1, Experimental conclusion
1. Experimental task 1
- Task 1-1
- task1_1.asm source code
-
1 assume ds:data, cs:code, ss:stack 2 3 data segment 4 db 16 dup(0) 5 data ends 6 7 stack segment 8 db 16 dup(0) 9 stack ends 10 code segment 11 start: 12 mov ax, data 13 mov ds, ax 14 15 mov ax, stack 16 mov ss, ax 17 mov sp, 16 18 19 mov ah, 4ch 20 int 21h 21 code ends 22 end start
-
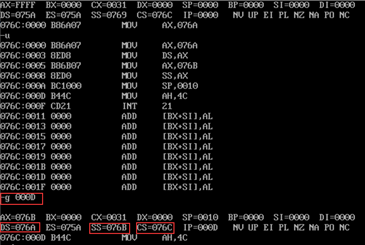
- task1_1 screenshot before the end of line17 and line19
- Question answer
- ① In debug, execute until the end of line17 and before line19, and record this time: register (DS)= 076A , Register (SS)= 076B , Register (CS)= 076C
- ② Assuming that the segment address of the code segment is X after the program is loaded, the segment address of the data segment is X X-2h, the segment address of stack is X-1h .
- task1_1.asm source code
- Task 1-2
- task1_2.asm source code
-
1 assume ds:data, cs:code, ss:stack 2 3 data segment 4 db 4 dup(0) 5 data ends 6 7 stack segment 8 db 8 dup(0) 9 stack ends 10 code segment 11 start: 12 mov ax, data 13 mov ds, ax 14 15 mov ax, stack 16 mov ss, ax 17 mov sp, 8 18 19 mov ah, 4ch 20 int 21h 21 code ends 22 end start
-
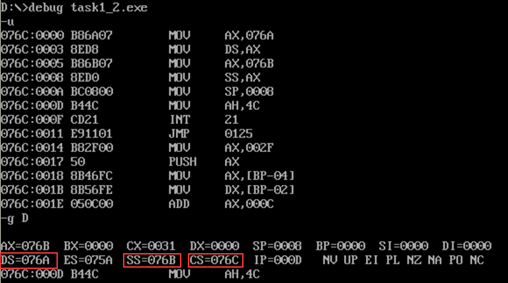
- task1_2. After debugging to the end of line17 and before line19, observe the screenshot of register DS, CS and SS values
- Question answer
- ① In debug, execute until the end of line17 and before line19, and record this time: register (DS)= 076A , Register (SS)= 076B , Register (CS)= 076C
- ② Suppose that after the program is loaded, the segment address of the code segment is x, and the segment address of the data segment is X X-2h , The segment address of stack is X-1h .
- task1_2.asm source code
- Task 1-3
- Task task1_3.asm source code
-
1 assume ds:data, cs:code, ss:stack 2 3 data segment 4 db 20 dup(0) 5 data ends 6 7 stack segment 8 db 20 dup(0) 9 stack ends 10 code segment 11 start: 12 mov ax, data 13 mov ds, ax 14 15 mov ax, stack 16 mov ss, ax 17 mov sp, 20 18 19 mov ah, 4ch 20 int 21h 21 code ends 22 end start
-
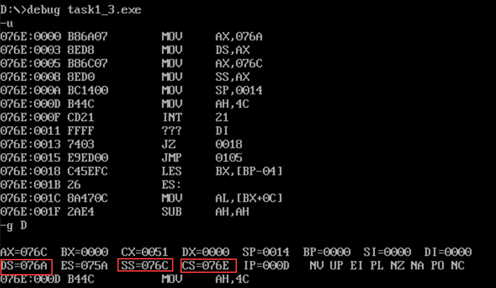
- task1_3. Screenshot of the values of registers DS, CS and SS before the end of debugging to line17 and line19
- Question answer
- ① In debug, execute until the end of line17 and before line19, and record this time: register (DS)= 076A , Register (SS)= 076C , Register (CS)= 076E
- ② Assuming that the segment address of the code segment is X after the program is loaded, the segment address of the data segment is X X-4h , The segment address of stack is X-2h
- Task task1_3.asm source code
- Tasks 1-4
- Task task1_4.asm source code
-
1 assume ds:data, cs:code, ss:stack 2 code segment 3 start: 4 mov ax, data 5 mov ds, ax 6 7 mov ax, stack 8 mov ss, ax 9 mov sp, 20 10 11 mov ah, 4ch 12 int 21h 13 code ends 14 15 data segment 16 db 20 dup(0) 17 data ends 18 19 stack segment 20 db 20 dup(0) 21 stack ends 22 end start
-
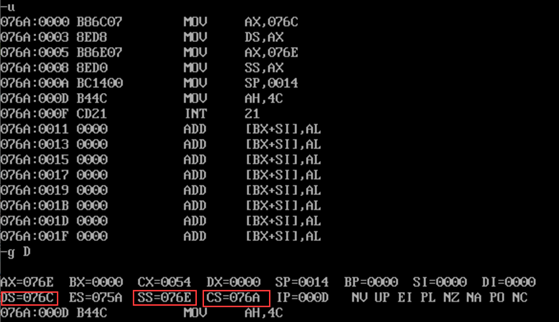
- task1_4. After debugging to the end of line17 and before line19, observe the screenshot of register DS, CS and SS values
- Question answer
- ① In debug, execute until the end of line9 and before line11, and record this time: register (DS)= 076C , Register (SS)= 076E , Register (CS)= 076A
- ② Suppose that after the program is loaded, the segment address of the code segment is x, and the segment address of the data segment is X X+2h , The segment address of stack is X+4h .
- Task task1_4.asm source code
- Tasks 1-5
- Based on the practice and observation of the above four experimental tasks, summarize and answer:
- ① For the segment defined below, after the program is loaded, the actual memory space allocated to the segment is N/16 is rounded up and multiplied by 16 .
-
1 xxx segment 2 db N dup(0) 3 xxx ends
-
- ② If the program Task1_ 1.asm, task1_ 2.asm, task1_ 3.asm, task1_ 4. In ASM, if the pseudo instruction end start is changed to end, which program can still be executed correctly. The reasons are analyzed and explained in combination with the conclusions obtained from practical observation.
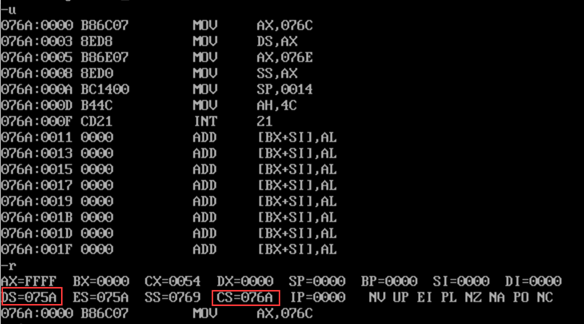
- Answer: task1_4.asm can operate normally. end start not only informs the compiler of the end of the program, but also informs the compiler of where the entry of the program is. If the end is not used to indicate the program start label, the program runs from DS+10h at the beginning of the program by default. As shown in the figure, only task1_4.asm program meets the requirements.
- ① For the segment defined below, after the program is loaded, the actual memory space allocated to the segment is N/16 is rounded up and multiplied by 16 .
- Based on the practice and observation of the above four experimental tasks, summarize and answer:
2. Experimental task 2
- Assembly source code
-
1 assume cs:code 2 code segment 3 start: 4 mov ax, 0b800h 5 mov ds, ax 6 mov bx,0f00h 7 mov cx,50h 8 9 s: mov [bx],0403h 10 add bx,2 11 loop s 12 13 mov ah, 4ch 14 int 21h 15 code ends 16 end start
-
- Screenshot of operation results
- -f b800:0f00 0f9f 03 04 operation results
-
Screenshot of task2 running results
- -f b800:0f00 0f9f 03 04 operation results
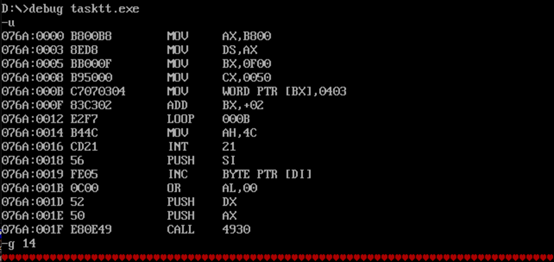
3. Experimental task 3
- Complete assembly source code
-
1 assume cs:code 2 data1 segment 3 db 50, 48, 50, 50, 0, 48, 49, 0, 48, 49 ; ten numbers 4 data1 ends 5 6 data2 segment 7 db 0, 0, 0, 0, 47, 0, 0, 47, 0, 0 ; ten numbers 8 data2 ends 9 10 data3 segment 11 db 16 dup(0) 12 data3 ends 13 14 code segment 15 start: 16 mov ax,data1 17 mov ds,ax 18 mov bx,0 19 mov cx,000ah 20 21 s: mov ax,[bx] 22 add ax,[bx+10h] 23 mov [bx+20h],ax 24 inc bx 25 loop s 26 27 mov ah,4ch 28 int 21h 29 code ends 30 end start
-
- Load, disassemble and debug screenshots in debug
- Disassembly:
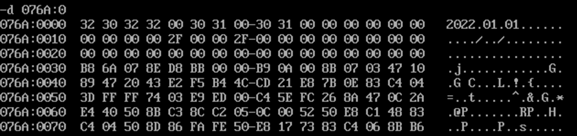
- Before adding data items in turn, check the debug command and screenshot of the original value of memory space data corresponding to logical segments data1, data2 and data3
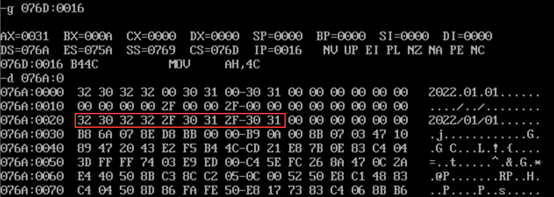
- After adding in sequence, view the debug command and screenshot of the original value of memory space data corresponding to logical segments data1, data2 and data3
- Disassembly:
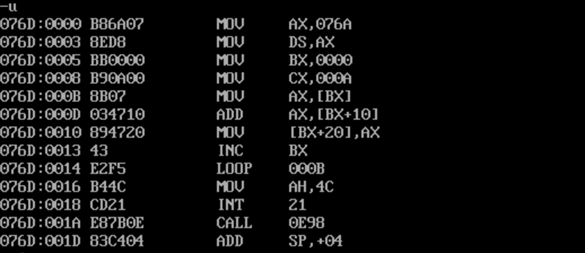
4. Experimental task 4
- Complete assembly source code
-
1 assume cs:code 2 3 data1 segment 4 dw 2, 0, 4, 9, 2, 0, 1, 9 5 data1 ends 6 7 data2 segment 8 dw 8 dup(?) 9 data2 ends 10 11 stack segment 12 dw 8 dup(?) 13 stack ends 14 15 code segment 16 start: 17 mov ax,data1 18 mov ds,ax 19 mov bx,0 20 mov sp,10h 21 mov cx,8 22 23 s0: push [bx] 24 add bx,2h 25 loop s0 26 27 mov cx,8 28 mov bx,0 29 s1: pop [bx+10h] 30 add bx,2h 31 loop s1 32 33 mov ah, 4ch 34 int 21h 35 code ends 36 end start
-
- Load, disassemble and debug screenshots in debug
- Disassembly
- Disassembly
-
- Before the program is executed, the d command checks the screenshot of the memory space corresponding to the data segment data2
- Before the program is executed, the d command checks the screenshot of the memory space corresponding to the data segment data2
-
- After the program is executed, the d command views a screenshot of the memory space corresponding to the data segment data2
- After the program is executed, the d command views a screenshot of the memory space corresponding to the data segment data2
5. Experimental task 5
- task5.asm source code
-
1 assume cs:code, ds:data 2 data segment 3 db 'Nuist' 4 db 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 5 data ends 6 7 code segment 8 start: 9 mov ax, data 10 mov ds, ax 11 12 mov ax, 0b800H 13 mov es, ax 14 15 mov cx, 5 16 mov si, 0 17 mov di, 0f00h 18 s: mov al, [si] 19 and al, 0dfh 20 mov es:[di], al 21 mov al, [5+si] 22 mov es:[di+1], al 23 inc si 24 add di, 2 25 loop s 26 27 mov ah, 4ch 28 int 21h 29 code ends 30 end start
-
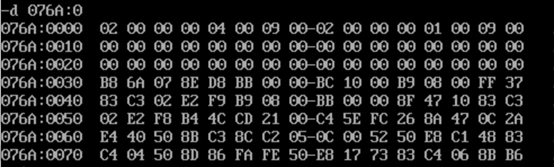
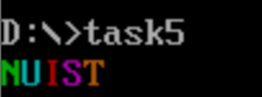
- Screenshot of operation results
-
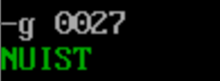
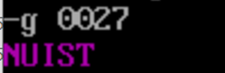
- Use the debug tool to debug the program, and use the g command to execute the screenshot before the program returns (i.e. after ine25 and before line27)
- db 2,3,4,5,6
-
db 5 dup(2)
- db 5 dup(5)
- db 2,3,4,5,6
- What is the function of line19 in the source code?
- Answer: 0dfh binary is 0000 1101 1111. And operation to change lowercase letters into uppercase letters, and uppercase letters remain uppercase letters.
- What is the purpose of the byte data in the data segment line4 in the source code?
- A: color code, letters are displayed in corresponding colors.
6. Experimental task 6
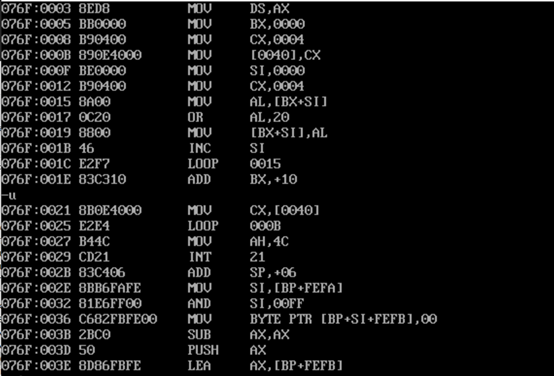
- task6.asm source code
-
1 assume cs:code, ds:data 2 3 data segment 4 db 'Pink Floyd ' 5 db 'JOAN Baez ' 6 db 'NEIL Young ' 7 db 'Joan Lennon ' 8 dw 0 9 data ends 10 11 code segment 12 start: 13 mov ax,data 14 mov ds,ax 15 mov bx,0 16 mov cx,4 17 18 s0: mov ds:[40h],cx 19 mov si,0 20 mov cx,4 21 22 s: mov al,[bx+si] 23 or al,00100000b 24 mov [bx+si],al 25 inc si 26 loop s 27 28 add bx,16 29 mov cx,ds:[40h] 30 loop s0 31 32 mov ah, 4ch 33 int 21h 34 code ends 35 end start
-
- Load, disassemble and debug screenshots in debug
- Disassembly
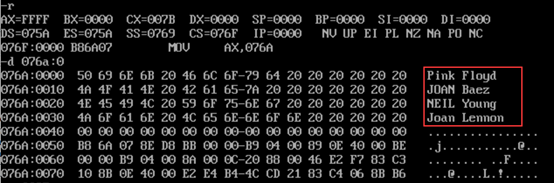
- Before executing the program, use the d command to check the memory space corresponding to the data segment
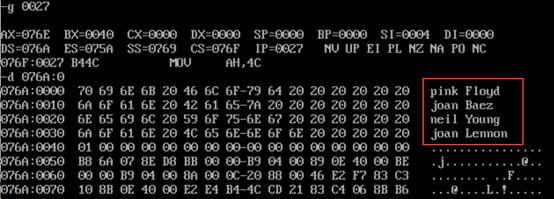
- After the program is executed, use the d command to view the memory space corresponding to the data segment
- Disassembly
7. Experimental task 7
- task7.asm source code
-
1 assume cs:code, ds:data, es:table 2 3 data segment 4 db '1975', '1976', '1977', '1978', '1979' 5 dd 16, 22, 382, 1356, 2390 6 dw 3, 7, 9, 13, 28 7 data ends 8 9 table segment 10 db 5 dup( 16 dup(' ') ) ; 11 table ends 12 13 code segment 14 start: 15 mov ax,data 16 mov ds,ax 17 mov ax,table 18 mov es,ax 19 mov bx,0 20 mov si,0 21 mov di,0 22 mov cx,5 23 s0: mov ax,[bx+si] 24 mov es:[di],ax 25 add si,2h 26 mov ax,[bx+si] 27 mov es:[di+2h],ax 28 add si,2h 29 add di,10h 30 loop s0 31 32 mov di,0 33 mov si,0 34 mov bx,20 35 mov cx,5 36 s1: mov ax,[bx+si] 37 mov es:[di+5h],ax 38 add si,2h 39 mov ax,[bx+si] 40 mov es:[di+7h],ax 41 add si,2h 42 add di,10h 43 loop s1 44 45 mov di,0 46 mov si,0 47 mov bx,40 48 mov cx,5 49 s2: mov ax,[bx+si] 50 mov es:[di+10],ax 51 add si,2 52 add di,10h 53 loop s2 54 55 mov cx,5 56 mov di,0 57 s3: mov ax,es:[di+5] 58 mov dx,es:[di+7] 59 div word ptr es:[di+10] 60 mov es:[di+13],ax 61 add di,10h 62 loop s3 63 64 mov ah, 4ch 65 int 21h 66 code ends 67 end start
-
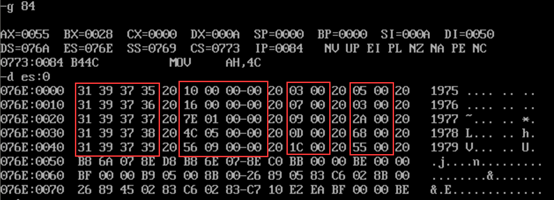
- Debug screenshot
- Screenshot of data segment data information
- View screenshot of original data information of table segment
- Run in debug until the program exits, use the d command to view the screenshot of the memory space corresponding to the table segment, and confirm whether the information is structurally written to the specified memory as required
- Screenshot of data segment data information
2, Experimental summary
- The actual memory space allocated to the segment by db N dup(0) in the segment is N/16 is rounded up and multiplied by 16.
- end start in addition to notifying the compiler of the end of the program, it can also notify the compiler of where the entry of the program is. If the end is not used to indicate the program start label, the program runs from DS+10h at the beginning of the program by default.
- If the divisor is 8 bits, the divisor is 16 bits, which is stored in AX by default. If the divisor is 16 bits, the divisor is 32 bits, which is stored in DX and AX. DX stores the high 16 bits and AX stores the low 16 bits.
- The stack can be used to store in reverse order.
- mov ax,[bx+bp] is wrong. bp memory can only be mixed with si or di or used alone.
- In case of multiple cycles, enter the inner cycle, save the cycle times of the outer cycle, and return the outer cycle times to the CX memory when the inner cycle ends.