Spring/Spring MVC/MyBatis(SSM) integration configuration process
Usage of mybatis plus agile development plug-in
Main knowledge points
SSM consolidation configuration
Mybatis plus configuration and Application
SSM consolidation configuration
Manage the third-party framework objects through the Spring IoC container, so that multiple frameworks form a whole
Spring/Spring MVC/MyBatis(SSM) is the most mainstream framework in the industry
Three stages of SSM integration
- Spring and Spring MVC environment configuration
- Integrated configuration of Spring and MyBatis
- Consolidate other components: declarative transactions / logs / task scheduling
1, Spring and Spring MVC environment configuration
Rely on spring webmvc
Configure DispatcherServlet
Enable Spring MVC annotation mode
Configure request and response character sets
Configure FreeMarker template engine
Configure Json serialization component
1. Rely on spring webmvc
pom.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>synu.edu.cn</groupId>
<artifactId>book-review</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<properties>
<maven.compiler.source>8</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>8</maven.compiler.target>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
<version>5.2.16.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<!--Freemarker-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.freemarker</groupId>
<artifactId>freemarker</artifactId>
<version>2.3.28</version>
</dependency>
<!--springmvc integration Freemarker assembly-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context-support</artifactId>
<version>5.2.16.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<!--Jackson Serialized package-->
<dependency><!--Core package-->
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-core</artifactId>
<version>2.9.8</version>
</dependency>
<dependency><!--Annotation package-->
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-annotations</artifactId>
<version>2.9.8</version>
</dependency>
<dependency><!--Data binding package-->
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId>
<version>2.9.8</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
2. Configure DispatcherServlet
web.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_4_0.xsd"
version="4.0">
<!--DispatchServlet-->
<servlet>
<servlet-name>springmvc</servlet-name>
<!--
DispatcherServlet yes Spring MVC The core object
DispatcherServlet For interception Http Request,
And on request URL Call the corresponding controller Method to complete Http Processing of requests
-->
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<!--applicationContext.xml-->
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath:applicationContext.xml</param-value>
</init-param>
<!--
stay web Automatically created when application starts spring Ioc Container and initialize DispatcherServlet
It can also be run if you forget to write, but it is created during the first access. In order to improve efficiency, it is recommended to web When does the program start but create
-->
<load-on-startup>0</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<!--mapping-->
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>springmvc</servlet-name>
<!--"/"Intercepts all requests on behalf of-->
<url-pattern>/</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>
3. Enable Spring MVC annotation mode
applicationContext.xml
xmlns introduces tx declarative transaction, which will be described in detail later in the configuration
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd">
<!--
context:component-scan Label function
stay Spring IOC During initialization, it is automatically created and managed springmvc And sub packages
Have the following annotation objects
@Repository Usually, the classes that use this are those that interact directly with the data
@Service Business logic class, usually placed in xxxService
@Controller Controller class Spring controller
@Component It's hard to distinguish between types. Use this
-->
<context:component-scan base-package="bookReview"/>
<!--Enable Spring MVC Annotation development mode-->
<mvc:annotation-driven>
<mvc:message-converters> <!--Message converter, solving html Chinese garbled code in Chinese-->
<bean class="org.springframework.http.converter.StringHttpMessageConverter">
<property name="supportedMediaTypes">
<list>
<!--response.setContentType=("text/html;charset=utf-8")-->
<value>text/html;charset=utf-8</value>
<!-- <value>application/json;charset=utf-8</value>-->
</list>
</property>
</bean>
</mvc:message-converters>
</mvc:annotation-driven>
<!--Will picture/js/css And other static resources can be excluded to improve execution efficiency-->
<mvc:default-servlet-handler/>
</beans>
4. Configure the request and response character set
Request character set configuration, only effective for post
web.xml
<!-- filter-CharacterEncodingFilter yes post All requests converted to UTF-8-->
<filter>
<filter-name>characterFilter</filter-name>
<filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>encoding</param-name>
<param-value>UTF-8</param-value>
</init-param>
</filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>characterFilter</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>
After tomcat 8, the default tomcat get request is UTF-8 encoding; The get request needs to configure tomcat's server.xml
In response to the character set configuration, it has been written in the code in step 3
applicationContext.xml
Additional message converters in annotation driven
<context:component-scan base-package="restful"/>
<!--Enable Spring MVC Annotation development mode-->
<mvc:annotation-driven>
<mvc:message-converters> <!--Message converter, solving html Chinese garbled code in Chinese-->
<bean class="org.springframework.http.converter.StringHttpMessageConverter">
<property name="supportedMediaTypes">
<list>
<value>text/html;charset=utf-8</value>
</list>
</property>
</bean>
</mvc:message-converters>
</mvc:annotation-driven>
<!--Will picture/js/css And other static resources can be excluded to improve execution efficiency-->
<mvc:default-servlet-handler/>
5. Configure FreeMarker template engine
Create / WEB-INF/ftl directory
applicationContext.xml
<!-- start-up Freemarker template engine -->
<bean id="ViewResolver" class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.freemarker.FreeMarkerViewResolver">
<!--What character set is used to display the response text when outputting content to the client after the result is generated-->
<property name="contentType" value="text/html;charset=utf-8"/>
<!--appoint Freemarker Template file extension-->
<property name="suffix" value=".ftl"/>
</bean>
<!-- to configure Freemarker parameter -->
<bean id="freemarkerConfig" class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.freemarker.FreeMarkerConfigurer">
<!--Set the directory where the template is saved-->
<property name="templateLoaderPath" value="/WEB-INF/ftl"/>
<!--Other template engine settings-->
<property name="freemarkerSettings">
<props>
<!--set up Freemarker Character set used in script and data rendering-->
<prop key="defaultEncoding">UTF-8</prop>
</props>
</property>
</bean>
6. Configure Json serialization component
applicationContext.xml
Add a new item value in the list to < value > Application / JSON; charset=utf-8</value>
<context:component-scan base-package="restful"/>
<!--Enable Spring MVC Annotation development mode-->
<mvc:annotation-driven>
<mvc:message-converters> <!--Message converter, solving html Chinese garbled code in Chinese-->
<bean class="org.springframework.http.converter.StringHttpMessageConverter">
<property name="supportedMediaTypes">
<list>
<value>text/html;charset=utf-8</value>
<value>application/json;charset=utf-8</value>
</list>
</property>
</bean>
</mvc:message-converters>
</mvc:annotation-driven>
<!--Will picture/js/css And other static resources can be excluded to improve execution efficiency-->
<mvc:default-servlet-handler/>
test
Create a test.ftl file in the FTL directory, and write a test line in the html content
Create bookReview.controller.TestController.java
The test1 method tests the configuration of ftl, and the test2 method tests json serialization
Start the project and access test/t1 and test/t2 successfully
package bookReview.controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
@Controller
public class TestController {
@GetMapping("/test/t1")
public ModelAndView test1(){
//Point to the test file in the ftl directory
return new ModelAndView("/test");
}
@GetMapping("/test/t2")
@ResponseBody
public Map test2(){
Map result = new HashMap();
result.put("test","Test text");
return result;
}
}
2, Integrated configuration of Spring and MyBatis
Rely on mybatis spring and driver
Configure data sources and connection pools
Configure SqlSessionFactory
Configure Mapper scanner
Create mybatis-config.xml
First create the database and test table
Database book_review
Table test, content id (auto increment of primary key) and context fields
1. Rely on mybatis spring and driver
pom.xml
<!--Mybatis Integration components-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-jdbc</artifactId>
<version>5.2.6.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis</artifactId>
<version>3.5.4</version>
</dependency>
<dependency> <!--Integration package-->
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring</artifactId>
<version>2.0.6</version>
</dependency>
<dependency> <!--mysql The driver shall be consistent with that installed locally-->
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>8.0.25</version>
</dependency>
<dependency> <!--Connection pool alibaba of druid-->
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid</artifactId>
<version>1.2.8</version>
</dependency>
2. Configure data source and connection pool
applicationContext.xml
<!--Configure data sources and connection pools-->
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/book_review?useSSL=false&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai&allowPublicKeyRetrieval=true"/>
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="root1024"/>
<property name="initialSize" value="5"/>
<property name="maxActive" value="20"/>
</bean>
3. Configure SqlSessionFactory
applicationContext.xml
The SqlSessionFactory object is automatically implemented during initialization through the IoC container
<!--SqlSessionFactoryBean Used to create a profile based on configuration information SqlSessionFactory,We no longer need to create our own code-->
<bean id="sessionFactory" class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
<property name="mapperLocations" value="classpath:mappers/*.xml"/>
<!--MyBatis Profile address-->
</bean>
4. Configure Mapper scanner
Used to scan all mapper interfaces under the specified package
applicationContext.xml
<!--to configure Mapper Scanner-->
<bean class="org.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperScannerConfigurer">
<property name="basePackage" value="bookReview.mapper"/>
</bean>
Add bookReview.mapper package
5. Create mybatis-config.xml
Add the space left in the note of step 3; This configuration may not be written, but it will be used in mybatis plus advanced usage. It is written together
applicationContext.xml
<!--SqlSessionFactoryBean Used to create a profile based on configuration information SqlSessionFactory,We no longer need to create our own code-->
<bean id="sessionFactory" class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
<property name="mapperLocations" value="classpath:mappers/*.xml"/>
<!--MyBatis Profile address-->
<property name="configLocation" value="classpath:mybatis-config.xml"/>
</bean>
Create src/main/resources/mybatis-config.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http:mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
<settings>
<!--Realize the hump naming conversion between attribute name and field name-->
<setting name="mapUnderscoreToCame1Case" value="true"/>
</settings>
</configuration>
6. Integrate other components
In the actual project development, it also needs to inject, such as declarative transaction, log module, unit test framework and so on
- Configure logback log output
- Declarative transaction configuration
- Integrate JUnit unit testing
Join JUnit unit test framework
pom.xml
<!--Unit test framework-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-test</artifactId>
<version>5.2.6.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.12</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!--Solution test java In the environment sevlet-api The specific reasons will be written in the test section below-->
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.servlet-api</artifactId>
<version>3.1.0</version>
<scope>provided</scope> <!--Dependencies are loaded at run time, but not packaged at package time-->
</dependency>
test
After Mybatis scans the interface under the mapper package, it will automatically generate the implementation class corresponding to the interface, and who stores the corresponding Sql statement in the xml file
Create interface bookReview/mapper/TestMapper
package bookReview.mapper;
public interface TestMapper {
public void insert();
}
Create Src / main / resources / maps / test.xml
Note that the mapper namespace should correspond to the path of the interface
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http:mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="bookReview.mapper.TestMapper">
<insert id="insert"> <!--id Corresponding interface method name-->
insert into test(content) values('Test content');
</insert>
</mapper>
Create service class bookReview/service/TestService
Test insert 5 pieces of data
package bookReview.service;
import bookReview.mapper.TestMapper;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
@Service
public class TestService {
@Resource
private TestMapper testMapper;
public void batchImport(){
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
testMapper.insert();
}
}
}
Create a test case, click code - generate - Test in the TestService menu, and check the method to be tested; Add spring supported annotations to the automatically generated classes
package bookReview.service;
import junit.framework.TestCase;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration(locations = {"classpath:applicationContext.xml"})
public class TestServiceTest extends TestCase {
@Resource
private TestService testService;
@Test
public void testBatchImport() {
testService.batchImport();
System.out.println("Batch import succeeded");
}
}
When running the test method, an error will be reported for the first time: java.lang.NoClassDefFoundError: javax/servlet/ServletContext
The reason is that the javax/servlet/ServletContext class is provided by tomcat by default, and the current running environment is the java environment, which has no relationship with tomcat. In order to solve this problem, we also need to rely on javax/servlet/ServletContext in pom.xml
Under unit test junit, add:
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.servlet-api</artifactId>
<version>3.1.0</version>
<scope>provided</scope> <!--Dependencies are loaded at run time, but not packaged at package time-->
</dependency>
Rerun and execute successfully! Data is added to the database
Add logback log component
pom.xml
<!--logback Log component-->
<dependency>
<groupId>ch.qos.logback</groupId>
<artifactId>logback-classic</artifactId>
<version>1.2.3</version>
</dependency>
You can adjust the log format
Create the specified file src/main/resources/logback.xml
Configure declarative transactions
Simplify annotation management in the program through configuration or annotation
For example, if an exception occurs during the insertion of the above program, the data integrity will be destroyed
TestService
public void batchImport(){
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
if(i==3){
throw new RuntimeException("Unexpected exception");
}
testMapper.insert();
}
}
The configuration declarative transaction must have spring TX in the current dependency package, which is included in spring JDBC
applicationContext.xml
Introducing tx namespace
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd">
Configure declarative transactions
<!--Declarative transaction configuration-->
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/> <!--Because the previously configured data source dataSource-->
</bean>
<!--Enable annotation mode transaction, see annotation-driven Is to enable xxx Corresponding annotation mode-->
<tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="transactionManager"/>
After configuration, add @ Transactional annotation to the method that needs to call transaction
The program successfully runs the global commit. If a runtime exception is thrown, the transaction will be rolled back
package bookReview.service;
import bookReview.mapper.TestMapper;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
@Service
public class TestService {
@Resource
private TestMapper testMapper;
@Transactional
public void batchImport(){
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
if (i == 3) {
throw new RuntimeException("Unexpected exception");
}
testMapper.insert5();
}
}
}
3, Mybatis plus introduction and integration steps
Mybatis plus is an agile development plug-in based on mybatis, which can help us quickly complete the addition, deletion, modification and query of the corresponding data table
- MyBatis plus (MP) is an enhanced tool for MyBatis developed by Chinese people
- Automatically implement Mapper CRUD operation to improve database development efficiency
- MP is only enhanced on the basis of MyBatis without change
In the previous program, to add, delete, change and query, you need to declare the interface, write the corresponding sql statement, and then call it. It's not very convenient
Mybatyis plus integration
- Introduction of mybatis plus dependency into pom
- Spring XML change configuration SqlSessionFactory implementation class
- mybatis-config.xml add MP paging plug-in
Introduction of mybatis plus dependency into pom
<!--MyBatis-Plus rely on-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.baomidou</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-plus</artifactId>
<version>3.4.3.4</version>
</dependency>
Spring XML change configuration SqlSessionFactory implementation class
Just adjust the original SqlSessionFactory implementation to one line and change the class
<!--SqlSessionFactoryBean Used to create a profile based on configuration information SqlSessionFactory,We no longer need to create our own code-->
<!--Native Mybatis And spring integration-->
<!-- <bean id="sessionFactory" class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean">-->
<bean id="sessionFactory" class="com.baomidou.mybatisplus.extension.spring.MybatisSqlSessionFactoryBean">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
<property name="mapperLocations" value="classpath:mappers/*.xml"/>
<!--MyBatis Profile address-->
<property name="configLocation" value="classpath:mybatis-config.xml"/>
</bean>
mybatis-config.xml adds MP paging plug-in; Note that the plug-in version is 3.3.2. I tried it with 3.4 and found that the plug-in name is different, resulting in an error. I don't know where to change the configuration, so I continued with version 3.3.2
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http:mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
<settings>
<!--Realize the hump naming conversion between attribute name and field name-->
<setting name="mapUnderscoreToCamelCase" value="true"/>
</settings>
<plugins>
<plugin interceptor="com.baomidou.mybatisplus.extension.plugins.PaginationInterceptor"></plugin>
</plugins>
</configuration>
Mybatis plus development
- Create an entity class and map @ TableName/@TableId/@TableFieId
- Create Mapper interface, inherit BaseMapper, and create Mapper XML
- Mapper object is injected during development, and CRUD operation is realized through built-in API
Mybatis plus core notes
@TableName maps entity classes to table names
@TableId describes the primary key of the table when the corresponding attribute is
@TableFieId sets the correspondence between the property and the list
BaseMapper interface core API
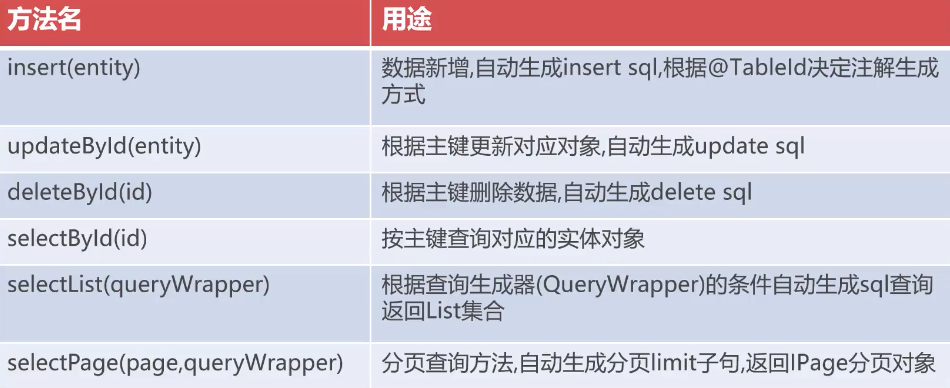
case
Create an entity class and map @ TableName/@TableId/@TableFieId
Each MP table must have a corresponding entity, and add entity package and entity class
bookReview/eneity/Test
package bookReview.entity;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.annotation.IdType;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.annotation.TableField;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.annotation.TableId;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.annotation.TableName;
@TableName("test") //Describe which table the entity class corresponds to
public class Test {
@TableId(type = IdType.AUTO) //Primary key; Auto increment
@TableField("id") //Describe which field the attribute corresponds to
private Integer id;
@TableField("content") //If the field name is the same as the attribute name or conforms to the hump naming conversion rules, TableField can be omitted; Such as Article_ The content attribute name is written as articleContent
private String content;
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getContent() {
return content;
}
public void setContent(String content) {
this.content = content;
}
}
Create Mapper interface, inherit BaseMapper, and create Mapper XML
bookReview/mapper/TestMapper
package bookReview.mapper;
import bookReview.entity.Test;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.mapper.BaseMapper;
public interface TestMapper extends BaseMapper<Test> {
public void insert5(); //The previously customized insert5 method can also be used. Be careful not to have the same name as the BaseMapper interface method
}
Note that the custom method name should correspond to the id in src/main/resources/mappers/test.xml created earlier
Mapper object is injected during development, and CRUD operation is realized through built-in API
Create a new test case method TestMyBatisPlus; Note that the TestMapper interface is injected instead of the previous TestService class; The customized TestMapper interface inherits the BaseMapper interface and includes CRUD methods;
package bookReview.service;
import bookReview.entity.Test;
import bookReview.mapper.TestMapper;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.conditions.query.QueryWrapper;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import java.util.List;
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration(locations = {"classpath:applicationContext.xml"})
public class TestMyBatisPlus {
@Resource
private TestMapper testMapper;
@org.junit.Test
public void testInsert(){
Test test = new Test();
test.setContent("MyBatis Plus test");
testMapper.insert(test);
}
@org.junit.Test
public void testUpdate(){
Test test = testMapper.selectById(52);
test.setContent("MyBatis Plus Test 1");
testMapper.updateById(test);
}
@org.junit.Test
public void testDelete(){
testMapper.deleteById(9);
}
@org.junit.Test
public void testSelect(){
QueryWrapper<Test> queryWrapper = new QueryWrapper<Test>();
queryWrapper.eq("id",52); //Equivalent comparison
queryWrapper.gt("id", 52); //If the id is greater than 5, the two conditions can be added together
List<Test> list = testMapper.selectList(queryWrapper);
System.out.println(list.get(0));
}
}
Through mybatis plus, we can automatically generate sql statements according to the configured mapping relationship, which greatly reduces our workload