In a binary tree, the root node is at the depth of 0, and the child nodes of each node with a depth of k are at the depth of k+1.
If two nodes of a binary tree have the same depth but different parent nodes, they are a pair of cousins.
We give the root node root of a binary tree with unique values, and the values x and y of two different nodes in the tree.
true is returned only if the nodes corresponding to the values x and y are cousins. Otherwise, return false.
Example 1:
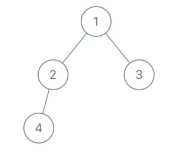
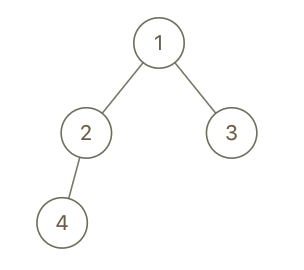
Input: root = [1,2,3,4], x = 4, y = 3 output: false
Example 2:
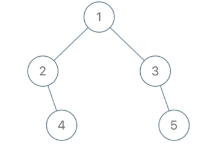
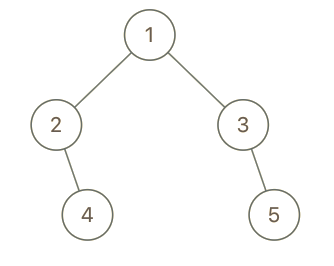
Input: root = [1,2,3,null,4,null,5], x = 5, y = 4 Output: true
Example 3:
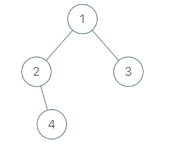
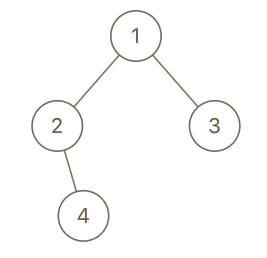
Input: root = [1,2,3,null,4], x = 2, y = 3 Output: false
Tips:
- The number of nodes in a binary tree is between 2 and 100.
- The value of each node is a unique integer in the range of 1 to 100.
# Definition for a binary tree node.
class TreeNode:
def __init__(self, x):
self.val = x
self.left = None
self.right = None
class Solution:
# Find out the depth of each node and the time O(N) space O(N) of the parent node by depth first traversal
def isCousins(self, root: TreeNode, x: 'int', y: 'int') -> 'bool':
parent = {}
depth = {}
def dfs(node, par=None):
if node:
depth[node.val] = 1 + depth[par.val] if par else 0
parent[node.val] = par
dfs(node.left, node)
dfs(node.right, node)
dfs(root)
return depth[x] == depth[y] and parent[x] != parent[y]
# Sequence traversal: if x and y are left and right subtrees of the same node, return False; otherwise, continue traversing
# return True if x, y are in the same layer, but not left and right subtrees
def isCousins2(self, root: TreeNode, x: 'int', y: 'int') -> 'bool':
queue = [root]
while queue:
now = []
next_queue = []
for node in queue:
# If it is empty
if not node:
now.append(None)
continue
# Add the left and right values of the node
if node.left:
now.append(node.left.val)
else:
now.append(None)
if node.right:
now.append(node.right.val)
else:
now.append(None)
# If same as parent node
if x in now[-2:] and y in now[-2:]:
return False
# Add lower cycle
next_queue.append(node.left)
next_queue.append(node.right)
# If in the list
if x in now and y in now:
return True
queue = next_queue
return False
if __name__ == '__main__':
s = Solution()
root = TreeNode(10)
root.left = TreeNode(5)
root.right = TreeNode(-3)
root.left.left = TreeNode(3)
root.left.left.left = TreeNode(9)
root.left.left.right = TreeNode(-2)
root.left.right = TreeNode(2)
root.left.right.right = TreeNode(1)
root.right.right = TreeNode(11)
'''
//Input:
10
/ \
5 -3
/ \ \
3 2 11
/ \ \
9 -2 1
'''
print(s.isCousins2(root, 3, 11))