In general, a cloud function completes a single logical function, which is the same method as a class, as shown in the figure:
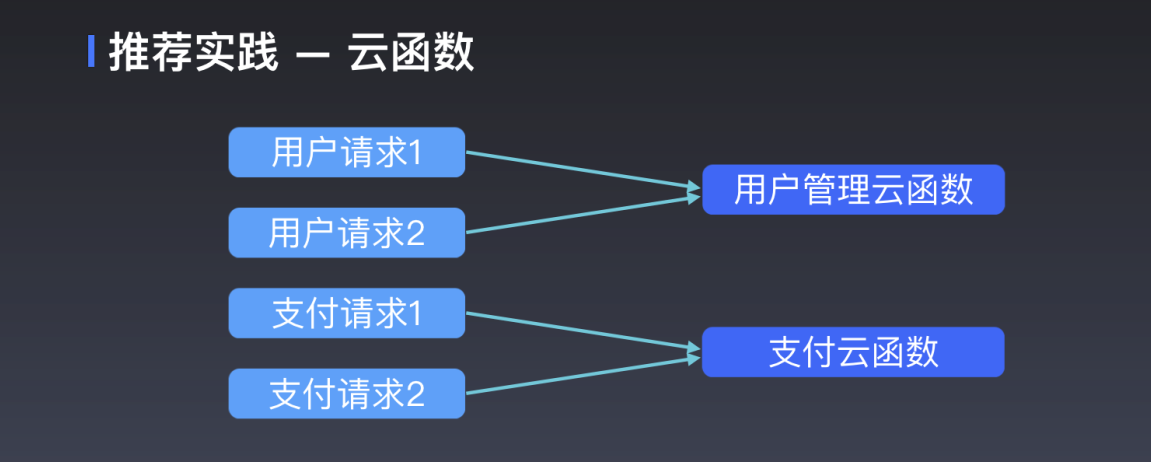
However, limited free users can only use 20 cloud functions at most. To realize multiple complex functions in a single cloud function, it is necessary to distinguish them by parameters, which is not easy to read and manage. By routing, we try to categorize requests. A cloud function handles certain types of requests, such as those dealing with users or paying. As shown in the picture:
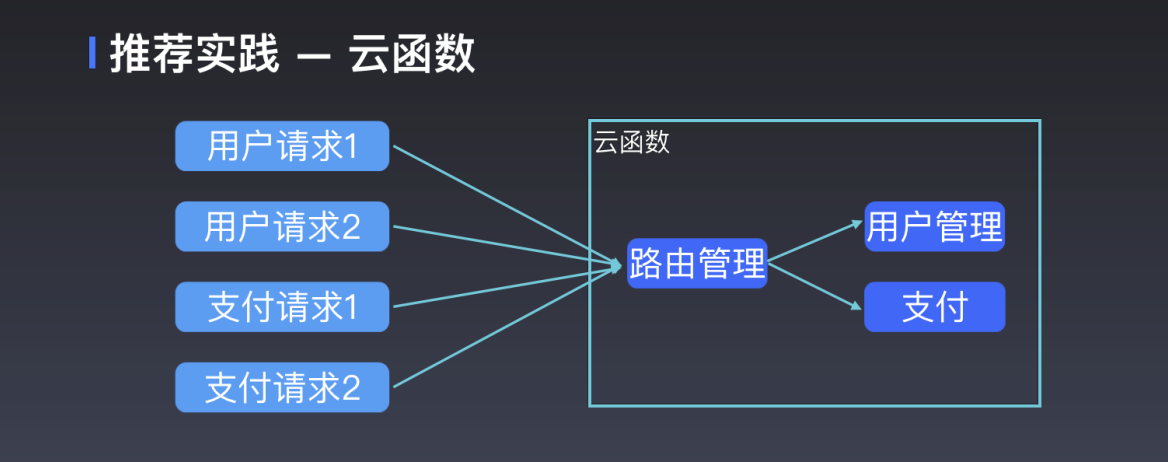
In order to facilitate your trial, Tencent Cloud Base team developed tcb-router, cloud function routing management library for your use.
Developing lightweight routing libraries of cloud functions based on koa-style small programs and cloud, which are mainly used to optimize service-side function processing logic
Use
npm install --save tcb-router
Cloud function end
// index.js of cloud function
const TcbRouter = require('./router');
exports.main = (event, context) => {
const app = new TcbRouter({ event });
// app.use indicates that the middleware will be applicable to all routes
app.use(async (ctx, next) => {
ctx.data = {};
await next(); // Execute the next Middleware
});
// Routing is represented as an array, and the middleware is suitable for both user and timer routes.
app.router(['user', 'timer'], async (ctx, next) => {
ctx.data.company = 'Tencent';
await next(); // Execute the next Middleware
});
// Routing is a string, and this middleware is only applicable to user routing
app.router('user', async (ctx, next) => {
ctx.data.name = 'heyli';
await next(); // Execute the next Middleware
}, async (ctx, next) => {
ctx.data.sex = 'male';
await next(); // Execute the next Middleware
}, async (ctx) => {
ctx.data.city = 'Foshan';
// ctx.body returns data to the small program side
ctx.body = { code: 0, data: ctx.data};
});
// Routing is a string, and this middleware is only suitable for timer routing
app.router('timer', async (ctx, next) => {
ctx.data.name = 'flytam';
await next(); // Execute the next Middleware
}, async (ctx, next) => {
ctx.data.sex = await new Promise(resolve => {
// Wait 500 ms to execute the next Middleware
setTimeout(() => {
resolve('male');
}, 500);
});
await next(); // Execute the next Middleware
}, async (ctx)=> {
ctx.data.city = 'Taishan';
// ctx.body returns data to the small program side
ctx.body = { code: 0, data: ctx.data };
});
return app.serve();
}tips: The node environment of the applet cloud function supports the async/await grammar by default. It is recommended that the asynchronous operations involved be used as in demo.
Small program end
// Call a cloud function called router and route it with the name user
wx.cloud.callFunction({
// The name of the cloud function to be invoked
name: "router",
// Parameters passed to cloud functions
data: {
$url: "user", // The path of the route to be invoked, passing in the exact path or wildcard character*
other: "xxx"
}
});For a complete example, please refer to my other blog: Share SDK, a cloud function short message platform developed with tcb-router routing, Please add link description