Learning today
Part I: pandas package
1, Introduction to pandas
pandas: a set of tools for analyzing structured data in python.
Based on numpy: providing high performance matrix operation
Graph library matplotlib: provide data visualization
2, pandas basic operation
1. Creation and basic operation of one-dimensional and two-dimensional arrays:
import numpy as np import pandas as pd s = pd.Series([1,2,3,4,np.NaN]) #One dimensional data Series in pandas dates = pd.date_range('20200301',periods=6) # Two dimensional array DataFrame, row index and column index in pandas #Create DataFrame method 1: data = pd.DataFrame(np.random.randn(6,4),index=dates,columns=list('abcd')) data Out[12]: a b c d 2020-03-01 0.974217 1.415198 0.449173 0.309444 2020-03-02 -0.783394 1.642082 1.929648 -1.730744 2020-03-03 -1.412779 2.459838 0.793193 1.093348 2020-03-04 -2.860147 -1.633533 1.972606 -1.106984 2020-03-05 1.312970 -0.240283 -0.411076 -0.175680 2020-03-06 -0.277543 -0.525772 0.556319 0.938473 #Create DataFrame method 2: d = {'A':1,'B':pd.Timestamp('20200301'),'C':range(4)} df = pd.DataFrame(d,index = list('abcd')) df Out[16]: A B C a 1 2020-03-01 0 b 1 2020-03-01 1 c 1 2020-03-01 2 d 1 2020-03-01 3 ------------------------ df.head(2) #Output first 2 lines, default 5 lines Out[25]: A B C a 1 2020-03-01 0 b 1 2020-03-01 1 df.tail(1) #1 line after output, 5 lines by default Out[26]: A B C d 1 2020-03-01 3
For a 2D array df:
df.index ---- return row index
df.columns ---- return column index
df.values ---- array of returned values
df.describe() -- return some data of the array
2. ranking:
1) Sort by index, axis=0 by column index, axis=1 by row index, and acsending is in ascending order. The default is True:
data.sort_index(axis=1,ascending=False) Out[30]: d c b a 2020-03-01 0.309444 0.449173 1.415198 0.974217 2020-03-02 -1.730744 1.929648 1.642082 -0.783394 2020-03-03 1.093348 0.793193 2.459838 -1.412779 2020-03-04 -1.106984 1.972606 -1.633533 -2.860147 2020-03-05 -0.175680 -0.411076 -0.240283 1.312970 2020-03-06 0.938473 0.556319 -0.525772 -0.277543
2) Sort by value:
data.sort_values(by='a') Out[34]: a b c d 2020-03-04 -2.860147 -1.633533 1.972606 -1.106984 2020-03-03 -1.412779 2.459838 0.793193 1.093348 2020-03-02 -0.783394 1.642082 1.929648 -1.730744 2020-03-06 -0.277543 -0.525772 0.556319 0.938473 2020-03-01 0.974217 1.415198 0.449173 0.309444 2020-03-05 1.312970 -0.240283 -0.411076 -0.175680
3. Selection: compared with the slower location index data[2:4], the index speed is faster through tag. loc() and number. iloc() (judgment is omitted):
data.loc[:,['b','c']] Out[46]: b c 2020-03-01 1.415198 0.449173 2020-03-02 1.642082 1.929648 2020-03-03 2.459838 0.793193 2020-03-04 -1.633533 1.972606 2020-03-05 -0.240283 -0.411076 2020-03-06 -0.525772 0.556319 data.iloc[1:3,:3] Out[47]: a b c 2020-03-02 -0.783394 1.642082 1.929648 2020-03-03 -1.412779 2.459838 0.793193
4. Processing of DataFrame data:
For the processing of np.NaN (not a number), NaN does not participate in the calculation: df1.dropna(how='any '). If there is NaN, the whole line will be discarded df1.fillna(value=5) × replace NaN with a value
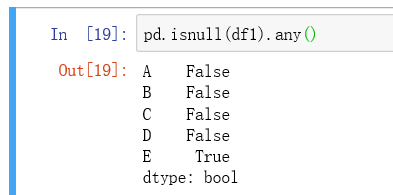
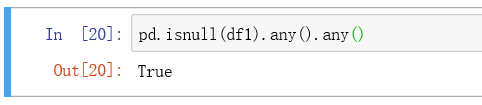
5. The difference between. any() and. all():
. any() -- treat a sequence as a whole and return True if one of the conditions is satisfied
. all() -- treat a sequence as a whole, and return True if each of them meets the conditions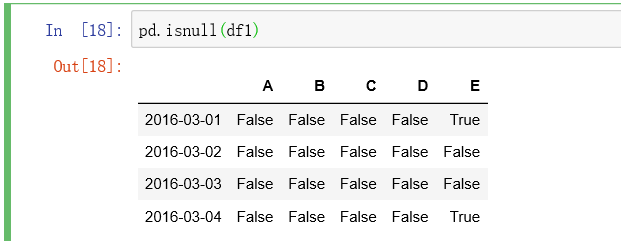
 6. statistics:
6. statistics:
df1.mean(axis=1) --- returns an array of average values per row (default axis=0, return average values per column)
df1.sum(axis=1) --- returns the array of the sum of values in each row (default axis=0, returns the sum of values in each column)
df.sub(s, axis = 'index') -- subtract s array from 2D array df by column
df.apply(func) --- incoming function. By default, the data in each column is transferred into the function (axis=0). The apply function will traverse the data in each row of DataFrame and return a Series data structure
Group statistics:
df.groupby('A ') or df.groupby(['A','b ']) -- group with label A, or labels A and B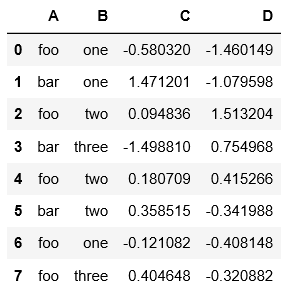
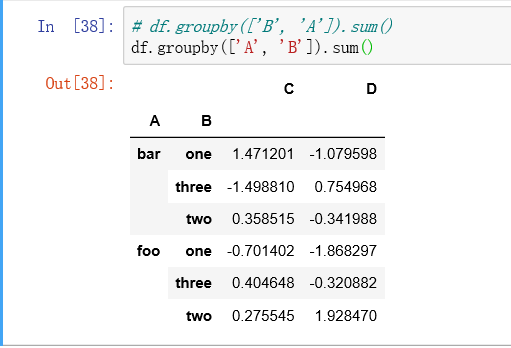
7. Data consolidation:
1) Vertical merge: pd.concat([xxx,xxx])
df1 = pd.concat([df.iloc[:3], df.iloc[3:7], df.iloc[7:]])
2) Merge with column label: pd.merge()
pd.merge(left, right, on = 'key') -- merge left and right according to 'key'
3) Add a row of data:
df.append(s,ignore_index=True)
8. Data perspective:
1)pivot table / axial rotation table:
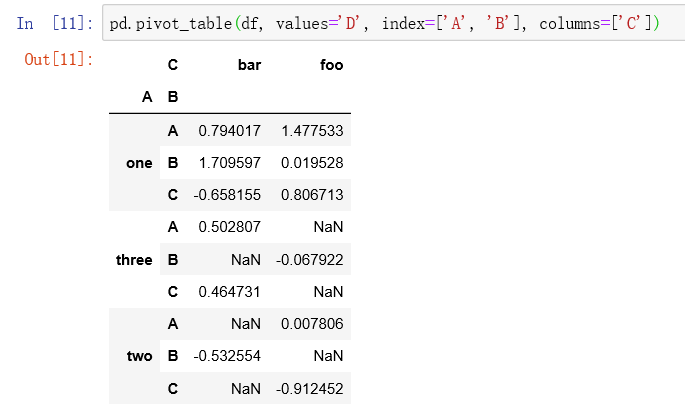
PD. Pivot table (df, values = 'd', index = ['a ','b'], columns = ['c ') -- operate on df. The value is the value of column D, row index is the value of column A and B, and column index is the value of column C.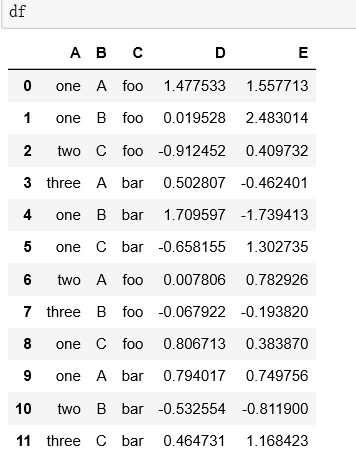
2)df[df.A = = 'one']. groupby('c '). mean() -- for the row with a column as one in df, group by the value of C column, and return the average value of D and E columns.
9. Time series:
rng = pd.date_range('20160301 ', periods=600, freq =' s') -- in date form, cycle is 600, unit is s second, default is' D ', unit is day.
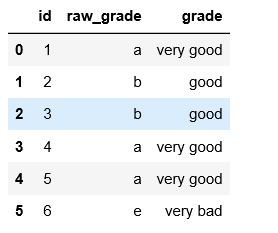
10.category:
df = pd.DataFrame({"id":[1,2,3,4,5,6], "raw_grade":['a', 'b', 'b', 'a', 'a', 'e']}) df["grade"] = df["raw_grade"].astype("category") df["grade"].cat.categories out: Index([u'a', u'b', u'e'], dtype='object') df["grade"].cat.categories = ["very good", "good", "very bad"]