
ACL Access Control List Structure Diagram
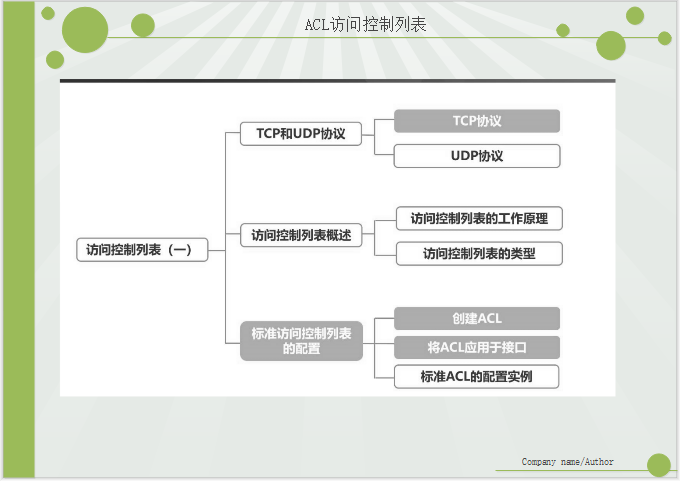
Objective of this chapter
Learn TCP and UDP protocols
Overview of access control list, how access control list works
Type of access control list.
Configuration of standard access control class table
Create ACL
Apply ACLy to interface
Configuration instance of standard ACL
I. access control list (ACL)
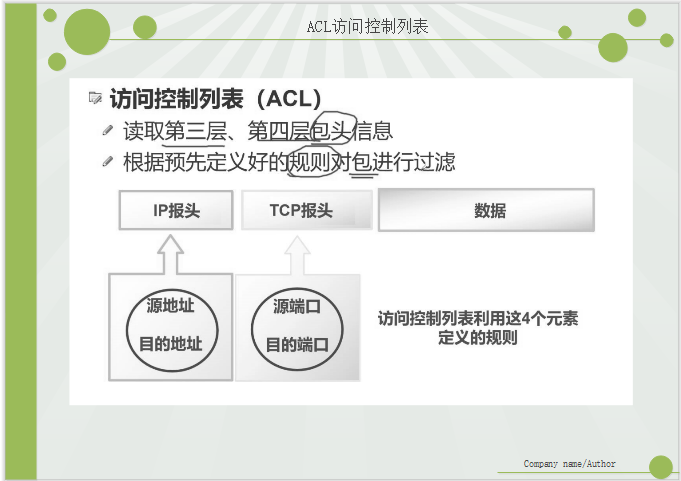
2. TCP port number to be backed up
| port | Agreement | Explain |
|---|---|---|
| 20 | FTP | FTP server data connection |
| 21 | FTP | FTP service open control port |
| 22 | ssh | Remote login |
| 23 | TELNET | For remote login, remote login can be used to control and manage the target computer |
| 25 | SMTP | smtp server open port for sending mail |
| 53 | DNS | DNS port |
| 67 | DHCP | DHCP server |
| 68 | DHCP | DHCP client |
| 80 | HTTP | Hypertext transfer |
| 110 | POP3 | For receiving mail |
| 443 | HTTPS | Simple text transfer |
III. working principle of access control list

IV. Processing of Access Control List
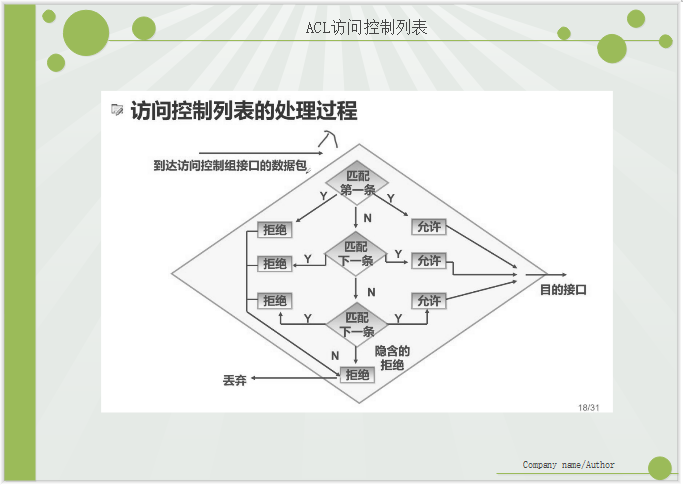
Match the first one. Know that there will be an implicit denial at the end of the last one. By default, all host accesses except those you allow will be denied.

V. types of access control lists

Vi. experiments in this chapter
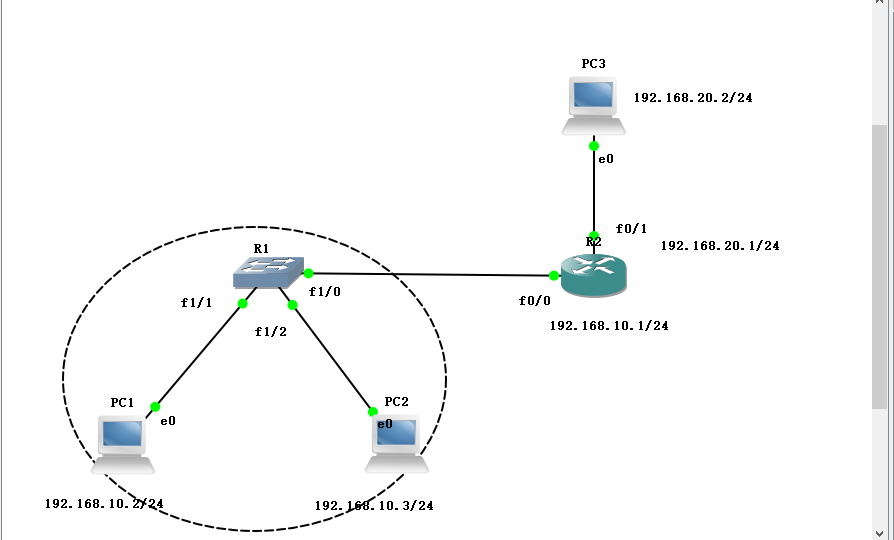
PC1: 192.168.10.2/24
PC2: 192.168.10.3/24
PC3: 192.168.20.2/24
1. Configure switch R1
Turn off the routing function, enter the port configuration rate, and configure the full duplex mode.
R1#conf t Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. R1(config)#no ip routing R1(config)#int f1/0 R1(config-if)#speed 100 R1(config-if)#dup full R1(config-if)#
2. Configure router R2
Input interface with address
R2#conf t
R2(config)#int f0/0
R2(config-if)#ip add 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0
R2(config-if)#no shut
R2(config-if)#int f0/
R2(config-if)#int f0/1
R2(config-if)#ip add 192.168.20.1 255.255.255.0
R2(config-if)#no shut
R2(config-if)#do show ip route
Codes: C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2
i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2
ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route
o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route
Gateway of last resort is not set
C 192.168.10.0/24 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0
C 192.168.20.0/24 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/13. Configure IP address for PC
1. IP address and gateway to PC 1
ip 192.168.10.2 192.168.10.1
2. IP address and gateway to PC 2
ip 192.168.10.3 192.168.10.1
3. IP address and gateway to PC 3
PC3> ip 192.168.20.2 192.168.20.1 Checking for duplicate address... PC1 : 192.168.20.2 255.255.255.0 gateway 192.168.20.1
4. Test the communication between PC s
PC3> ping 192.168.10.2 192.168.10.2 icmp_seq=1 timeout 84 bytes from 192.168.10.2 icmp_seq=2 ttl=63 time=19.967 ms 84 bytes from 192.168.10.2 icmp_seq=3 ttl=63 time=21.941 ms 84 bytes from 192.168.10.2 icmp_seq=4 ttl=63 time=15.958 ms 84 bytes from 192.168.10.2 icmp_seq=5 ttl=63 time=15.959 ms PC3> ping 192.168.10.3 192.168.10.3 icmp_seq=1 timeout 84 bytes from 192.168.10.3 icmp_seq=2 ttl=63 time=11.968 ms 84 bytes from 192.168.10.3 icmp_seq=3 ttl=63 time=11.970 ms 84 bytes from 192.168.10.3 icmp_seq=4 ttl=63 time=19.946 ms 84 bytes from 192.168.10.3 icmp_seq=5 ttl=63 time=15.921 ms
5. Create ACL Standard Access Control List on Router
R1(config)#access-list 1 deny host 192.168.10.2 / / deny 192.168.10.2 host access. Host represents a fixed address. You can also write an inverse code after the address.
R1(config)#Access list 1 permit any / / allows all other hosts to access. Any represents all addresses and can also write an inverse code after the address.
R1(config)#int f0/0
R1(config-if)#IP access group 1 in / / the direction to configure the interface
R1(config-if)#Do show access list / / view ACL control list
Standard IP access list 1
10 deny 192.168.10.2
20 permit any6. Verify whether PC1 can access PC3
PC1> ping 192.168.20.2 *192.168.10.1 icmp_seq=1 ttl=255 time=31.223 ms (ICMP type:3, code:13, Communication administratively prohibited) *192.168.10.1 icmp_seq=2 ttl=255 time=15.618 ms (ICMP type:3, code:13, Communication administratively prohibited) *192.168.10.1 icmp_seq=3 ttl=255 time=15.621 ms (ICMP type:3, code:13, Communication administratively prohibited) *192.168.10.1 icmp_seq=4 ttl=255 time=15.622 ms (ICMP type:3, code:13, Communication administratively prohibited) *192.168.10.1 icmp_seq=5 ttl=255 time=15.620 ms (ICMP type:3, code:13, Communication administratively prohibited)
7.PC1 can access PC2
PC1> ping 192.168.10.3 84 bytes from 192.168.10.3 icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=0.000 ms 84 bytes from 192.168.10.3 icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=0.000 ms 84 bytes from 192.168.10.3 icmp_seq=3 ttl=64 time=0.000 ms 84 bytes from 192.168.10.3 icmp_seq=4 ttl=64 time=0.000 ms 84 bytes from 192.168.10.3 icmp_seq=5 ttl=64 time=0.000 ms