Great! Someone introduced Ansible Playbook like this!
After a series of basic training and honing, it finally came to the application of relatively tall.
(Nani is just starting to review his future: https://blog.csdn.net/qq_41765918/category_11512932.html)

1. What is playbook
Chinese Name: script, which is an automatic processing script. Playbook is written in YAML language.
2. playbook demo
The following is a simple operation demonstration. Write the host list before writing the script.
(so, the foundation is very important. If you don't remember the host list https://blog.csdn.net/qq_41765918/article/details/121676991 And configuration files https://blog.csdn.net/qq_41765918/article/details/121706648 How to use it, learn it quickly.)

[student@servera ~]$ cat hosts
servera
[student@servera ~]$ cat webserver.yml
---
- name: play to setup web server
hosts: servera
remote_user: root
become: yes
become_method: sudo
tasks:
- name: latest httpd version install
yum:
name: httpd
state: latest
[student@servera ~]$ ansible-playbook -i hosts webserver.yml
PLAY [play to setup web server] *********************************************************
TASK [Gathering Facts] ******************************************************************
ok: [servera]
TASK [latest httpd version install]******************************************************
changed: [servera]
PLAY RECAP ******************************************************************************
servera : ok=2 changed=1 unreachable=0 failed=0
3. Playbook workflow
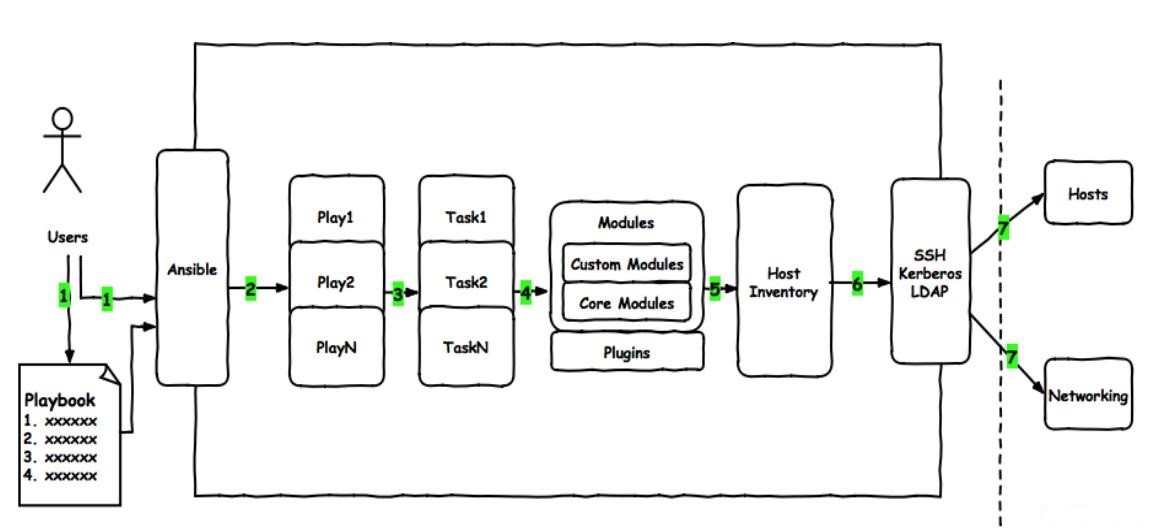
- A playbook script is a list of one or more "plays"
- The main function of play is to dress up a predefined group of hosts as roles defined in advance through the task in ansible
In fact, it calls a module of ansible to organize multiple plays in a playbook, that is, they can be combined
To perform predefined actions according to a pre choreographed mechanism. - Playbook files are written in YAML language
(just like the picture comic book, scripts are "scripts" written by us according to specific needs. This "script" uses various modules to meet the needs by acting on a specific host list.)

4. Introduction to yaml syntax
Only the playbook related syntax is involved here (please refer to the official website for more information) http://www.yaml.org ).
The grammar is very strict. Please be careful.
In a single file, three consecutive hyphens can be used(---)Distinguish multiple files. In addition, there are optional three consecutive periods( ... )Used to indicate the end of a file
The next line starts writing normally Playbook It is generally recommended to specify the content of the Playbook Function of
• use#No. comment code
• Indents must be uniform, not spaces and tab Mixed use,Generally indent 2 spaces (can be modified) tab (indent as)
• The indent level must also be consistent. The same indent represents the same level. The program determines the level of configuration by indenting and line feed
• YAML Document content and Linux The case judgment method of the system is consistent, which is case sensitive, key/value All values must be case sensitive
• key/value The value of can be written on the same line or wrapped. The same line is used , Comma separated
• value It can be a string or another list
• A complete code block function needs to include at least one element name and task
• One name Only one can be included task
• use | and > To separate multiple lines, which is actually just one line.
include_newlines: |
exactly as you see
will appear these three
lines of poetry
ignore_newlines: >
this is really a
single line of text
despite appearances
• Yaml Escape symbols are not allowed in double quotation marks, so single quotation marks are used to avoid escape symbol errors
• YAML The file extension is usually yml or yaml
Many students who have just learned often hang on the grammar when they report an error. They can understand it through continuous practice.
(the basis of grammar is really important. Stop talking, you don't listen, you don't understand, you don't do when you understand, you make mistakes when you do, you don't recognize when you're wrong, you don't change when you recognize you, and you don't accept when you change.)

List: List
All its elements begin with "-"
- web - dns -Space web # Writing format
Dictionary: Dictionary (key value pair)
It usually consists of multiple key s and value s
Multiline writing:
name: hunk
blog: "xxxxx"
name:Space hunk > This colon must be followed by a space
Same line:
Need to use{ }
{name: hunk, blog: "xxxxxx"} > It is recommended to leave a space after the comma
Representation of Boolean values:
yes/no true/false
create_key: yes
needs_agent: no
knows_oop: True
likes_emacs: TRUE
uses_cvs: false
5. Playbook core elements
name
Optional configuration item, which can help record the operation instructions of playbook.
hosts
The contents of the hosts line are the patterns of one or more groups or hosts, separated by commas. It is usually a list of hosts defined by / etc/ansible/hosts
remote_user is the account name for remote task execution:
--- - hosts: web,dns remote_user: root
tasks
Task set
tasks:
- name: install httpd
yum:
name: httpd
- name: start httpd
service: name=httpd state=started
6. Transform the tab function in vi
In order to edit the playbook more easily, you can set that when vi edits yaml files, pressing tab will make a double space indent.
Add the following to $HOME/.vimrc
autocmd FileType yaml setlocal ai ts=2 sw=2 et
Parameter interpretation:
set ai # Auto indent set ts=2 # tabstop means that after pressing a tab, the displayed is equivalent to several spaces. The default is 8. set sw=2 # shiftwidth, indicating the indented length of each level set et # expandtab, convert the tab into a space, and the indentation is represented by a space
(don't ask me why I want to rewrite it, because when you see others clattering their keyboards and writing playbook, you may still silently recite how many spaces you pressed. >. <)

7. playbook writing style
In the following writing examples, the shorthand format is an old writing method:
- name: copy new yum config to host copy: src=/etc/yum.repos.d/ dest=/etc/yum.repos.d/
Universal yaml format:
- name: copy new yum config to host
copy:
src: /etc/yum.repos.d/
dest: /etc/yum.repos.d/
Basically, new writing methods are used to facilitate reading and troubleshooting.

8. playbook execution
Detection syntax: ansible playbook -- syntax check webserver.yml
Simulation execution: ansible playbook - C webserver.yml
Real execution: ansible playbook webserver.yml
Level of detail of execution: -v : Displays the task results. -vv : The task results and task configuration are displayed -vvv : Contains information about connecting to the managed host -vvvv: Added additional detail level options related to the connection plug-in, including the user used to execute the script on the managed host and the script executed
9. Practice demonstration - how to write playbook
Set tab indent
[student@servera ~]$ cat .vimrc autocmd FileType yaml setlocal ai ts=2 sw=2 et
View configuration file and host list
[student@servera ~]$ mkdir playbook [student@servera playbook]$ cat ansible.cfg [defaults] inventory=inventory remote_user=student [privilege_escalation] become=True become_method=sudo become_user=root become_ask_pass=False [student@servera playbook]$ cat inventory [web] serverc serverd
Write the required script
[student@servera playbook]$ cat site.yml
---
- name: Install and start Aapche HTTPD
hosts: web
tasks:
- name: httpd package is present
yum:
name: httpd
state: present
- name: correct index.html is present
copy:
content: "This is a test page.\n"
dest: /var/www/html/index.html
- name: httpd is started
service:
name: httpd
state: started
enabled: true
Syntax check
[student@servera playbook]$ ansible-playbook --syntax-check site.yml playbook: site.yml
It is a good habit to check the grammar before running the script.
Execute script
[student@servera playbook]$ ansible-playbook site.yml PLAY [Install and start Aapche HTTPD] *************************************************** TASK [Gathering Facts] ****************************************************************** ok: [serverc] ok: [serverd] TASK [httpd package is present] ********************************************************* changed: [serverd] changed: [serverc] TASK [correct index.html is present] **************************************************** changed: [serverc] changed: [serverd] TASK [httpd is started] ***************************************************************** changed: [serverc] changed: [serverd] PLAY RECAP ****************************************************************************** serverc : ok=4 changed=3 unreachable=0 failed=0 serverd : ok=4 changed=3 unreachable=0 failed=0
Idempotency
[student@servera playbook]$ ansible-playbook site.yml ............
This is one of the important features of Ansible, which is easier to understand with practice demonstration.
Result access check
[student@servera playbook]$ curl serverc This is a test page. [student@servera playbook]$ curl serverd This is a test page.
10. playbook rights
It can be written in the script at the same level as hosts and tasks
- hosts: all
become: true
become_method: sudo
become_user: root
tasks:
- debug:
msg: "Test"
Of course, it's OK not to write in the script, but in the configuration file. If you write in both places, the priority in the script will be higher than that in the configuration file. For example, when the authorization is started in the configuration file, become: yes, but become: no is configured in the script, which will eventually take effect as the configuration in the script.

11. Module documentation
Ansible doc - L view list
Ansible doc modulenamiew the module help file
(summary of the previous article) https://blog.csdn.net/qq_41765918/article/details/121722471 Mentioned, it's really important to check the help ~ ~)

12. Practice demonstration - execute multiple playbook s
View configuration file and host list
[student@servera ~]$ mkdir playbook-multi [student@servera ~]$ cd playbook-multi/ [student@servera playbook-multi]$ cat ansible.cfg [defaults] inventory=inventory remote_user=student [privilege_escalation] become=False become_method=sudo become_user=root become_ask_pass=False [student@servera playbook-multi]$ cat inventory servera
Write the required script
[student@servera playbook-multi]$ cat web.yml
---
- name: Enable web services
hosts: servera
become: yes
tasks:
- name: latest version of httpd and firewalld installed
yum:
name:
- httpd
- firewalld
state: latest
- name: test html page is installed
copy:
content: "Hello World!\n"
dest: /var/www/html/index.html
- name: firewalld enabled and running
service:
name: firewalld
enabled: true
state: started
- name: firewalld permits http service
firewalld:
service: http
permanent: true
state: enabled
immediate: yes
- name: httpd enabled and running
service:
name: httpd
enabled: true
state: started
- name: Test web server
hosts: localhost
become: no
tasks:
- name: connect to web server
uri:
url: http://servera
return_content: yes
status_code: 200
Syntax check
[student@servera playbook-multi]$ ansible-playbook --syntax-check web.yml playbook: web.yml
Use - v to execute the script
[student@servera playbook-multi]$ ansible-playbook web.yml -v
PLAY [Enable web services] **************************************************************
TASK [Gathering Facts] ******************************************************************
ok: [servera]
TASK [latest version of httpd and firewalld installed] ******************************************
ok: [servera] => {"changed": false, "msg": "", "rc": 0, "results": ["All packages providing httpd are up to date", "All packages providing firewalld are up to date", ""]}
............
TASK [connect to web server] ************************************************************
ok: [localhost] => {"accept_ranges": "bytes", "changed": false, "connection": "close", "content": "Hello World!\n", "content_length": "37", "content_type": "text/html; charset=UTF-8", "cookies": {}, "cookies_string": "", "date": "Fri, 04 Sep 2020 12:54:49 GMT", "etag": "\"25-5ae7c5e78c9df\"", "last_modified": "Fri, 04 Sep 2020 12:54:27 GMT", "msg": "OK (37 bytes)", "redirected": false, "server": "Apache/2.4.6 (Red Hat Enterprise Linux)", "status": 200, "url": "http://servera"}
PLAY RECAP **********************************************************************************
localhost : ok=2 changed=0 unreachable=0 failed=0
servera : ok=6 changed=0 unreachable=0 failed=0
summary
- yaml syntax is very strict and written carefully.
- Modify the tab key to improve the efficiency of script writing.
- Grammar checking is a good habit.
- Make good use of module documents to view parameter descriptions and examples.
- Understand idempotency through practice and experiment.
- You can use the - v parameter to view the detailed output for troubleshooting.
- If you like brother goldfish's article, you can like it easily. You can also pay attention to it, because you will continue to get dry goods in the follow-up.
