8. abstract, static and final modifiers
8.1 abstract
-
Class abstract class
Abstract classes can only declare references and cannot create objects
For subclasses to inherit
In life, an abstract class is a parent class abstracted from different subclasses. It does not have its own objects, such as animals and vehicles
-
Method abstract method
Only the method declaration, no method implementation, and the method implementation part is semicolon
It only declares what functions the object has, and does not define how the object implements this function
8.1.2 relationship between abstract classes and abstract methods
If a class has abstract methods, the class must be abstract
Abstract methods do not necessarily exist in abstract classes
Subclasses inherit abstract classes. If subclasses do not want to become abstract classes, they must implement all abstract methods in the parent class
A reference can call all methods declared in its reference type, including abstract methods
The declaration and implementation are separated. The declaration is in the parent class and the implementation is left to the child class ----- the commonness of the data class is placed in the parent class
8.1.3 the role of polymorphism and abstraction
-
Improve weak coupling of code
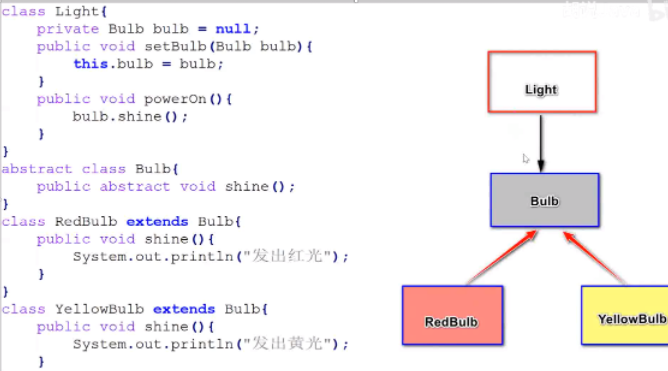
Abstract classes can be used as convenience, and specify the method specifications that the object should have
Weak coupling is achieved by isolating the user of the standard from the implementation of the standard
8.2 static
-
Static properties of member variables (properties)
The whole class is common and does not belong to any object
It can be accessed directly with the class name
-
Method static method
Can be called directly with the class name
Static methods can only access static members of a class, not non static members of a class, and this cannot occur
Subclasses can override the static methods of the parent class with static methods, without polymorphism
If we call a static method on a reference, the compiler will change the code to: call a static method on a reference type
package day05; /** * @author Xiaobai, sun Jiayao wants yangshijun * static static state */ public class textStatic { public static void main(String[] args) { Myclass mc1 =new Myclass(); Myclass mc2 =new Myclass(); mc1.a++; mc2.b++; System.out.println(mc2.a); System.out.println(mc2.b);//21 System.out.println(Myclass.b); Myclass mc = new Myclass(); mc.print(); Myclass.print();//Static methods are called directly with the class name ClassA a=new ClassB(); a.method();//It becomes ClassA.method() during execution; } } class Myclass{ int a=10; static int b= 20; public static void print(){ //System.out.println(a); error! Static methods can only access static members of a class, not non static members of a class System.out.println(b); } } class ClassA{ public static void method(){ System.out.println("ClassA method"); } } class ClassB extends ClassA { public static void method(){ System.out.println("Class B method"); } } -
Initial code block static initial code block
class A{
static {
Systerm.out.println("Init A");
}
}-
Execute once when the class is loaded
Class loading: when the JVM uses a class for the first time, it needs to read the bytecode file corresponding to the class into the JVM, so as to obtain all the information of the class (class parent, which properties, methods, construction methods, etc.) and save it. (saved in the method area of the JVM) a class will only be loaded once during the running of the JVM.
public class textStaticInitCode { public static void main(String[] args) { new A(); new A(); } } class A{ static { System.out.println("Init A"); } static int m =10; public A(){ System.out.println("A()"); } } // Output InitA A() A()
When will the class load?
Create this kind of object for the first time
Static member of the first access class
When loading subclasses, you may also need to load the parent class first
If it is only a reference to a life class, class loading is not required
Class loading process?
-
If necessary, load the parent class first
-
Allocate space for static properties of the class and assign default values
-
Initialize static properties or run static initialization code in the order of the code
8.3final
-
Class. This class cannot be inherited and cannot have subclasses
-
Method cannot be overridden by subclasses
-
Once the variable member variable + local variable constant is assigned, it cannot be changed
When final modifies a member variable, the system does not provide a default value, so it must be assigned once in the initialization attribute or construction method.
8.4 modifier combination
Neither private static final nor abstract can appear at the same time