Three ways to assign personal tasks
User task is the task of user operation. Personal task is one of user tasks. This blog will briefly introduce three ways to assign personal tasks.
I. flow chart
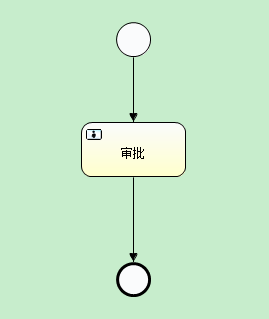
Figure 1 flow chart of user task allocation
2. Method 1: directly appoint the handler
1. Configure task nodes in the flowchart
Figure 2 configure task node handler
2.test Code
ProcessEngine processEngine = ProcessEngines.getDefaultProcessEngine();
//Deploy process definition and start process instance
@Test
public void testTask() throws Exception {
// 1 release process
InputStream inputStreamBpmn = this.getClass().getResourceAsStream("taskProcess.bpmn");
InputStream inputStreamPng = this.getClass().getResourceAsStream("taskProcess.png");
processEngine.getRepositoryService()//
.createDeployment()//
.addInputStream("userTask.bpmn", inputStreamBpmn)//
.addInputStream("userTask.png", inputStreamPng)//
.deploy();
// 2 start up process
//Set process variables when starting process instances
ProcessInstance pi = processEngine.getRuntimeService()//
.startProcessInstanceByKey("taskProcess");
System.out.println("pid:" + pi.getId());
}
//Query my personal task list
@Test
public void findMyTaskList(){
String userId = "zhangsan111";
List<Task> list = processEngine.getTaskService()//
.createTaskQuery()//
.taskAssignee(userId)//Specify personal task query
.list();
for(Task task:list ){
System.out.println("id="+task.getId());
System.out.println("name="+task.getName());
System.out.println("assinee="+task.getAssignee());
System.out.println("createTime="+task.getCreateTime());
System.out.println("executionId="+task.getExecutionId());
}
}
//Finish the task
@Test
public void completeTask(){
String taskId = "3209";
processEngine.getTaskService()//
.complete(taskId);//
System.out.println("Finish the task");
}Note: in the above example, Zhou Jiangxiao is the manager of individual tasks; however, the manager who assigns tasks in this way is not flexible enough, because he is responsible for
The handler of the service should not put it in the XML file.
3. Mode 2: directly appoint the handler
1. Configure task node variables in flowchart

Figure 3 configure task node variables
2. Test code
package cn.gome.k_personTask;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import org.activiti.engine.ProcessEngine;
import org.activiti.engine.ProcessEngines;
import org.activiti.engine.repository.Deployment;
import org.activiti.engine.runtime.ProcessInstance;
import org.activiti.engine.task.Task;
import org.junit.Test;
public class TaskTest {
//Process engine object
ProcessEngine processEngine = ProcessEngines.getDefaultProcessEngine();
/**Deploy process definition + start process instance*/
@Test
public void deployementAndStartProcess(){
InputStream inputStreamBpmn = this.getClass().getResourceAsStream("task.bpmn");
InputStream inputStreampng = this.getClass().getResourceAsStream("task.png");
//Deployment process definition
Deployment deployment = processEngine.getRepositoryService()//
.createDeployment()//Create deployment object
.addInputStream("task.bpmn", inputStreamBpmn)//Deploy load resource file
.addInputStream("task.png", inputStreampng)
.name("Personal task presentation")
.deploy();
System.out.println("deploy ID: "+deployment.getId());
//Start process instance
/**
* At the same time of starting the process instance, set the process variable to set the handler of the next task in the way of process variable
* The name of the process variable is the userID of {userID} defined in task.bpmn
* The value of process variable is the handler of task
*/
Map<String, Object> variables = new HashMap<String, Object>();
variables.put("userID", "zhangsan111");
ProcessInstance pi = processEngine.getRuntimeService()//
.startProcessInstanceByKey("task",variables);//Start the process with the latest version of the key defined by the process
System.out.println("Process instance ID: "+pi.getId());
System.out.println("Process defined ID: "+pi.getProcessDefinitionId());
}
/**Query my personal tasks*/
@Test
public void findPersonalTaskList(){
//Task Manager
String assignee = "zhangsan111";
List<Task> list = processEngine.getTaskService()
.createTaskQuery()
.taskAssignee(assignee)//Personal task query
.list();
if(list!=null && list.size()>0){
for(Task task:list){
System.out.println("task ID: "+task.getId());
System.out.println("Task Manager:"+task.getAssignee());
System.out.println("Task name:"+task.getName());
System.out.println("Task created:"+task.getCreateTime());
System.out.println("Process instance ID: "+task.getProcessInstanceId());
System.out.println("#######################################");
}
}
}
/**Finish the task*/
@Test
public void completeTask(){
//Task ID
String taskId = "5209";
processEngine.getTaskService()
.complete(taskId);
System.out.println("Complete the task:"+taskId);
}
}4. Mode 3: Usage
Tasklistenerimpl class, used to set the task handler
package cn.gome.l_personTask;
import org.activiti.engine.delegate.DelegateTask;
import org.activiti.engine.delegate.TaskListener;
public class TaskListenerImpl implements TaskListener{
/**Set the task handler (individual task and group task)*/
@Override
public void notify(DelegateTask delegateTask) {
//Assign personal tasks
delegateTask.setAssignee("zhangsan");
}
} Configure task node listening in flowchart
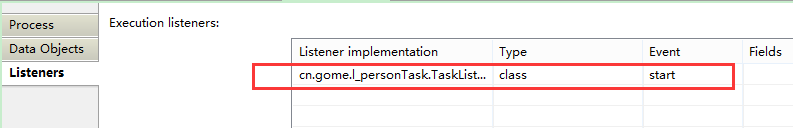
Figure 4 configure task node listening in the flowchart