If Hadoop has not been configured, you can click the link to see how to configure it
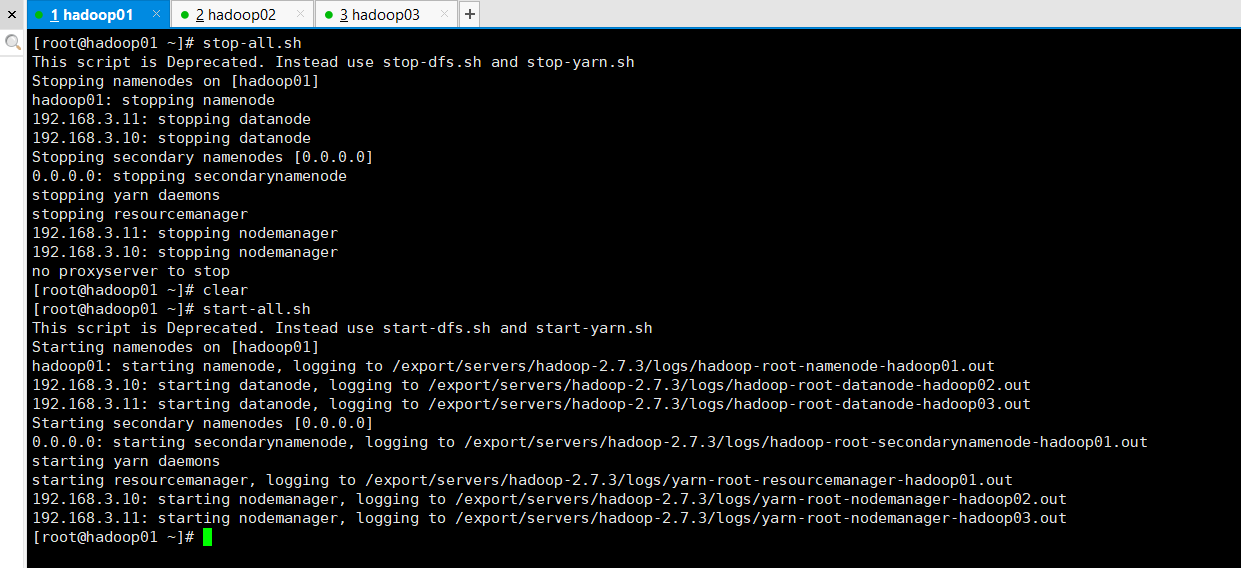
First, start the Hadoop cluster service
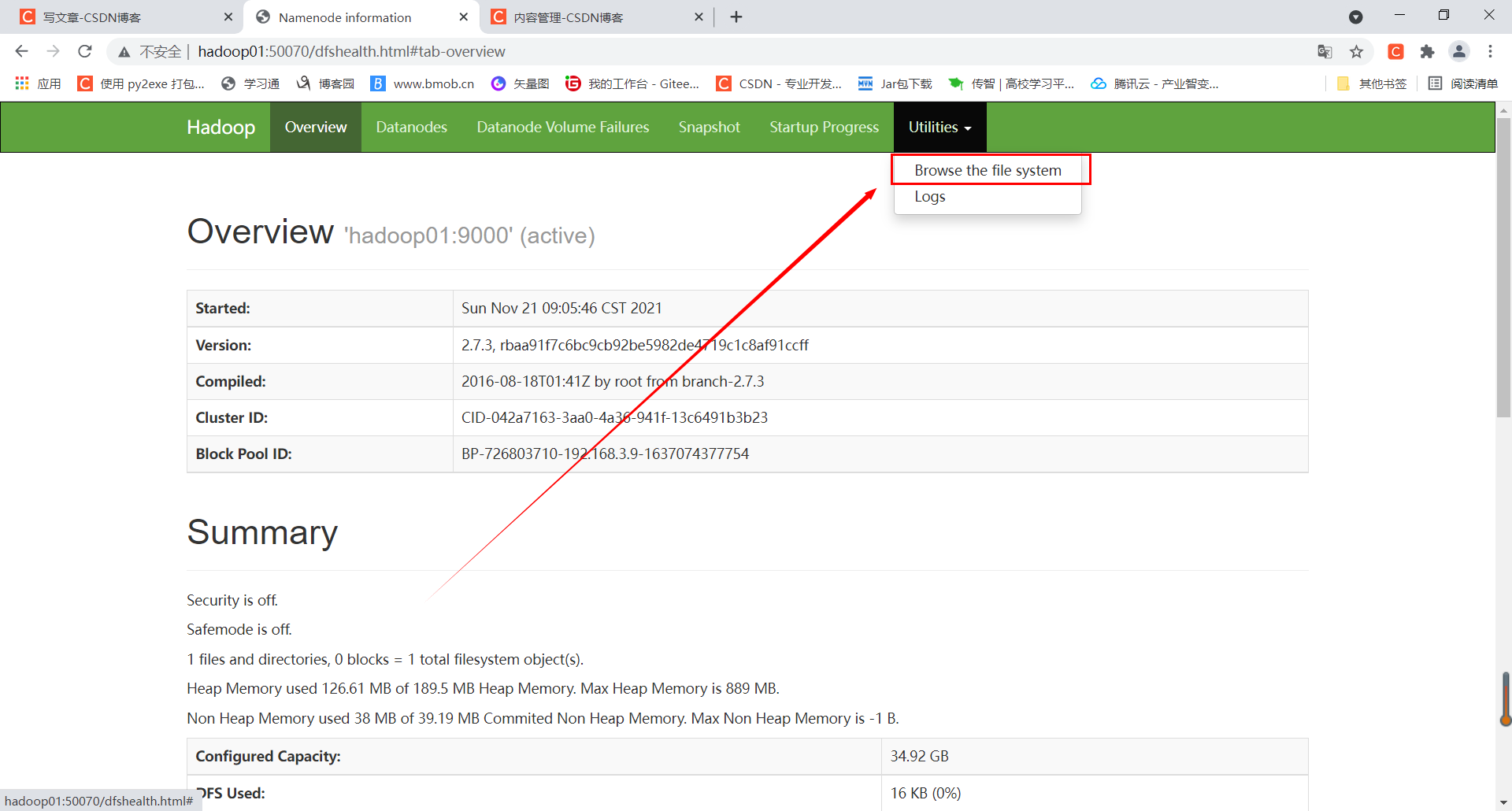
Then access Hadoop in the browser and click Browse the file system to view the directory of HDFS file system
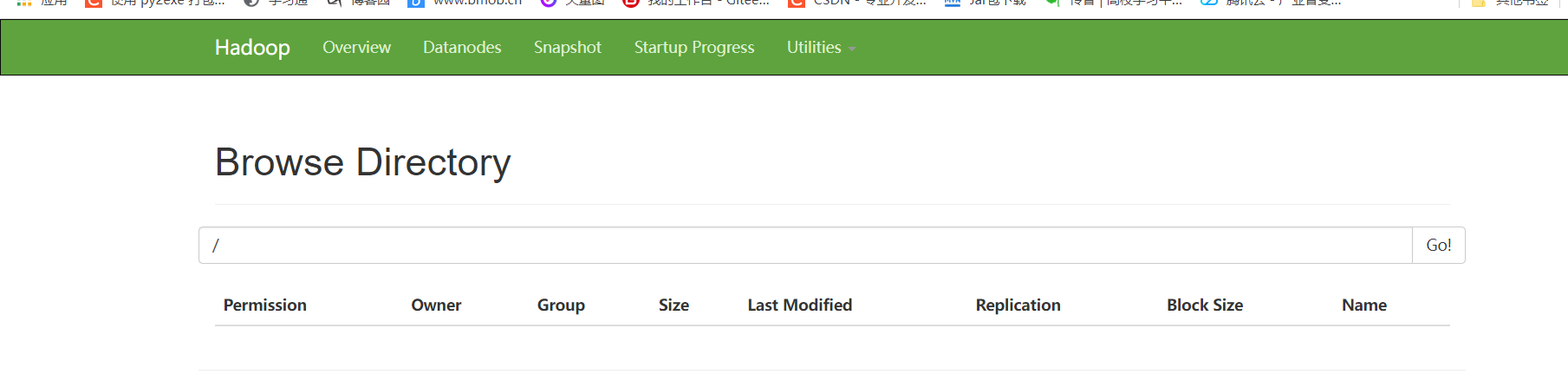
You can see that the directory of the current HDFS file system is empty without any files and folders. Let's start today's API operation
1, Create Maven project
First, open IDEA, click new project, select Maven on the left, and then click next
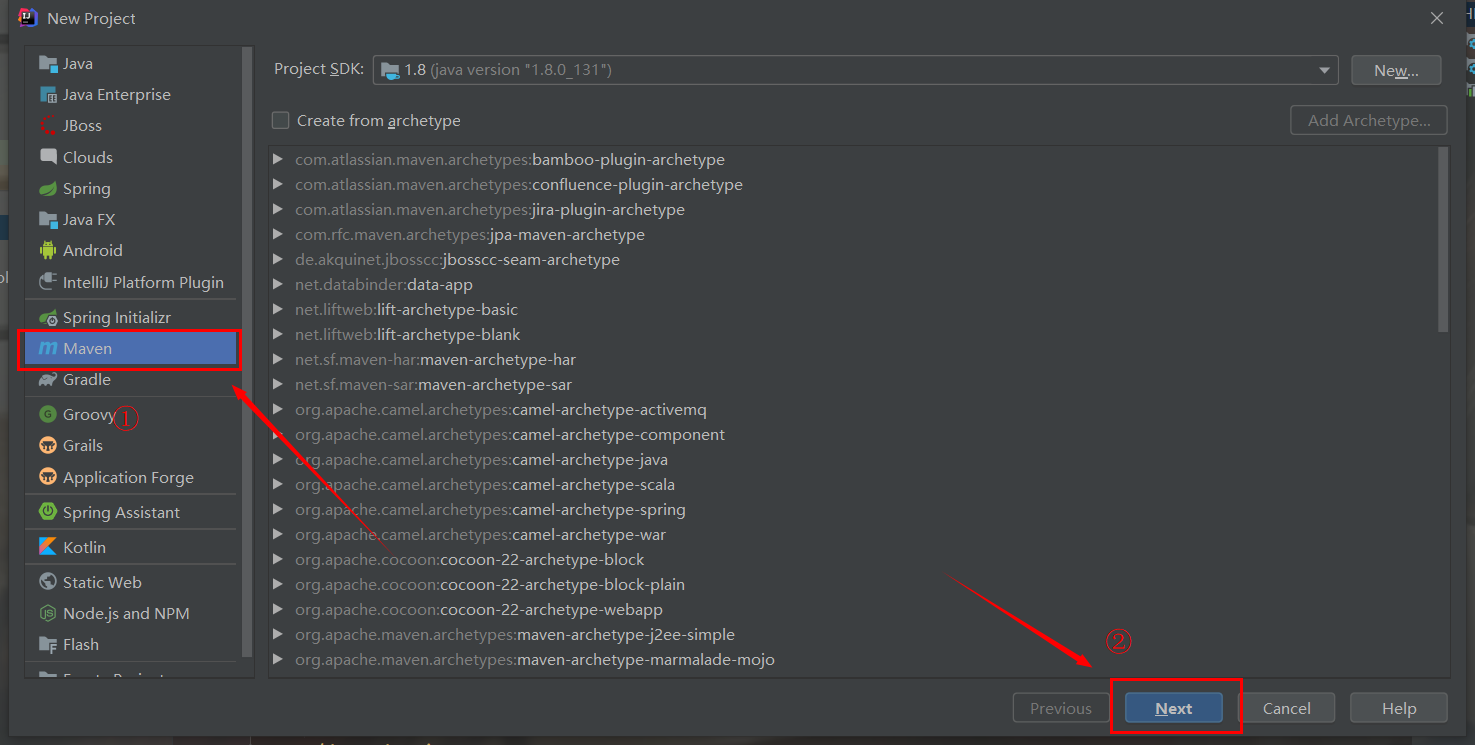
Set the project name and click Finish
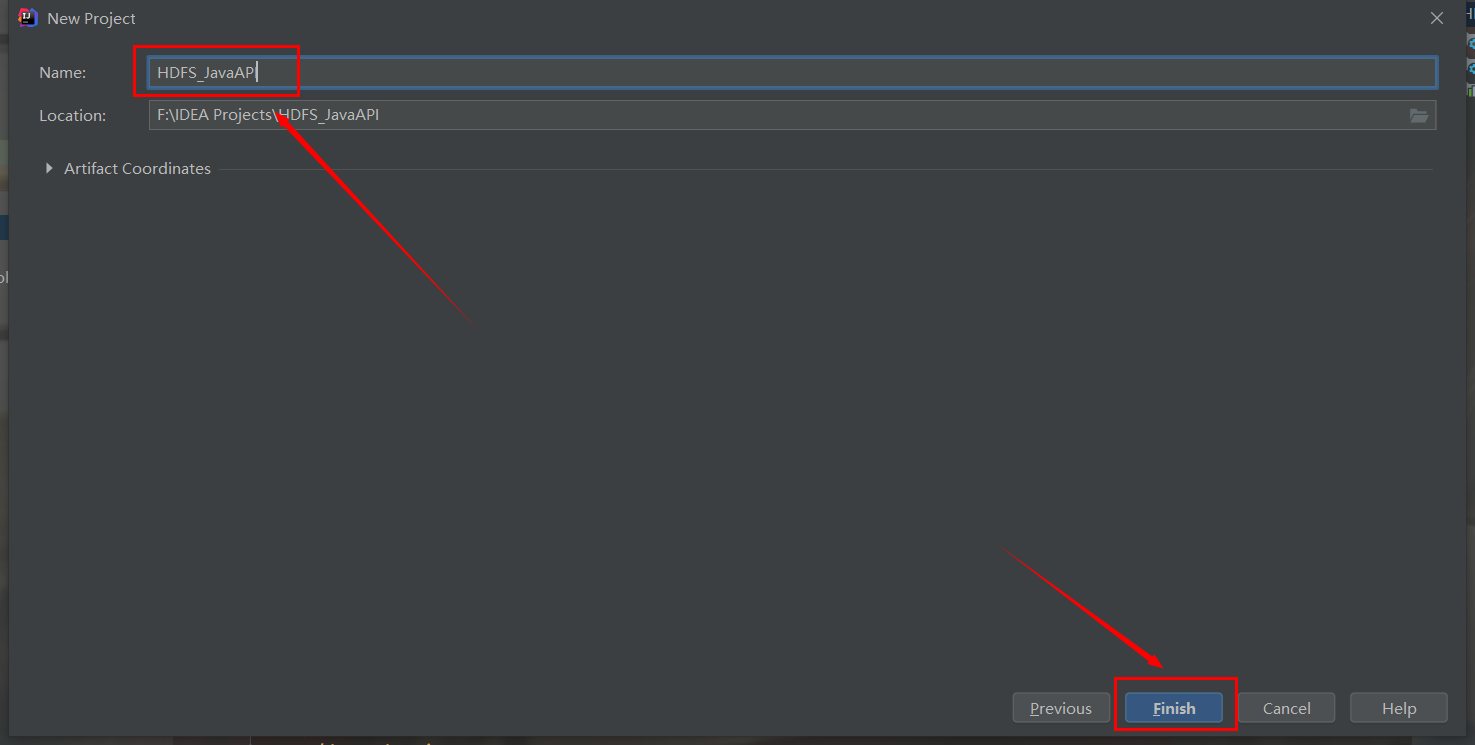
Click enable auto import in the lower right corner to create an empty Maven project
2, Import dependency
First, edit pom.xml (the core file of Maven project), add the following contents, and import the dependency (required jar package)
<dependencies>
<!-- Hadoop Required dependent packages -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.hadoop</groupId>
<artifactId>hadoop-common</artifactId>
<version>2.7.4</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.hadoop</groupId>
<artifactId>hadoop-hdfs</artifactId>
<version>2.7.4</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.hadoop</groupId>
<artifactId>hadoop-client</artifactId>
<version>2.7.4</version>
</dependency>
<!-- junit Test dependency -->
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.12</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>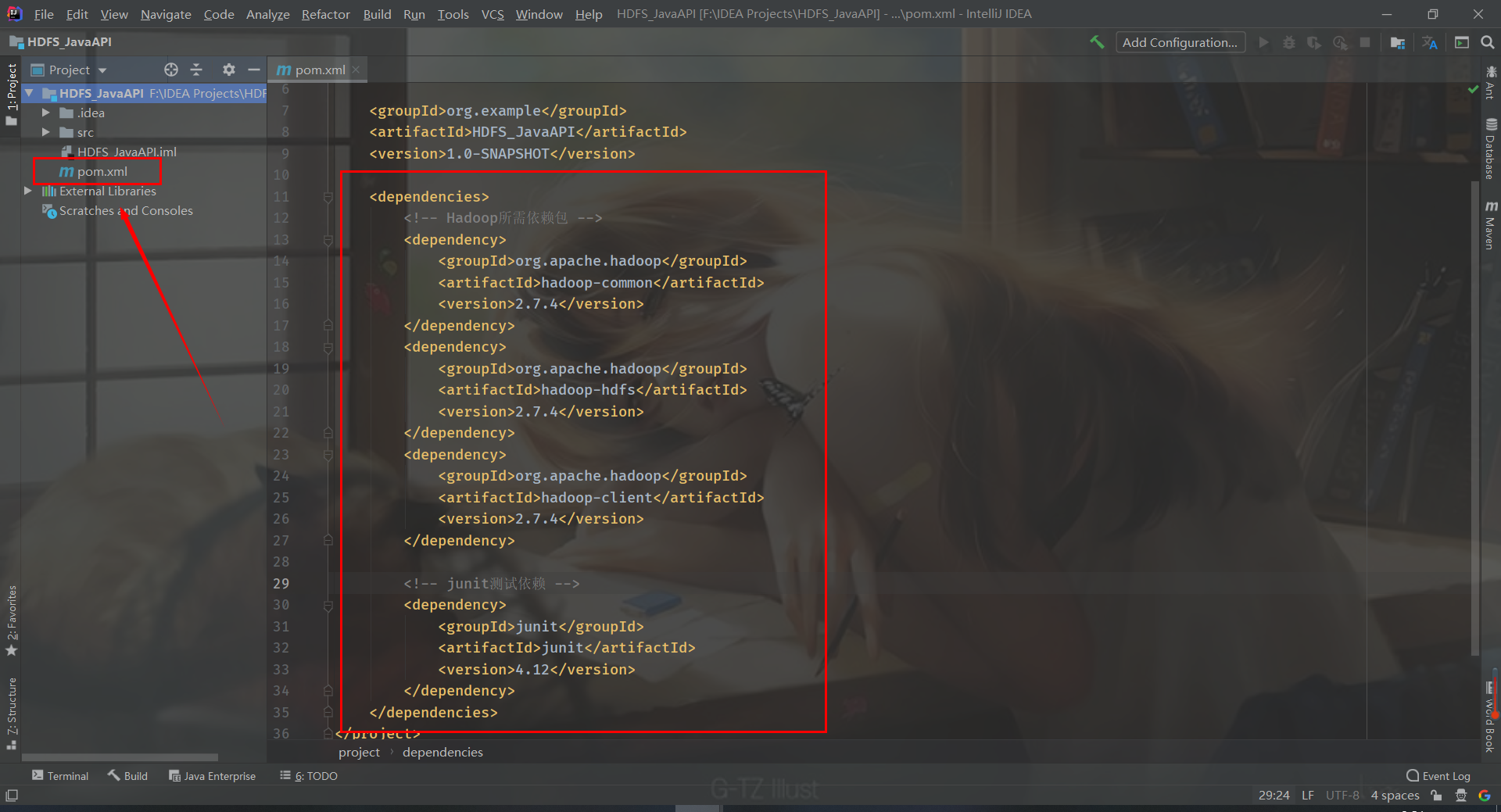
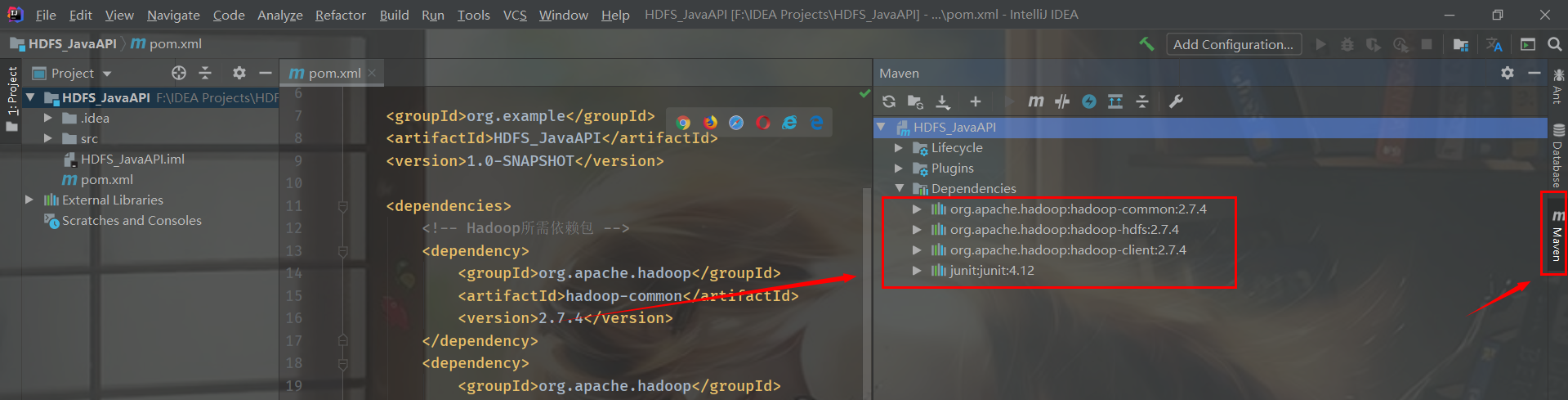
IDEA will automatically save the file and import the dependent packages. Click Maven on the right and expand Dependencies to see the four dependent packages and imported packages
3, Initialization
We use junit to test. First, create a class and add the following
public class JavaAPI {
// Objects that can operate on the HDFS file system
FileSystem hdfs = null;
// The test method is executed before execution. It is used for initialization to avoid frequent initialization
@Before
public void init() throws IOException {
// Construct a configuration parameter object and set a parameter: the URI of the HDFS to be accessed
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
// Specify access using HDFS
conf.set("fs.defaultFS","hdfs://hadoop01:9000");
// Set the client identity (root is the user name of the virtual machine, and any one of the hadoop cluster nodes can be used)
System.setProperty("HADOOP_USER_NAME","root");
// Get the HDFS file system client object through the static get() method of the file system
hdfs = FileSystem.get(conf);
}
// After the test method is executed, it is used to process the end operation and close the object
@After
public void close() throws IOException {
// Close file operation object
hdfs.close();
}
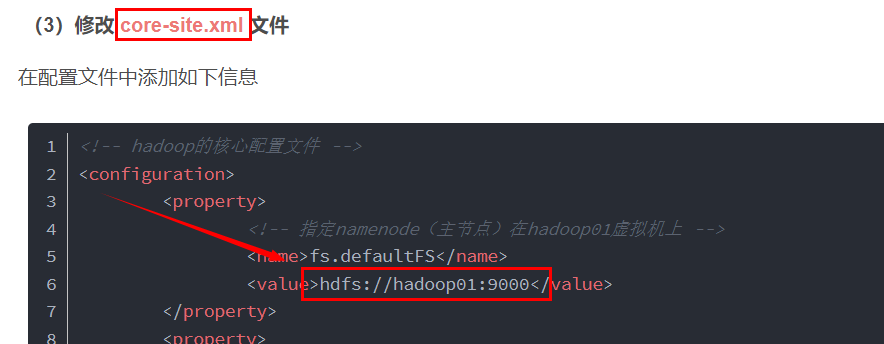
}Notice the parameters in the code above“ hdfs://hadoop01:9000 "This is the configuration information of core-site.xml in the Hadoop configuration file. If you don't remember, you can read my previous Hadoop configuration articles
4, HDFS code operation
(1) Upload files to HDFS file system
@Test
public void testUploadFileToHDFS() throws IOException {
// File path to upload (windows)
Path src = new Path("F:/HDFS/test.txt");
// Storage path after upload (HDFS)
Path dst = new Path("/test.txt");
// upload
hdfs.copyFromLocalFile(src,dst);
System.out.println("Upload succeeded");
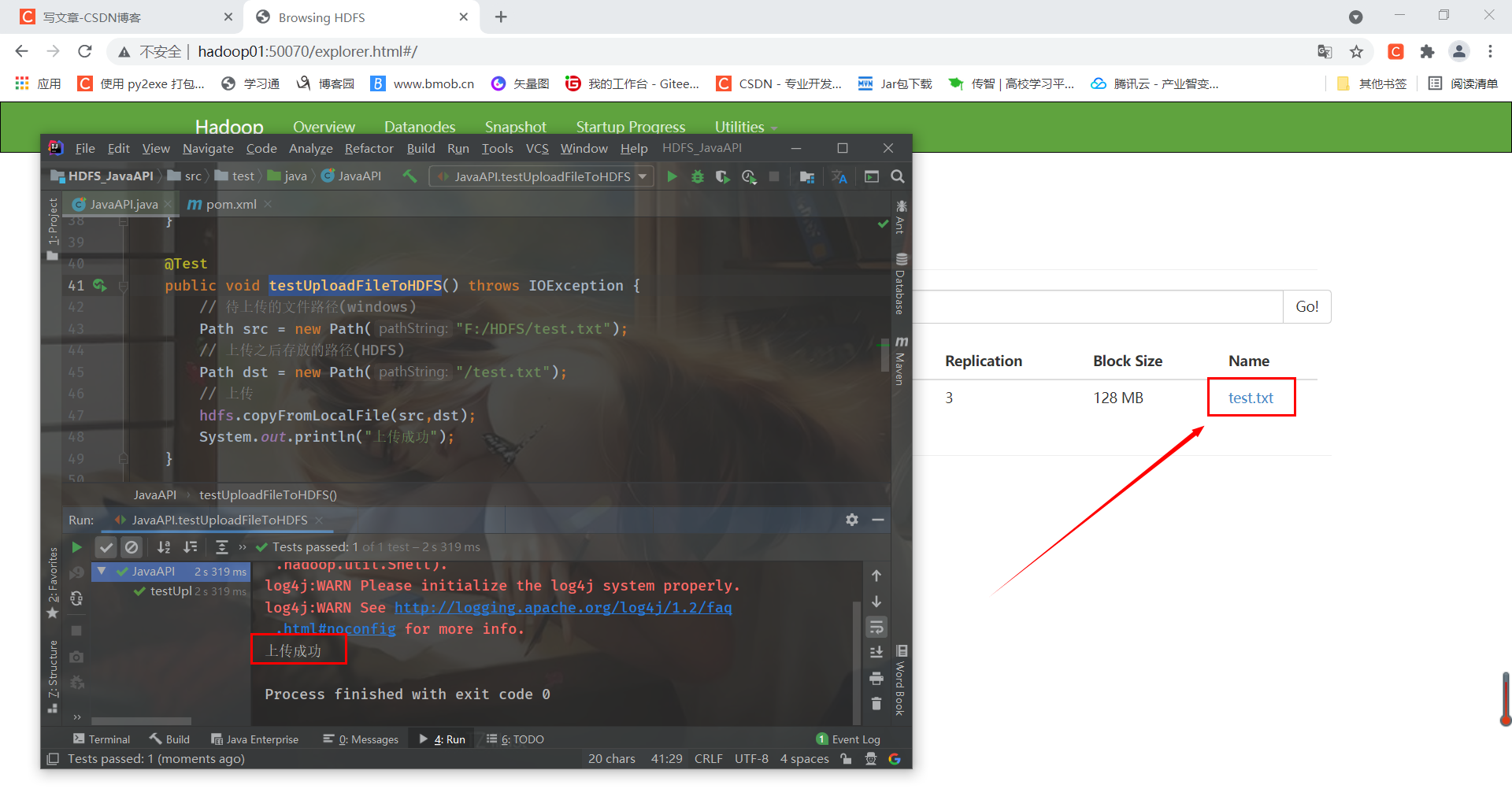
}I created a test.txt text under the HDFS folder on disk F

Run the test method and the file is uploaded successfully
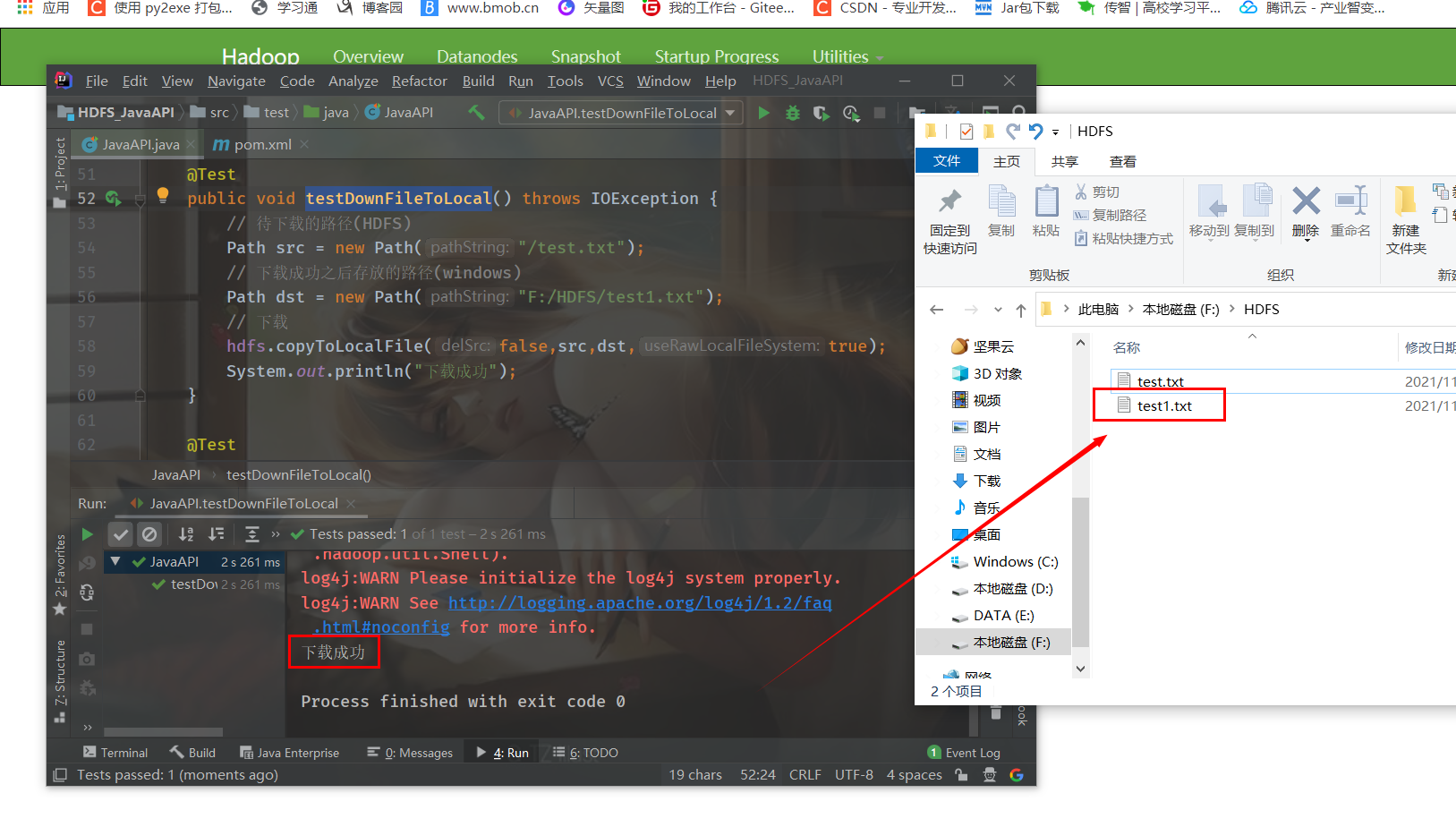
(2) Download files from HDFS to local
@Test
public void testDownFileToLocal() throws IOException {
// Path to download (HDFS)
Path src = new Path("/test.txt");
// Path to store after successful download (windows)
Path dst = new Path("F:/HDFS/test1.txt");
// download
hdfs.copyToLocalFile(false,src,dst,true);
ystem.out.println("Download succeeded");
}Run it and download it successfully
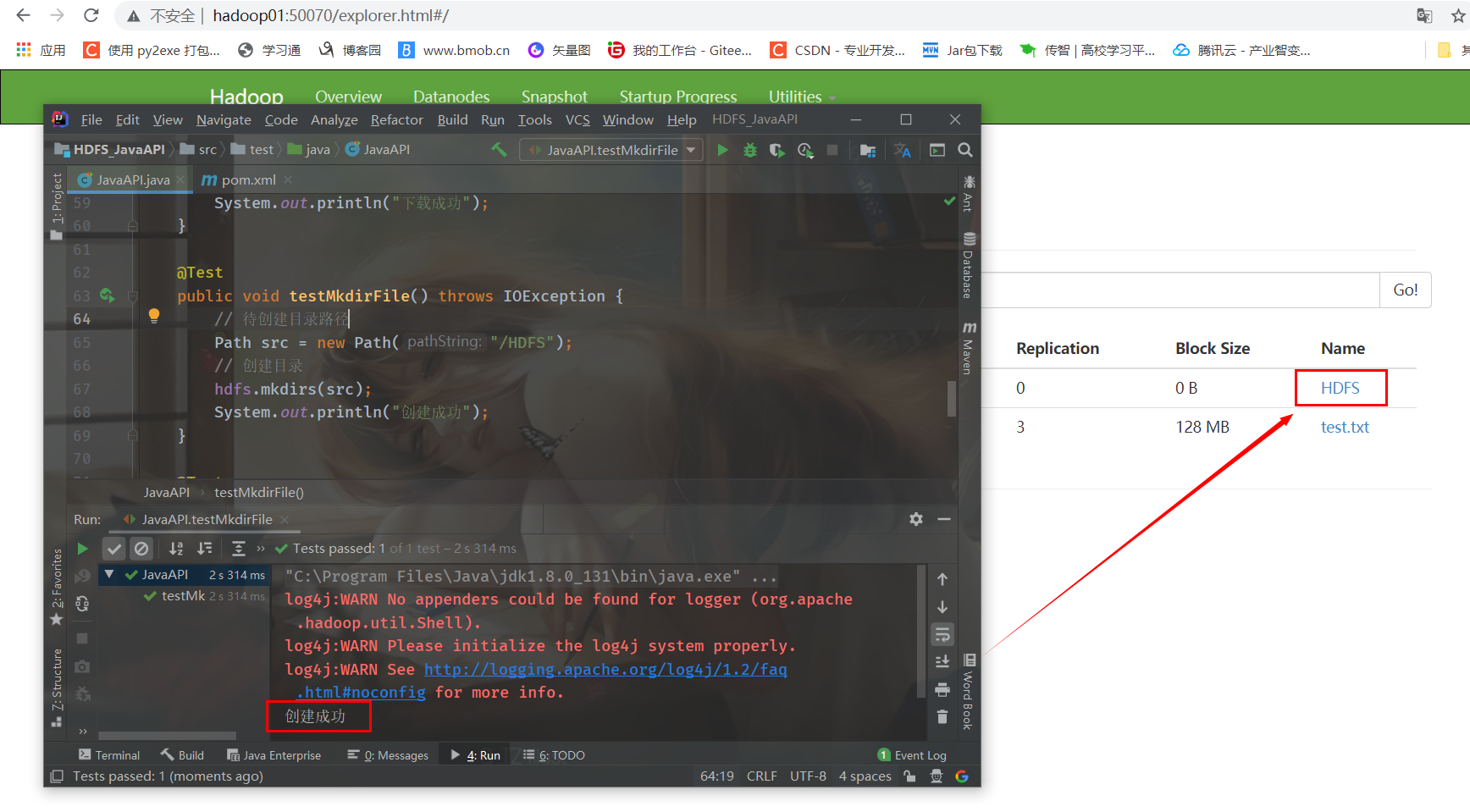
 (3) Create directory
(3) Create directory
@Test
public void testMkdirFile() throws IOException {
// Directory path to be created
Path src = new Path("/HDFS");
// Create directory
hdfs.mkdirs(src);
System.out.println("Created successfully");
}Run the test method and create it successfully
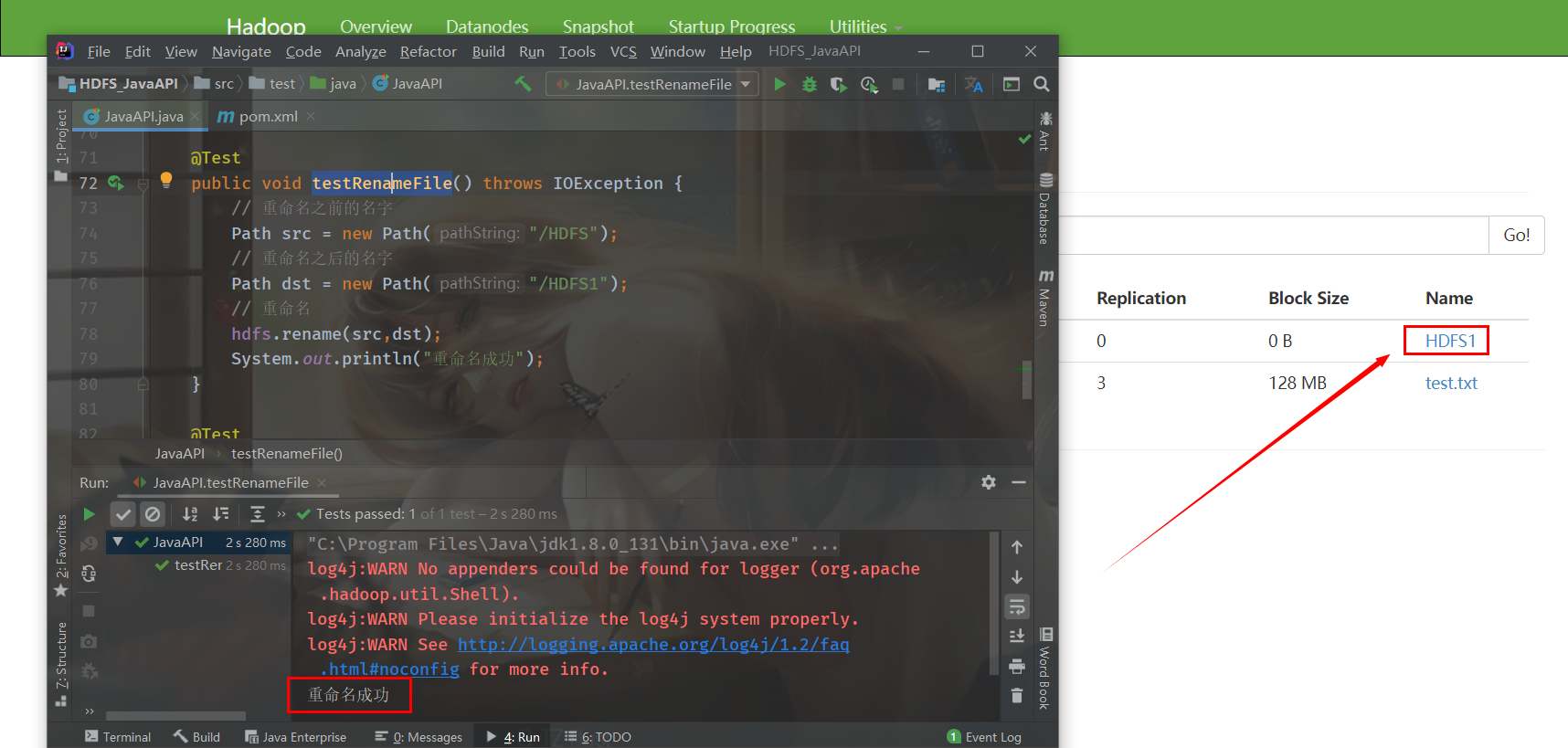
(4) Rename
@Test
public void testRenameFile() throws IOException {
// Rename previous name
Path src = new Path("/HDFS");
// Renamed name
Path dst = new Path("/HDFS1");
// rename
hdfs.rename(src,dst);
System.out.println("Rename succeeded");
}Run the test method and rename successfully
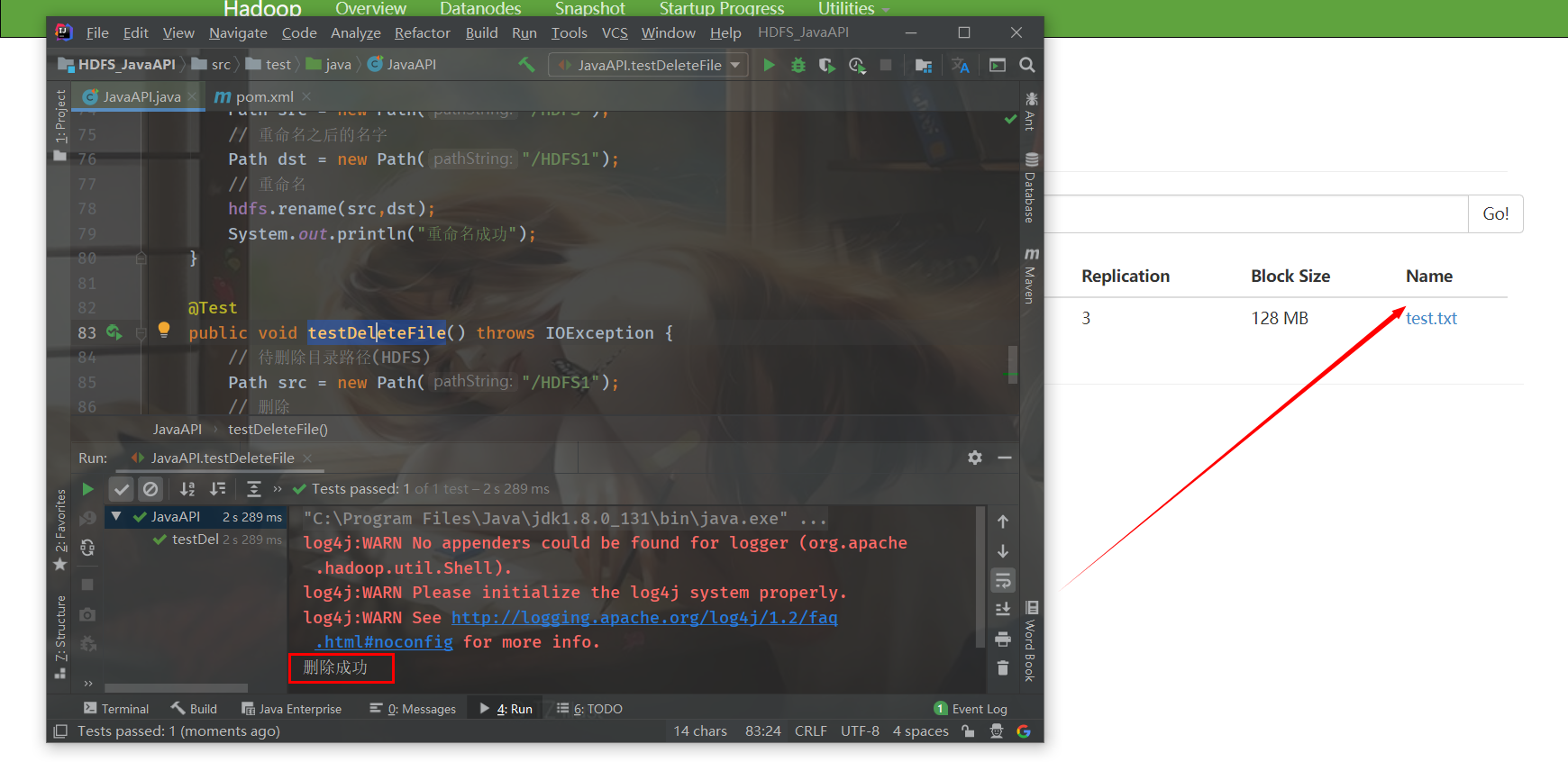
(5) Delete directory
@Test
public void testDeleteFile() throws IOException {
// Directory path to be deleted (HDFS)
Path src = new Path("/HDFS1");
// delete
hdfs.delete(src,true);
System.out.println("Delete succeeded");
}Run the test method and successfully delete the HDFS1 directory
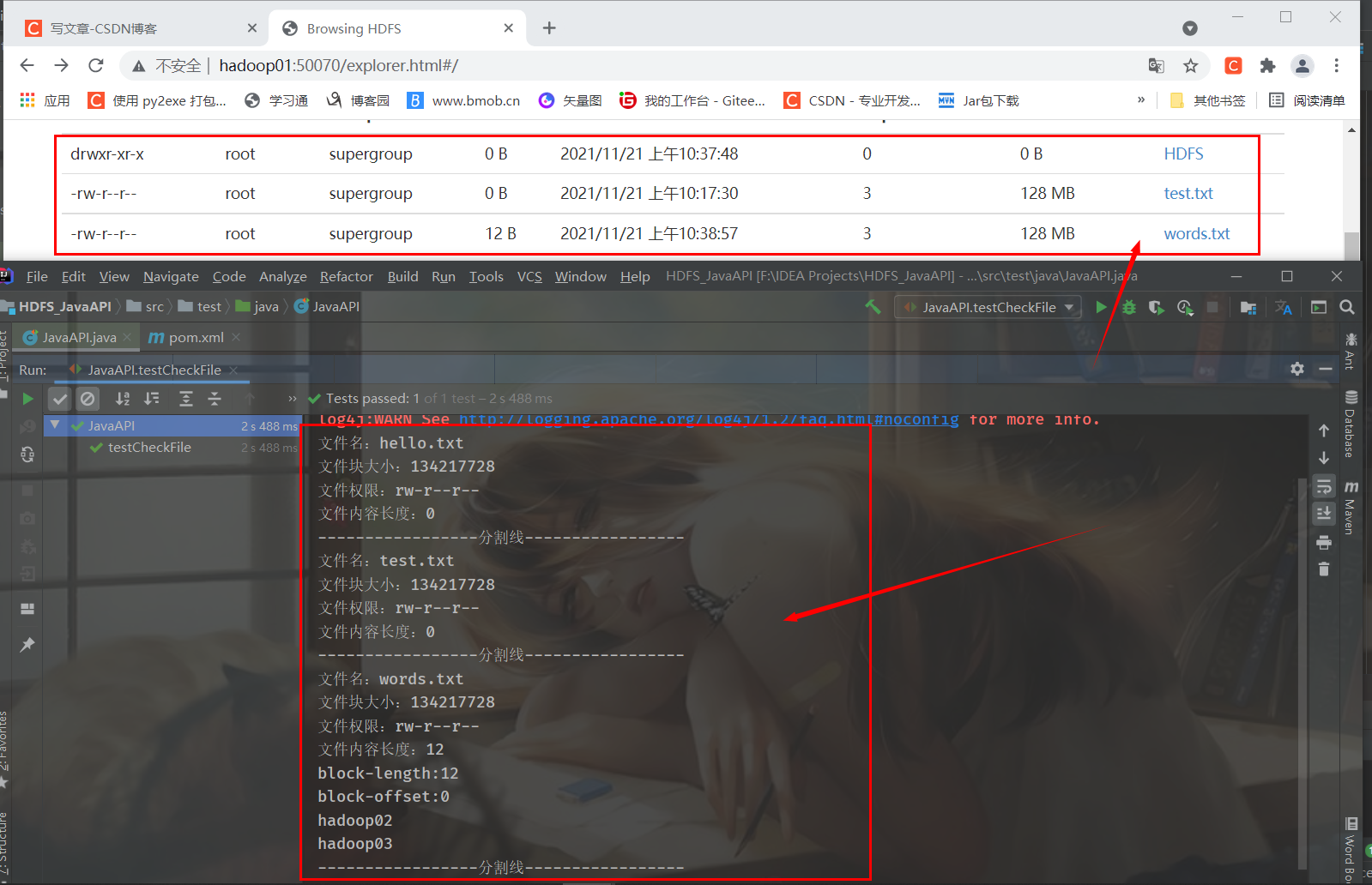
(6) View file information in the HDFS directory
To facilitate viewing, create several more files
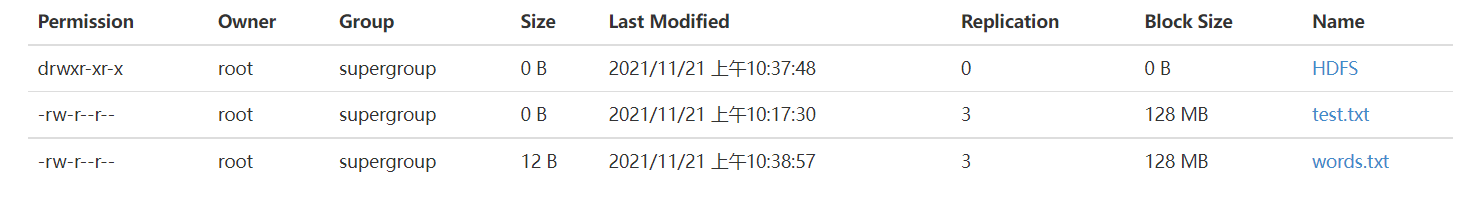
@Test
public void testCheckFile() throws IOException {
// Get iterator object ("/" means to get files in all directories)
RemoteIterator<LocatedFileStatus> listFiles = hdfs.listFiles(new Path("/"), true);
while (listFiles.hasNext()) {
LocatedFileStatus fileStatus = listFiles.next();
// Print current file name
System.out.println("File name:" + fileStatus.getPath().getName());
// Print current file block size
System.out.println("File block size:" + fileStatus.getBlockSize());
// Print current file permissions
System.out.println("File permissions:" + fileStatus.getPermission());
// Prints the length of the contents of the current file
System.out.println("File content length:" + fileStatus.getLen());
// Get the information of the file block (including length, data block and DataNodes)
BlockLocation[] blockLocations = fileStatus.getBlockLocations();
for (BlockLocation bl : blockLocations) {
System.out.println("block-length:" + bl.getLength());
System.out.println("block-offset:" + bl.getOffset());
// Gets the hostname of DataNodes
String[] hosts = bl.getHosts();
for (String host : hosts) {
System.out.println(host);
}
}
System.out.println("-----------------Split line-----------------");
}
}Run test method