authentication code. Please try again later."; 35 } 36 37 return response; 38 } 39 40 /// <summary> 41 /// Picture Verification Code 42 /// </summary> 43 /// <param name="request">Verification Code Request request</param> 44 /// <returns>Picture Verification Code Picture Stream and Picture Coordinates to be Verified</returns> 45 [Route("TuPianValidateCode")] 46 [HttpPost] 47 [UserValidate(MoEnumHelper.ApiKeyId.Picture Verification Code)] 48 public MoValidateCodeResponse GetTuPianValidateCode(MoValidateCodeRequest request) 49 { 50 51 var response = new MoValidateCodeResponse(); 52 53 try 54 { 55 //Get the picture type 56 var validateCode = ValidateCode.GetInitImgCode(); 57 if (validateCode == null || string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(validateCode.IndexType)) { response.Msg = "Failed to get the authentication code. Please try again later."; return response; } 58 59 //Generate pictures 60 var imgCode = new List<Stage.Com.Extend.MoImgCode>(); 61 response.CodeStream = ValidateCode.CreateImgValidateStream(validateCode.IndexType, ref imgCode, strLen: 8); 62 if (imgCode.Count <= 0 || response.CodeStream.Length <= 0 || imgCode.Count <= 0) { response.Msg = "Failed to get the authentication code. Please try again later."; return response; } 63 64 //Getting the coordinates of the verification code to be matched 65 foreach (var item in imgCode.Where(b=>b.IsChoice)) 66 { 67 response.ImgCode.Add(new Stage.Model.MoImgCode() 68 { 69 ImgUrl = item.ImgUrl, 70 Index = item.Index, 71 IndexType = item.IndexType, 72 IsChoice = item.IsChoice, 73 Point_A = item.Point_A, 74 Point_B = item.Point_B 75 }); 76 } 77 response.Code = validateCode.IndexType; 78 response.Status = (int)MoEnumHelper.EmApiStatus.Success; 79 } 80 catch (Exception ex) 81 { 82 response.Msg = "Failed to get the authentication code. Please try again later."; 83 } 84 85 return response; 86 } 87 88 }
Is it very simple to feel, in fact, the key point lies in the steps of verification in the filter, to understand what needs to be verified as an interface in order to ensure the security of the interface?
Sharing of ShenNiuApi.SDK Client Code
We also said that the nuget mode of SDK is convenient, fast and secure for the caller to use. Let's first look at the entity classes used by the client.
1 namespace ShenNiuApi.SDK 2 { 3 4 /// <summary> 5 /// Three Enumerations of Shenniu Walking 6 /// </summary> 7 public class MoEnumHelper 8 { 9 10 public enum EmStatus 11 { 12 Prohibit = 0, 13 Enable = 1 14 } 15 } 16 17 /// <summary> 18 /// Interface Verification Base Class 19 /// </summary> 20 public class MoShenNiuBaseRequest 21 { 22 /// <summary> 23 /// Account number 24 /// </summary> 25 public string UserName { get; set; } 26 27 /// <summary> 28 /// Password 29 /// </summary> 30 public string UserPwd { get; set; } 31 32 /// <summary> 33 /// encryption Token(Method: Md5(Account number_Secret key_Password) 34 /// </summary> 35 public string Token { get; set; } 36 37 } 38 39 /// <summary> 40 /// Shenniu interface returns base class 41 /// </summary> 42 public class MoShenNiuBaseResponse 43 { 44 /// <summary> 45 /// Return status: 0: Failure 1: Success 46 /// </summary> 47 public int Status { get; set; } 48 49 /// <summary> 50 /// error message 51 /// </summary> 52 public string Msg { get; set; } 53 } 54 55 /// <summary> 56 /// Verification Code Request Class 57 /// </summary> 58 public class MoValidateCodeRequest : MoShenNiuBaseRequest { } 59 60 /// <summary> 61 /// Verification code return class 62 /// </summary> 63 public class MoValidateCodeResponse : MoShenNiuBaseResponse 64 { 65 66 public MoValidateCodeResponse() 67 { 68 this.ImgCode = new List<MoImgCode>(); 69 } 70 71 /// <summary> 72 /// Verification code type 73 /// </summary> 74 public string Code { get; set; } 75 76 /// <summary> 77 /// Verification Code Picture Stream 78 /// </summary> 79 public byte[] CodeStream { get; set; } 80 81 /// <summary> 82 /// Picture Verification Coordinates 83 /// </summary> 84 public List<MoImgCode> ImgCode; 85 } 86 87 /// <summary> 88 /// Picture Verification Code Coordinates 89 /// </summary> 90 public class MoImgCode 91 { 92 public string Index { get; set; } 93 94 public string IndexType { get; set; } 95 96 public string ImgUrl { get; set; } 97 98 public Point Point_A { get; set; } 99 100 public Point Point_B { get; set; } 101 102 public bool IsChoice { get; set; } 103 } 104 105 }
It includes account entity, verification code request entity and return entity, which is very simple, because there are only two interfaces at present, when I continue to open the interface later, I believe that the client's entity code is far more than this; Look at the method, as a client, there will certainly be entry account, password and other places, I am not here by the way of configuration file input. Instead, it is passed directly through the client class constructor (the default parameter on the constructor is to facilitate friends to use the interface account, if there is a partner who wishes to open the account separately, he can contact me); the client class uses generic T to construct a unified non-empty account verification method, Validate, password and GetBaseRequest method constructed by Token, for the coded account. :
1 /// <summary> 2 /// Get the underlying request format 3 /// </summary> 4 /// <returns></returns> 5 private T GetBaseRequest<T>() where T : MoShenNiuBaseRequest, new() 6 { 7 var baseRequest = new T(); 8 9 baseRequest.UserName = this.UserName; 10 baseRequest.UserPwd = Md5Extend.GetMd5Hash(this.UserPwd); 11 baseRequest.Token = Md5Extend.GetMd5Hash(string.Format("{0}_{1}_{2}", 12 this.UserName.ToUpper(), 13 this.TokenKey.ToUpper(), 14 baseRequest.UserPwd.ToUpper())); 15 16 return baseRequest; 17 } 18 19 /// <summary> 20 /// Non empty verification 21 /// </summary> 22 /// <typeparam name="T"></typeparam> 23 /// <param name="t"></param> 24 public void Validate<T>(T t) 25 where T : MoValidateCodeResponse 26 { 27 if (string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(this.UserName) || 28 string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(this.UserPwd)) { t.Msg = "Account or password cannot be empty"; } 29 else if (string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(this.TokenKey)) 30 { 31 t.Msg = "The secret key cannot be empty"; 32 } 33 }
Well, the following code is directly posted to the corresponding client to invoke the text validation code and image validation code:
1 namespace ShenNiuApi.SDK 2 { 3 public class ShenNiuApiClient 4 { 5 #region attribute 6 7 public string ApiUrl { get; set; } 8 9 /// <summary> 10 /// Account number 11 /// </summary> 12 public string UserName { get; set; } 13 14 /// <summary> 15 /// Password 16 /// </summary> 17 public string UserPwd { get; set; } 18 19 /// <summary> 20 /// Secret key 21 /// </summary> 22 public string TokenKey { get; set; } 23 #endregion 24 25 public ShenNiuApiClient() { } 26 public ShenNiuApiClient(string userName = "Shenniu Walking 3", string userPwd = "123123", string tokenKey="Code changes the world, demand decides everything.", string apiUrl = "http://www.lovexins.com:1001/shenniuapi") 27 { 28 29 this.UserName = userName; 30 this.UserPwd = userPwd; 31 this.TokenKey = tokenKey; 32 this.ApiUrl = apiUrl; 33 } 34 35 /// <summary> 36 /// Get the underlying request format 37 /// </summary> 38 /// <returns></returns> 39 private T GetBaseRequest<T>() where T : MoShenNiuBaseRequest, new() 40 { 41 var baseRequest = new T(); 42 43 baseRequest.UserName = this.UserName; 44 baseRequest.UserPwd = Md5Extend.GetMd5Hash(this.UserPwd); 45 baseRequest.Token = Md5Extend.GetMd5Hash(string.Format("{0}_{1}_{2}", 46 this.UserName.ToUpper(), 47 this.TokenKey.ToUpper(), 48 baseRequest.UserPwd.ToUpper())); 49 50 return baseRequest; 51 } 52 53 /// <summary> 54 /// Non empty verification 55 /// </summary> 56 /// <typeparam name="T"></typeparam> 57 /// <param name="t"></param> 58 public void Validate<T>(T t) 59 where T : MoValidateCodeResponse 60 { 61 if (string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(this.UserName) || 62 string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(this.UserPwd)) { t.Msg = "Account or password cannot be empty"; } 63 else if (string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(this.TokenKey)) 64 { 65 t.Msg = "The secret key cannot be empty"; 66 } 67 } 68 69 /// <summary> 70 /// Getting Text Verification Codes 71 /// </summary> 72 /// <returns></returns> 73 public async Task<MoValidateCodeResponse> GetWenZiValidateCodeAsync() 74 { 75 76 var response = new MoValidateCodeResponse(); 77 try 78 { 79 //Non empty verification 80 Validate(response); 81 if (!string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(response.Msg)) { return response; } 82 83 //Get the basic request settings 84 var request = this.GetBaseRequest<MoValidateCodeRequest>(); 85 86 //json turn 87 var requestStr = JsonConvert.SerializeObject(request); 88 //Send request 89 var returnStr = string.Empty; 90 using (HttpClient client = new HttpClient()) 91 { 92 client.Timeout = TimeSpan.FromSeconds(60); 93 var stringContent = new StringContent(requestStr, Encoding.UTF8, "application/x-www-form-urlencoded"); 94 stringContent.Headers.ContentType = new MediaTypeHeaderValue("application/json"); 95 96 var httpResponseMessage = client.PostAsync(this.ApiUrl + "/WenZiValidateCode", stringContent).Result; 97 var stream = await httpResponseMessage.Content.ReadAsStreamAsync(); 98 using (StreamReader reader = new StreamReader(stream)) 99 { 100 returnStr = await reader.ReadToEndAsync(); 101 } 102 } 103 if (string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(returnStr)) 104 { 105 106 return response; 107 } 108 //analysis 109 response = JsonConvert.DeserializeObject<MoValidateCodeResponse>(returnStr); 110 } 111 catch (Exception ex) 112 { 113 response.Msg = ex.Message; 114 } 115 return response; 116 } 117 118 119 /// <summary> 120 /// Getting Picture Verification Code 121 /// </summary> 122 /// <returns></returns> 123 public async Task<MoValidateCodeResponse> GetTuPianValidateCodeAsync() 124 { 125 126 var response = new MoValidateCodeResponse(); 127 try 128 { 129 //Non empty verification 130 Validate(response); 131 if (!string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(response.Msg)) { return response; } 132 133 //Get the basic request settings 134 var request = this.GetBaseRequest<MoValidateCodeRequest>(); 135 136 //json turn 137 var requestStr = JsonConvert.SerializeObject(request); 138 //Send request 139 var returnStr = string.Empty; 140 using (HttpClient client = new HttpClient()) 141 { 142 client.Timeout = TimeSpan.FromSeconds(60); 143 var stringContent = new StringContent(requestStr, Encoding.UTF8, "application/x-www-form-urlencoded"); 144 stringContent.Headers.ContentType = new MediaTypeHeaderValue("application/json"); 145 146 var httpResponseMessage = client.PostAsync(this.ApiUrl + "/TuPianValidateCode", stringContent).Result; 147 var stream = await httpResponseMessage.Content.ReadAsStreamAsync(); 148 using (StreamReader reader = new StreamReader(stream)) 149 { 150 returnStr = await reader.ReadToEndAsync(); 151 } 152 } 153 if (string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(returnStr)) 154 { 155 156 return response; 157 } 158 //analysis 159 response = JsonConvert.DeserializeObject<MoValidateCodeResponse>(returnStr); 160 } 161 catch (Exception ex) 162 { 163 response.Msg = ex.Message; 164 } 165 return response; 166 } 167 168 } 169 }
NuGet Package Explorer tool is used to generate the nuget package of ShenNiuApi.SDK and publish it on the nuget website.
Because we want to publish Sdk's nuget package, we need to pack it. Instead of using the nuget command, we use the NuGet Package Explorer tool to pack it. After installing the tool first, we open a screen like this:
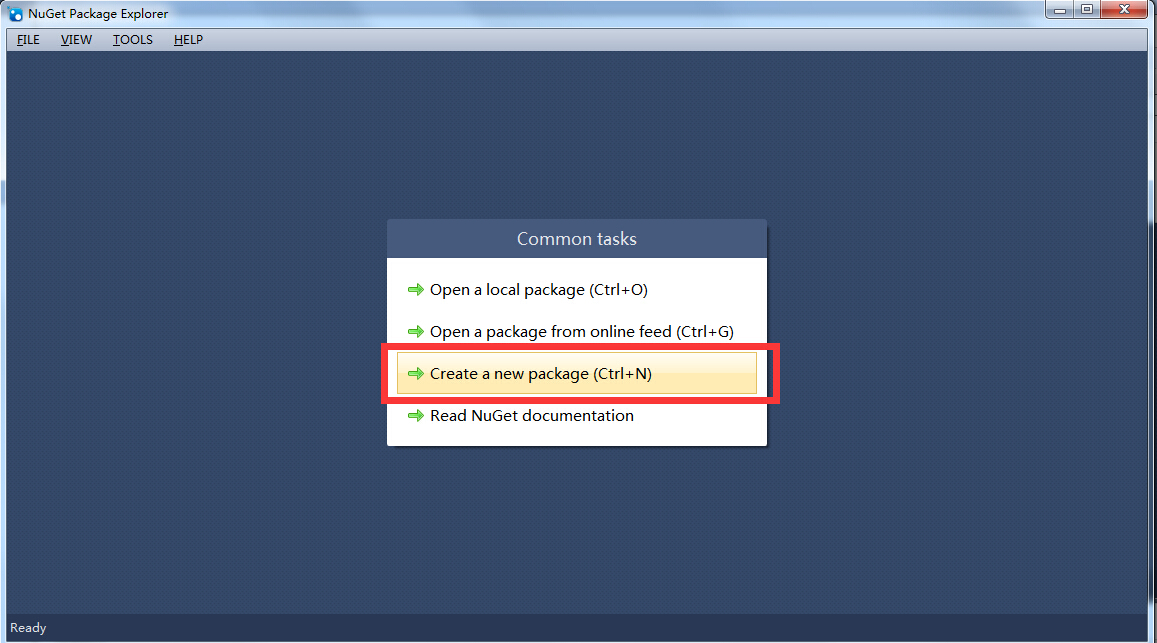
We select the options as shown in the figure above, and then select "Edit Options":
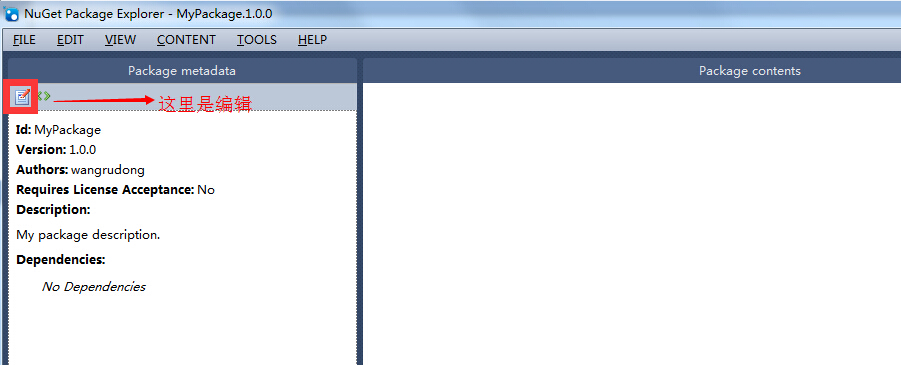
Then enter the following information, you can also enter more information about dependencies and other options:
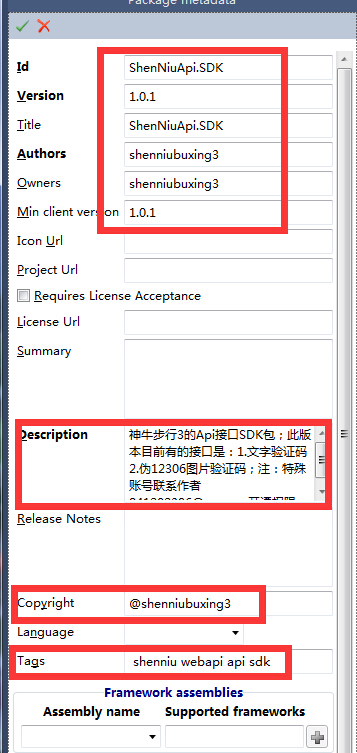
This information is my published sdk, you can not fill in so detailed haha, remember to fill in and then click on the green hook (save) just in the position, well the next focus is on the right side of the tool in the "Package Contents" area ="right mouse =" select the options shown in the following figure:
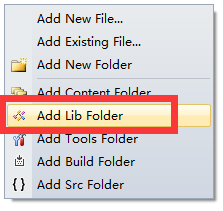
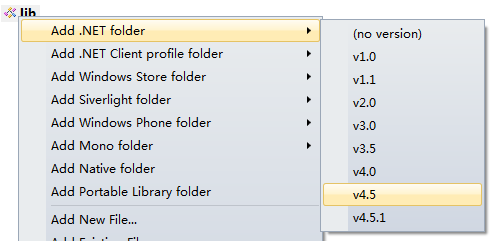
This option means adding class library dll. After clicking on it, a "Lib" appears. Then right-click Lib and select "Add.Net Folder"="and"V4.5", which is the version of your packaged project. My version is applicable to 4.5, as follows:
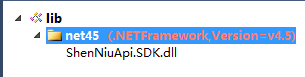
Then directly drag the dll generated under your project bin (ShenNiuApi.SDK.dll here) to the "Package Contents" area and to the "V4.5" level. The effect is as follows:
The last step is to "save" our nuget file. First, click "File" = "Save" in the upper left corner of the tool. If you have a hint about where to save the package file, you can see your nuget package under the folder you saved.
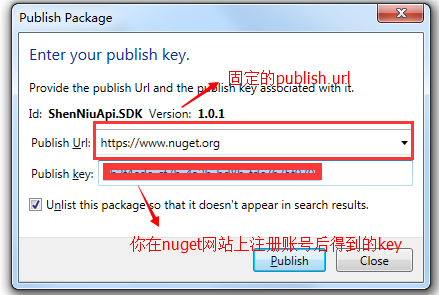
How to use the tool is not very simple, you successfully generated your own nuget package; if you want to package your package to be published to nuget all over the world. net apes use it, or use the tool "File" = "publish" = "figure:"?
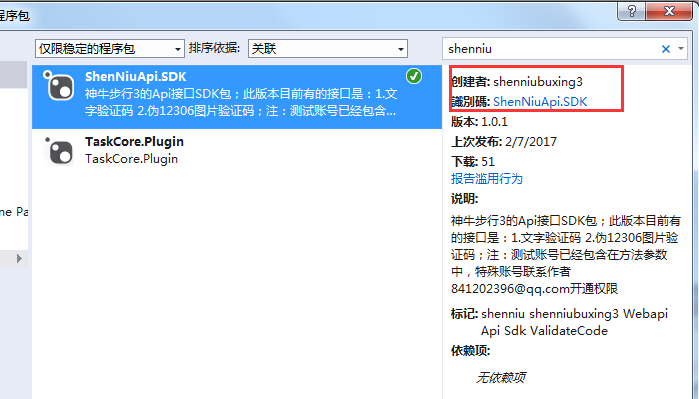
It's not a bad surprise that your nuget package was released, and you can see it through search package in vs. For example, my package here:
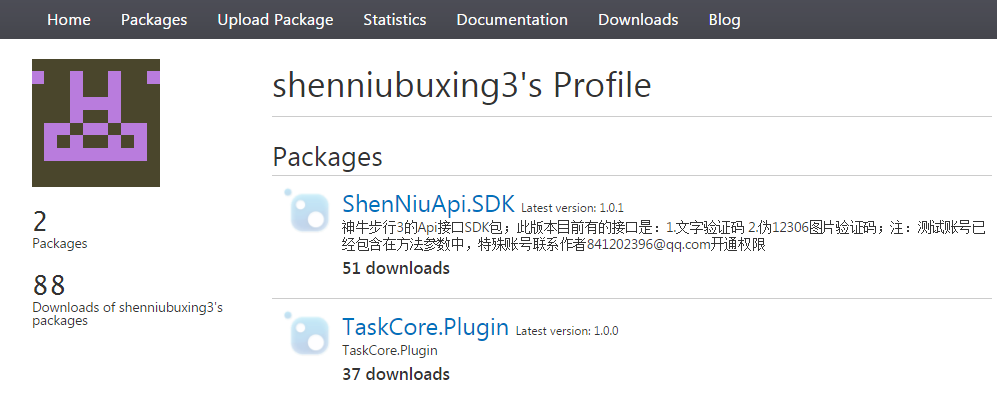
Would it be very exciting to receive your own nuget package? Haha, I also downloaded 51 sdk downloads in two days when the screenshot was released at the moment. Good. Description on the website:?
At this point, the content of this chapter is over, I hope to bring you learning help. If you thank me and consider buying a pair of shoes and clothes, you might as well come to my younger brother's clothing store to see: Shenniu Wardrobe 3 Thank you very much for your support and for your many compliments.